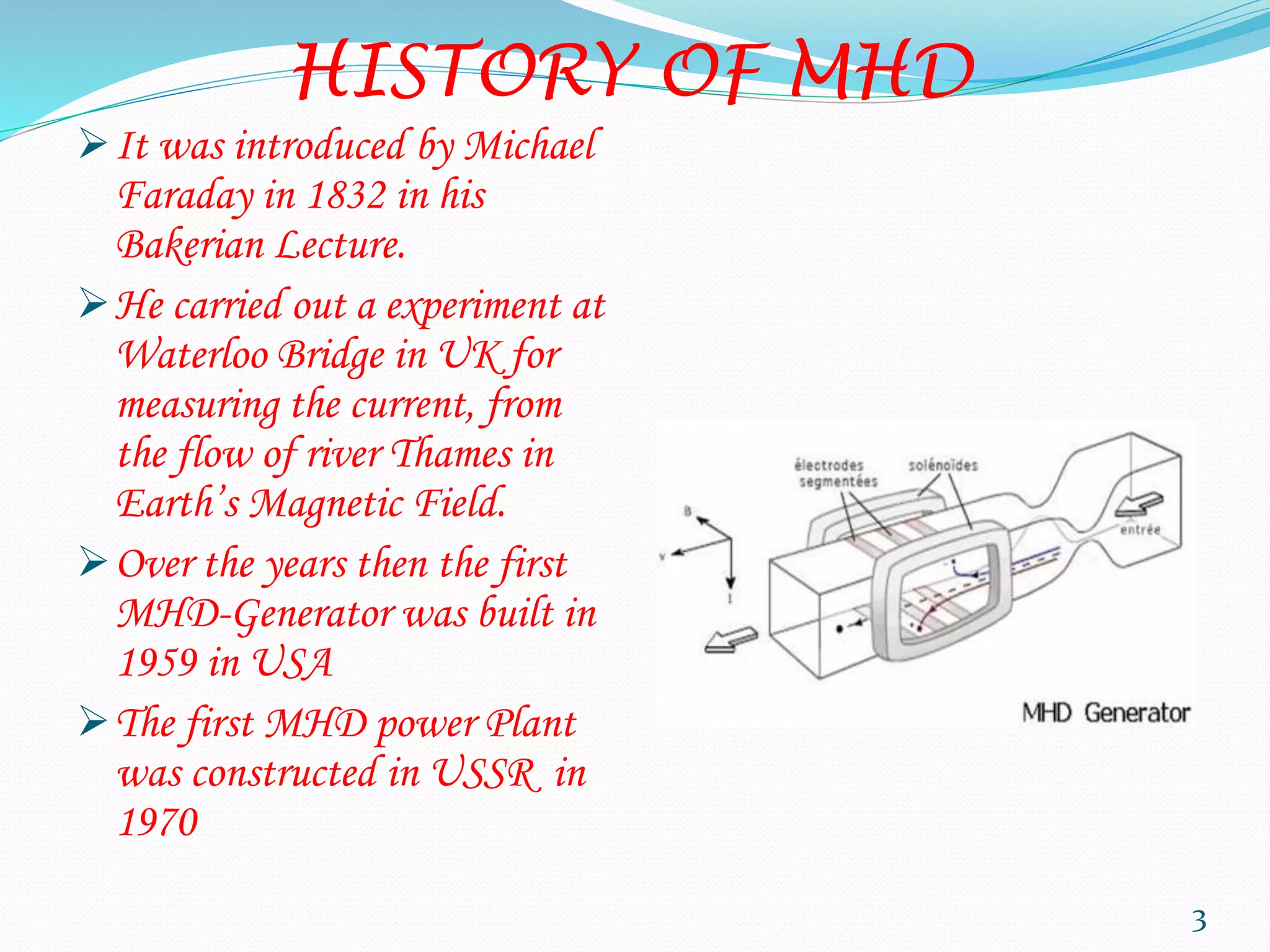
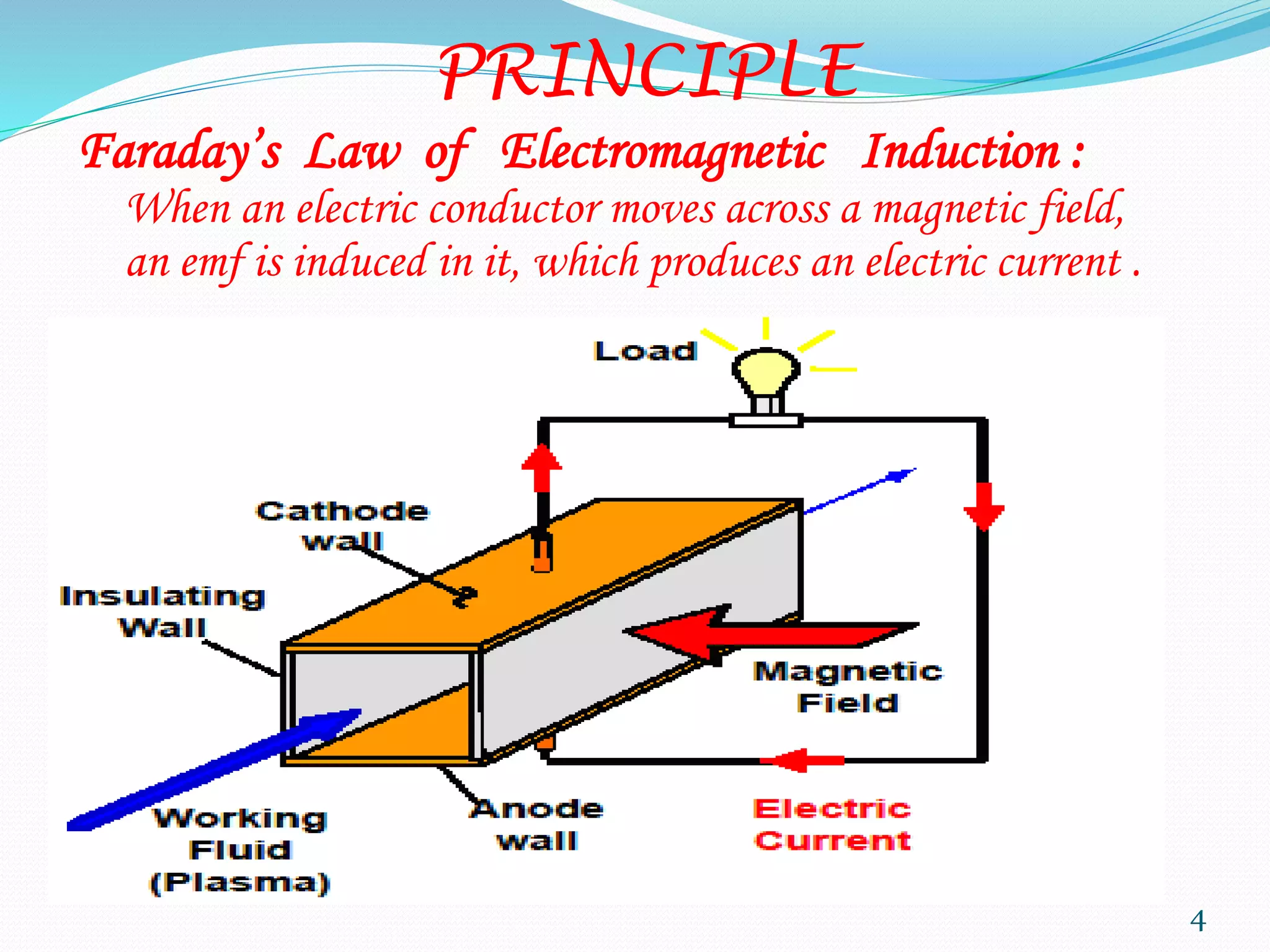
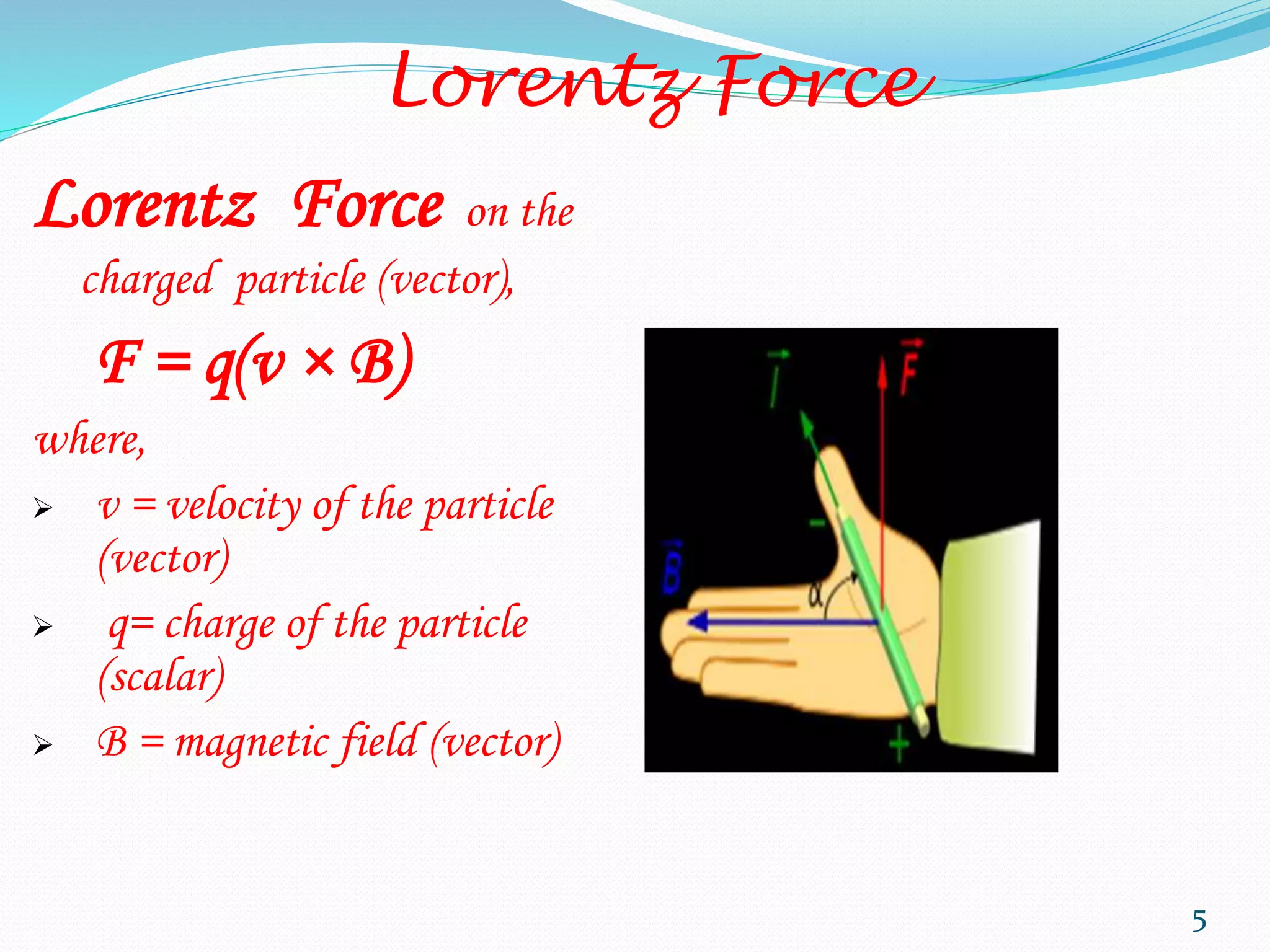
