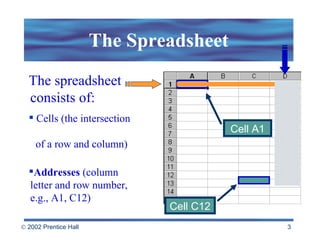
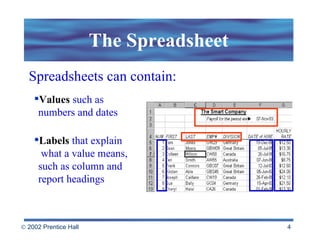
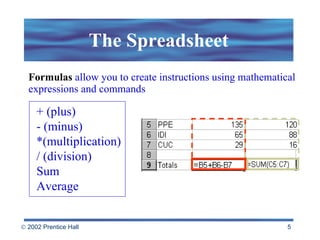
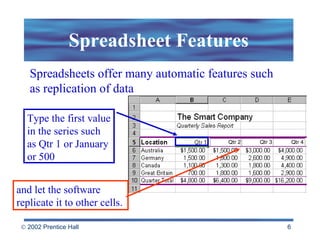
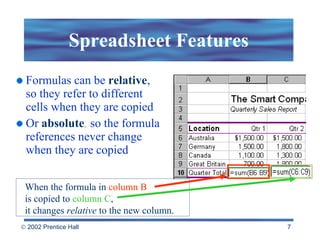
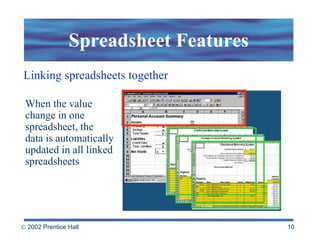
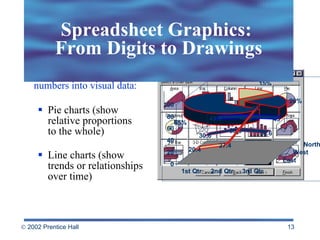
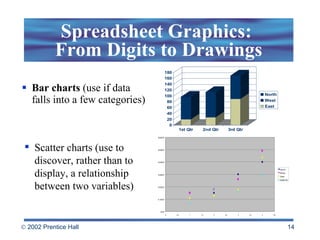
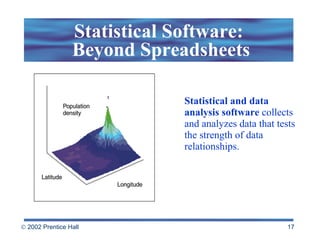
Spreadsheets allow users to enter values and formulas to perform calculations and visualize data. Formulas can be relative or absolute and automatically update when values change. Spreadsheets include functions, macros, templates, linking, and database capabilities. Statistical and visualization software extend spreadsheet capabilities to analyze data, test relationships, and create models and simulations. Computer modeling and simulation are used for research, training, and assessing risks by creating abstract representations of systems.