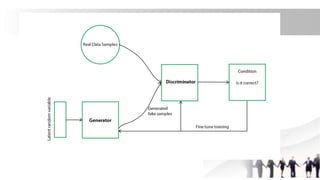
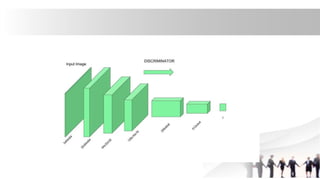
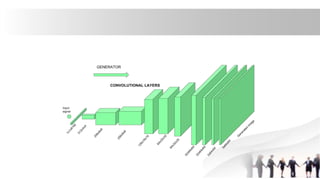
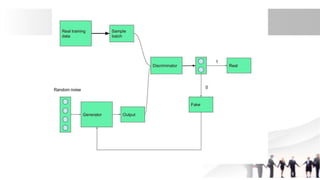
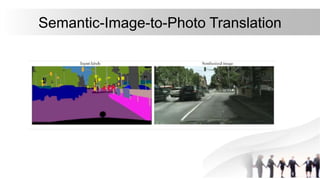
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a type of neural network introduced in 2014, comprising a generator that creates fake data and a discriminator that evaluates the authenticity of the data. They are used in various applications including image generation, data augmentation for restricted datasets, and enhancing data security against adversarial attacks. The competitive dynamic between the generator and discriminator drives both models to improve iteratively, resulting in increasingly realistic synthetic data.