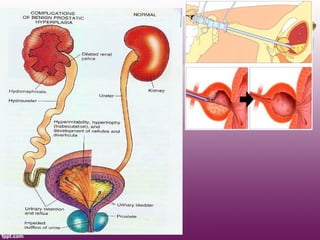
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that is common among aging men. It affects around 50% of men over 60 years of age and over 90% of men over 70. The hyperplasia is stimulated by hormones and affects prostate tissue. Common symptoms include difficulties with urination such as a weak stream, straining, and increased nighttime urination. Treatment options include medication, such as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and alpha blockers, as well as surgical procedures for more severe cases.