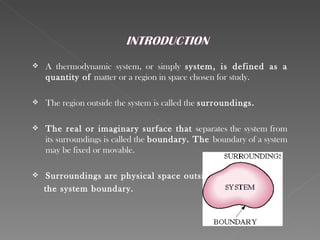
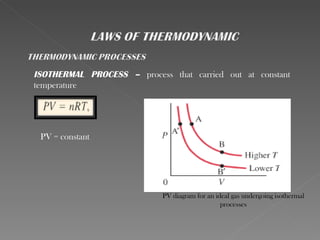
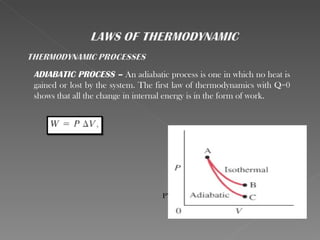
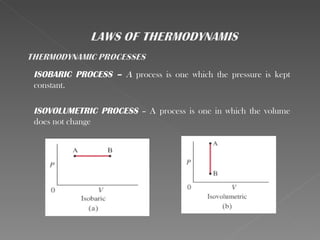
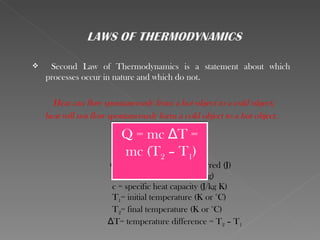
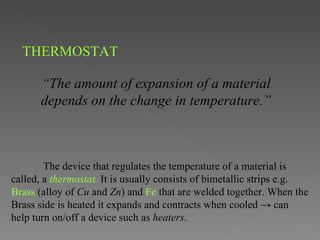
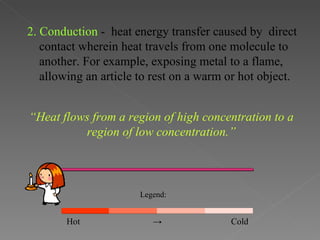
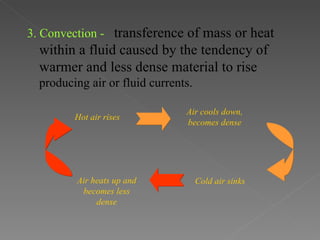
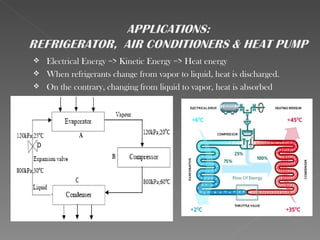
This document provides an overview of thermodynamics basics. It discusses that thermodynamics is concerned with how energy is stored and transformed through heat and work. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and cannot be created or destroyed. A thermodynamic system and its boundary with the surroundings are defined. Various thermodynamic processes like isothermal, adiabatic, and isobaric processes are also summarized. Key concepts like thermal energy, temperature, heat transfer methods, and the second law of thermodynamics are briefly explained.