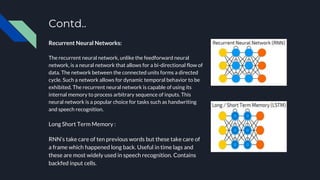
This document provides an overview of transfer learning in machine learning. It begins by explaining different types of machine learning including supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, and semi-supervised learning. It then describes artificial neural networks and some specific types including perceptrons, feedforward neural networks, radial basis function networks, recurrent neural networks, long short-term memory networks, and convolutional neural networks. The document defines transfer learning as transferring knowledge gained from training a model on one problem to improve training on another related problem. It lists applications of transfer learning and provides references for further reading.