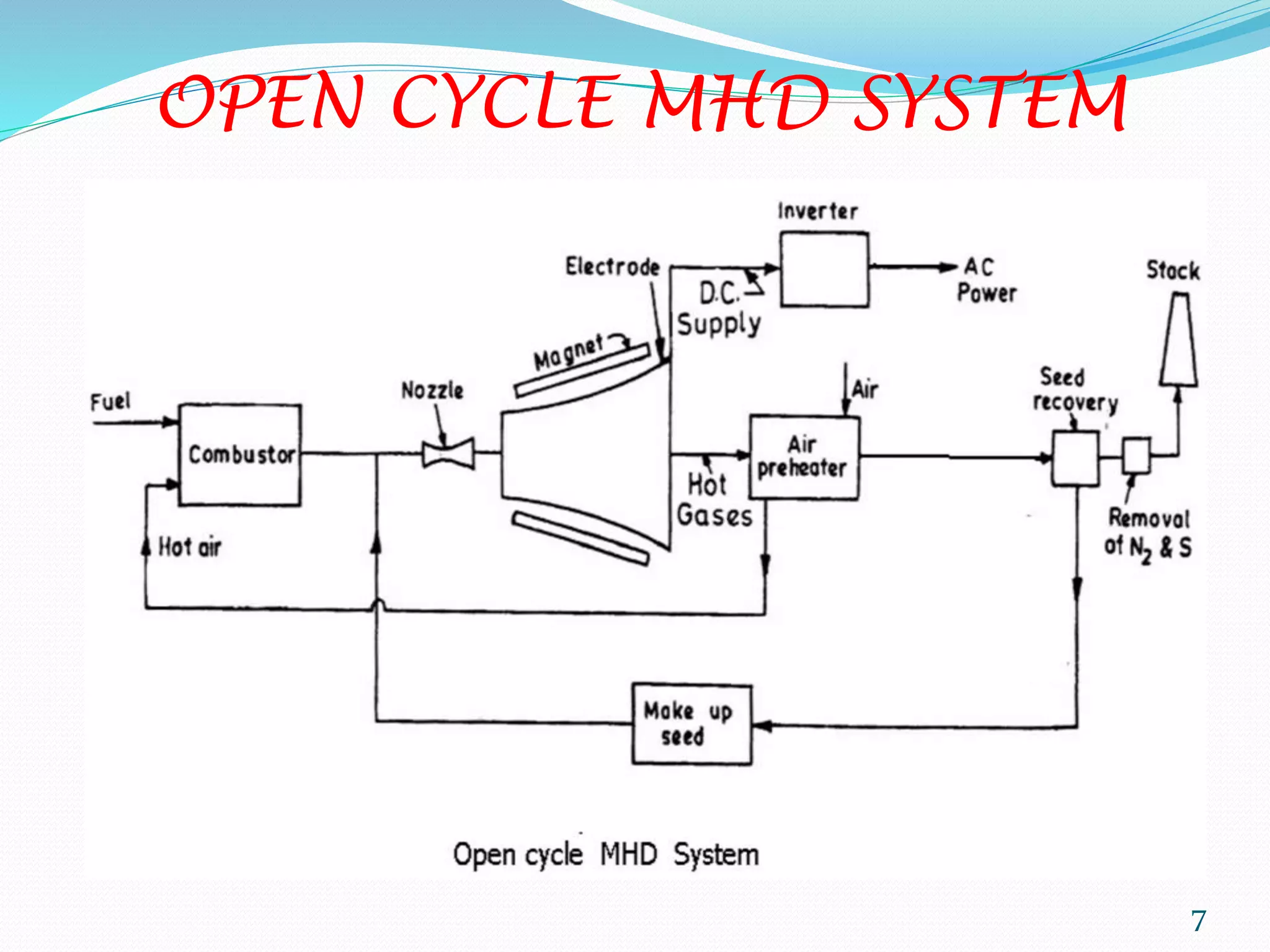
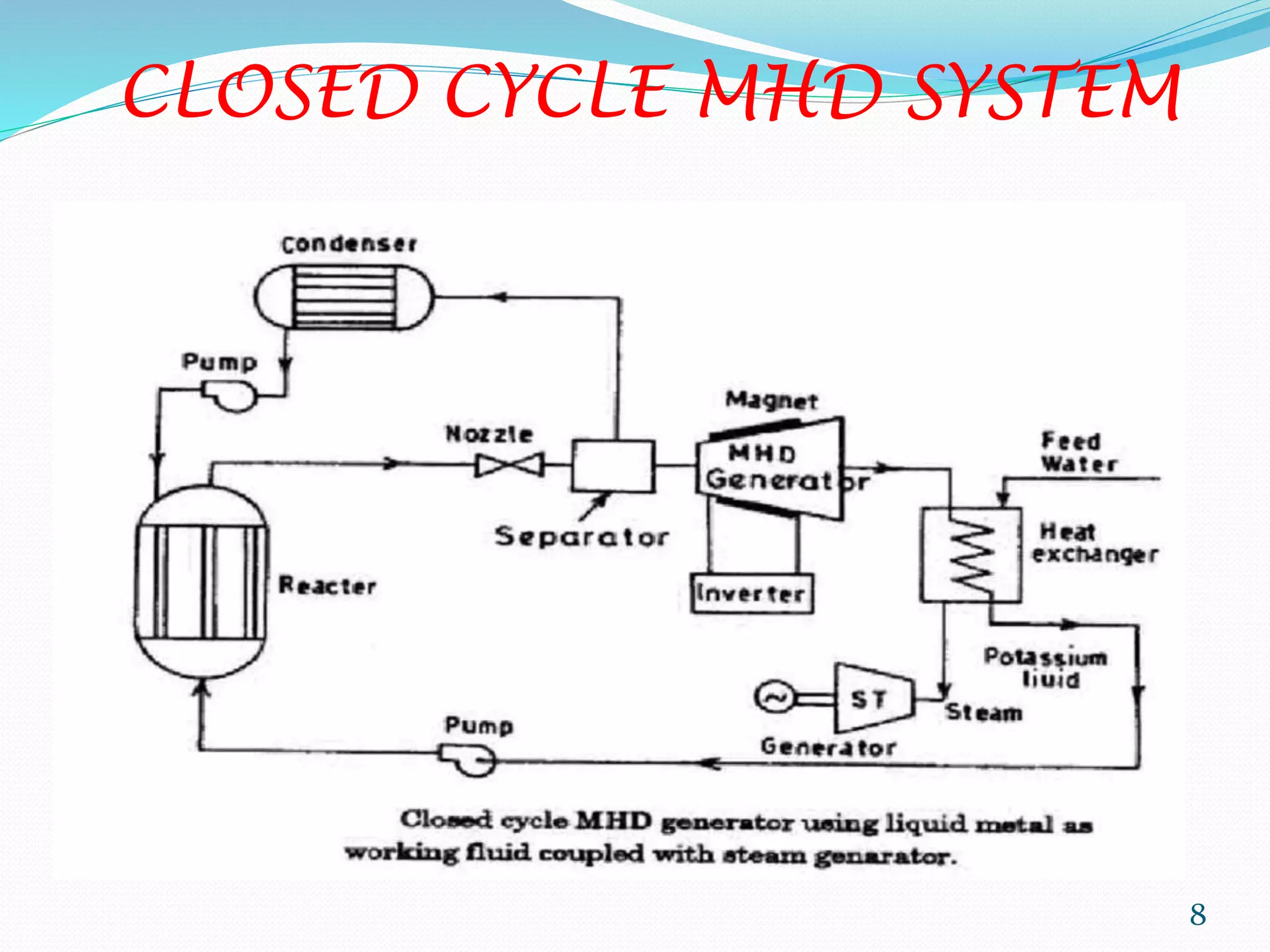
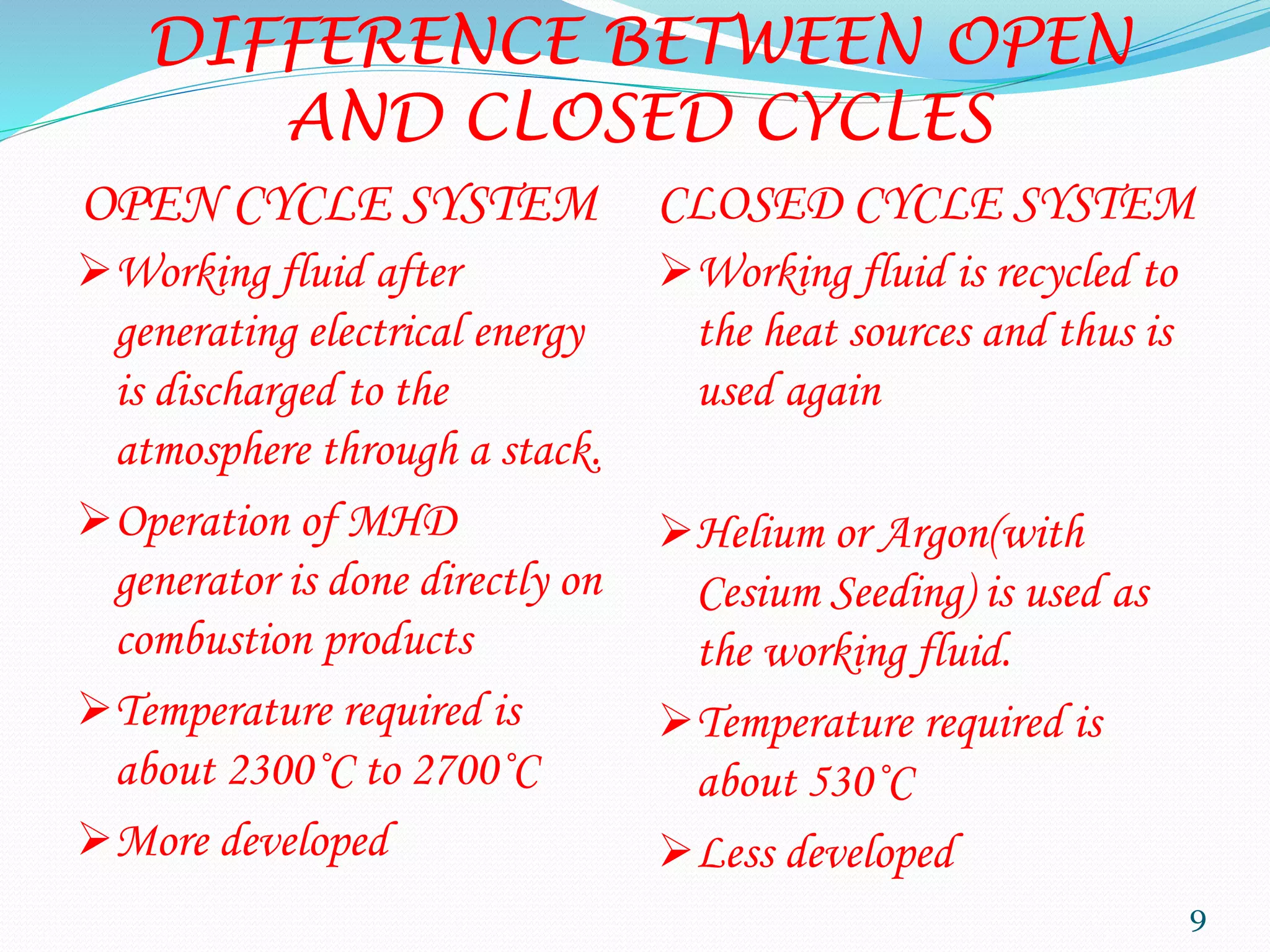
MHD power generation is a direct method of converting heat energy into electrical energy without mechanical energy conversion, focusing on electrically conducting fluids. It has origins dating back to Michael Faraday in 1832 and involves principles like Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and Lorentz force. The system has both open and closed cycle methods, offering advantages like high efficiency and low pollution, though it comes with challenges such as high costs and operating temperatures.