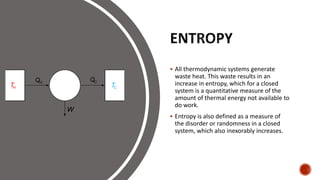
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with heat and other forms of energy. The first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of a system remains constant, such that any increase in one form of energy (such as heat) results in an equal decrease in another form (such as work). The second law states that heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body without an input of work. The third law states that the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero as the temperature approaches absolute zero.