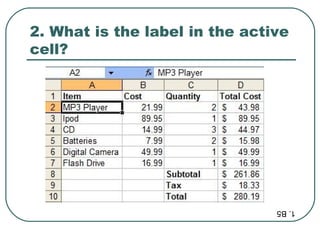
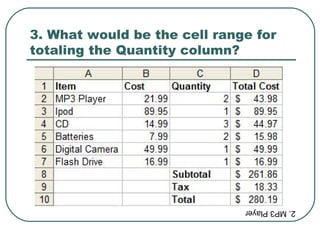
The document provides an introduction and overview of spreadsheet basics including:
- What a spreadsheet is and common uses such as budgets, grades, and personal finance
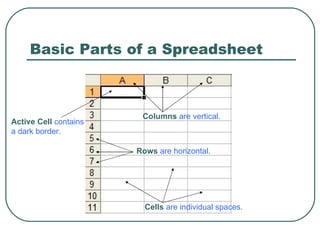
- Key spreadsheet components like cells, columns, rows, formulas, and functions
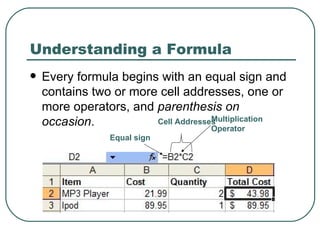
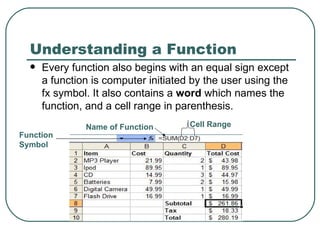
- Examples of common formulas and functions
- How to create basic spreadsheets, enter data, and calculate totals using formulas and functions
- How to visualize data through charts and graphs