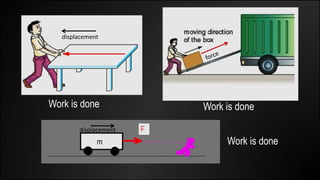
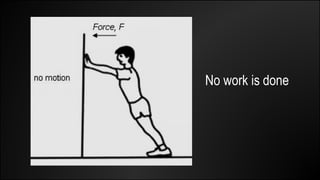
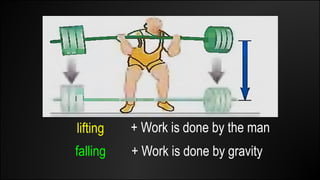
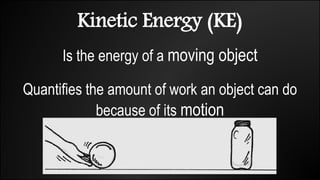
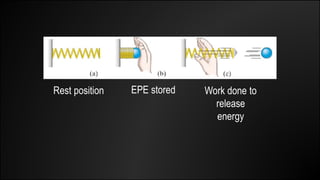
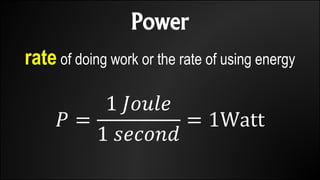
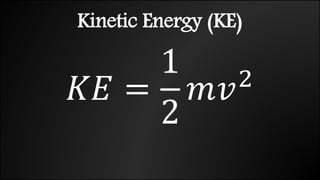Work is done when a force causes an object to be displaced in the same direction. It can be calculated as the product of the force magnitude and displacement magnitude. Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object and depends on its mass and velocity. The net work done on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy due to an object's position or state of deformation. It depends on mass, height, and elastic properties. Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is used and can be calculated as work over time or energy over time.