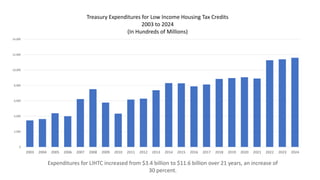
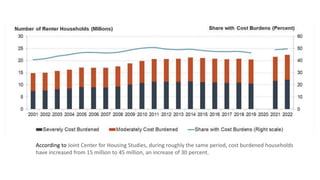
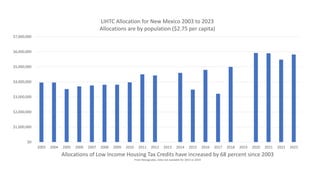
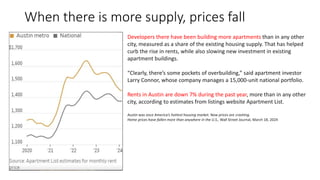
The document analyzes the effectiveness of the Low Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) over the past two decades, highlighting a significant increase in expenditures but a simultaneous rise in cost-burdened households, suggesting that LIHTC has not successfully alleviated housing affordability issues. Data indicates that despite increased funding and allocations, many households remain overburdened by housing costs, challenging the argument for further LIHTC spending. The document calls into question the correlation between LIHTC spending and housing prices, implying that market forces of supply and demand play a more critical role in determining housing costs.