Embed presentation
Downloaded 32 times

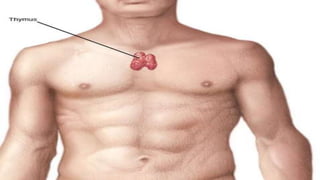


















The thymus gland is located behind the sternum and between the lungs. It produces the hormone thymosin, which is required for the development of T-lymphocytes and cell-mediated immunity, and is only active until puberty when it begins to shrink and be replaced by fat. Several tissues produce local hormones like histamine, serotonin, prostaglandins, and erythropoietin that act near their site of secretion to carry out functions like mediating inflammation, contracting smooth muscle, increasing capillary permeability, and stimulating red blood cell formation. Gastrointestinal hormones such as gastrin, secretin, and cholecystokinin also influence secretion of digestive juices.


















