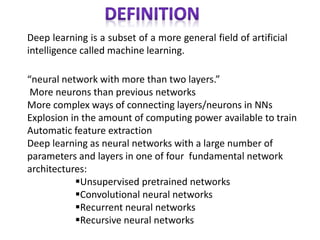
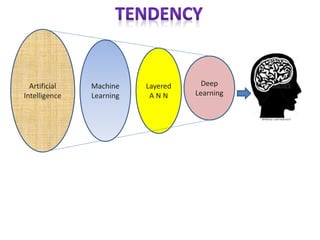
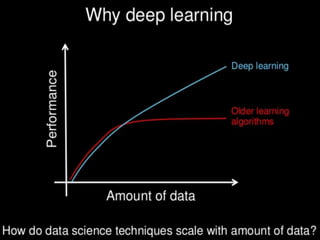
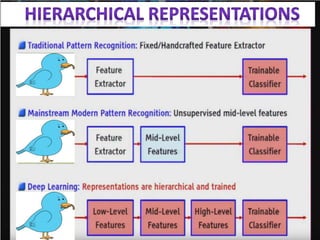
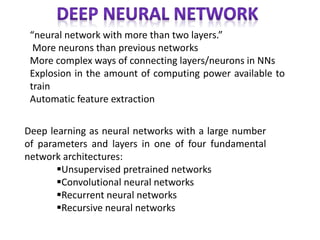
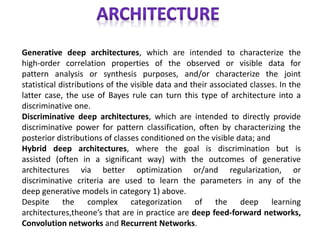
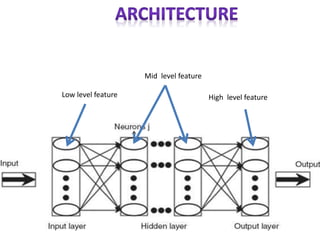
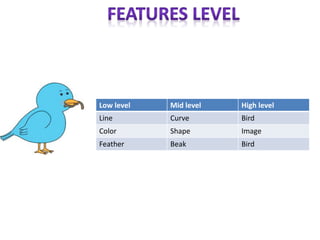
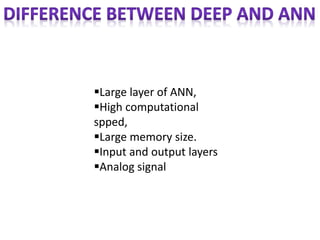
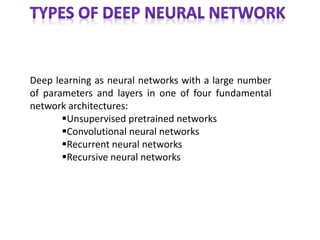
The document discusses artificial intelligence, particularly focusing on machine learning and deep learning, which enable machines to mimic human cognitive functions like learning and problem-solving. It outlines various architectures in deep learning, including convolutional and recurrent neural networks, and highlights applications such as image recognition and natural language processing. Additionally, it addresses challenges in training these systems and the importance of large datasets and computational power.