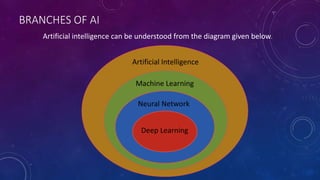
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its definition and purpose to replicate human intelligence through systems capable of learning and problem-solving. It details machine learning, supervised learning techniques (such as classification and regression), unsupervised learning methods (including clustering and association), and the principles of reinforcement learning. Additionally, it explores neural networks and deep learning, emphasizing their structures and the various types, including artificial neural networks, convolutional neural networks, and recurrent neural networks.