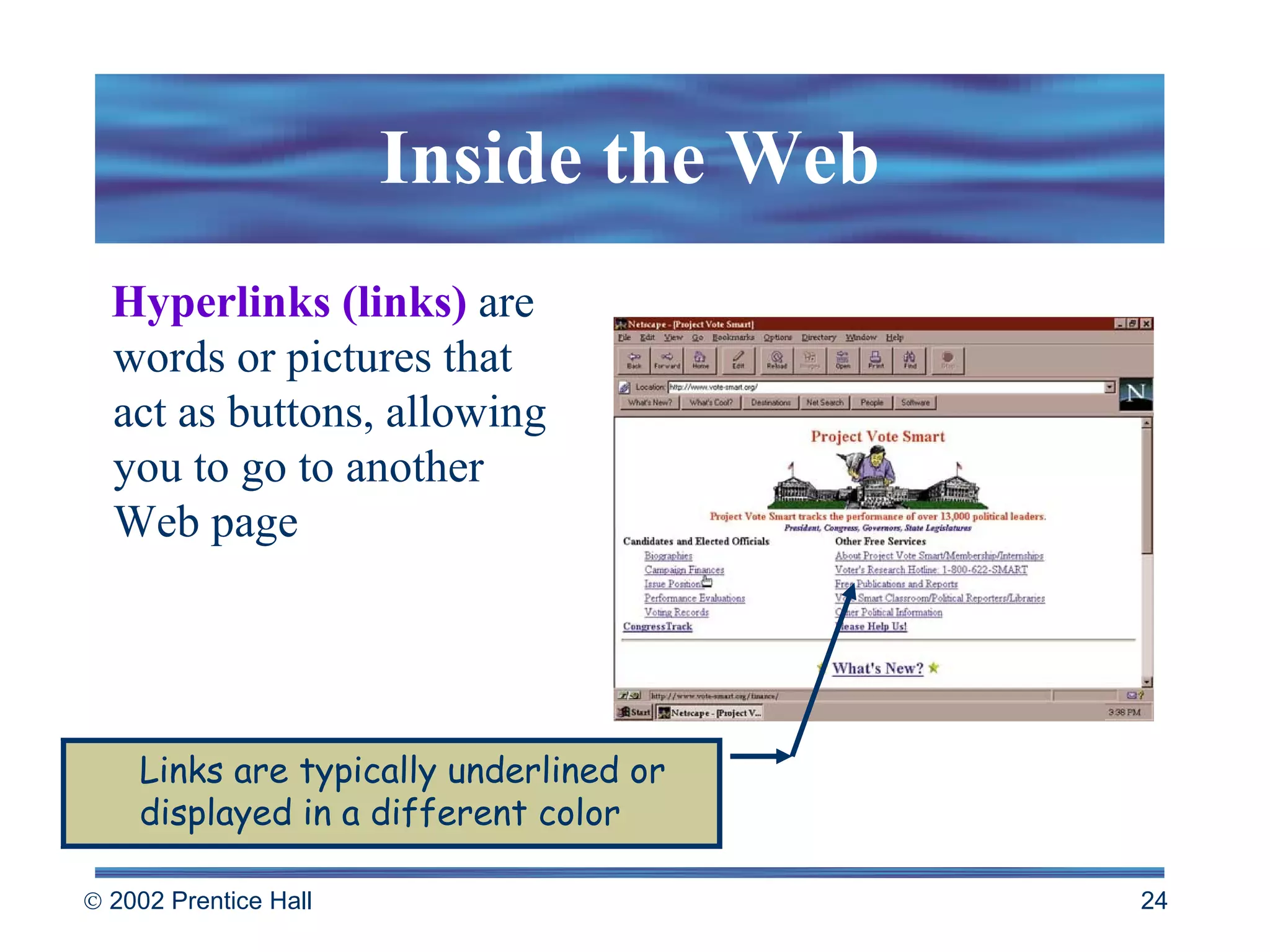
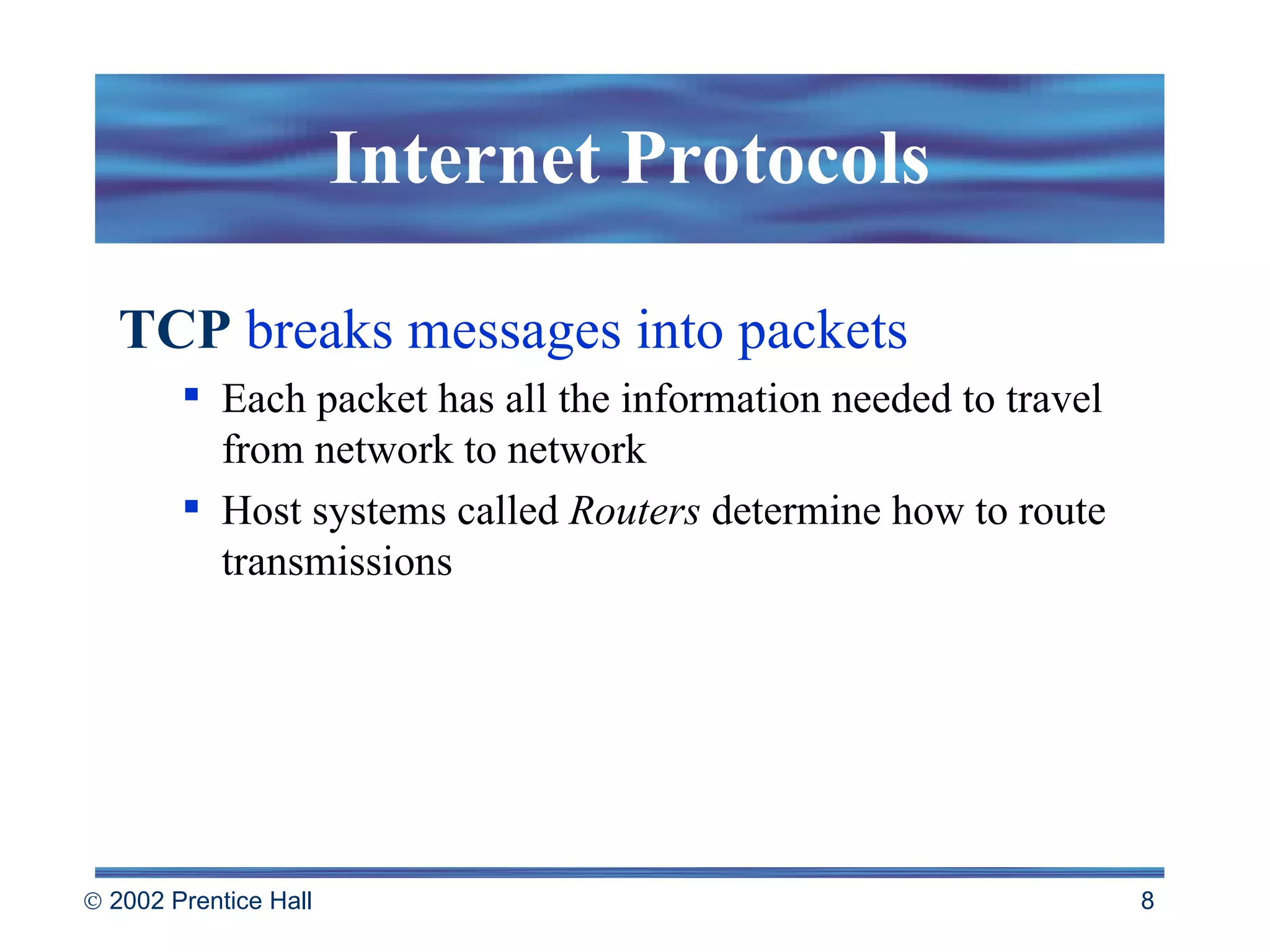
The document provides an overview of the Internet and the World Wide Web. It discusses how the Internet is a network of networks that connects computers worldwide using TCP/IP protocols. The Web is a system for browsing and searching distributed documents linked by hyperlinks that are accessed using Web browsers. Web pages use HTML codes to determine formatting and are hosted on Web servers at sites accessed by URLs.










![Internet Addresses [email_address] Examples: [email_address] User President whose mail is stored on the host whitehouse in the government domain User hazel_filbert at the server for Lane County, Oregon, k-12 school district](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beekman5stdppt10-100602045316-phpapp02/75/Beekman5-std-ppt_10-13-2048.jpg)