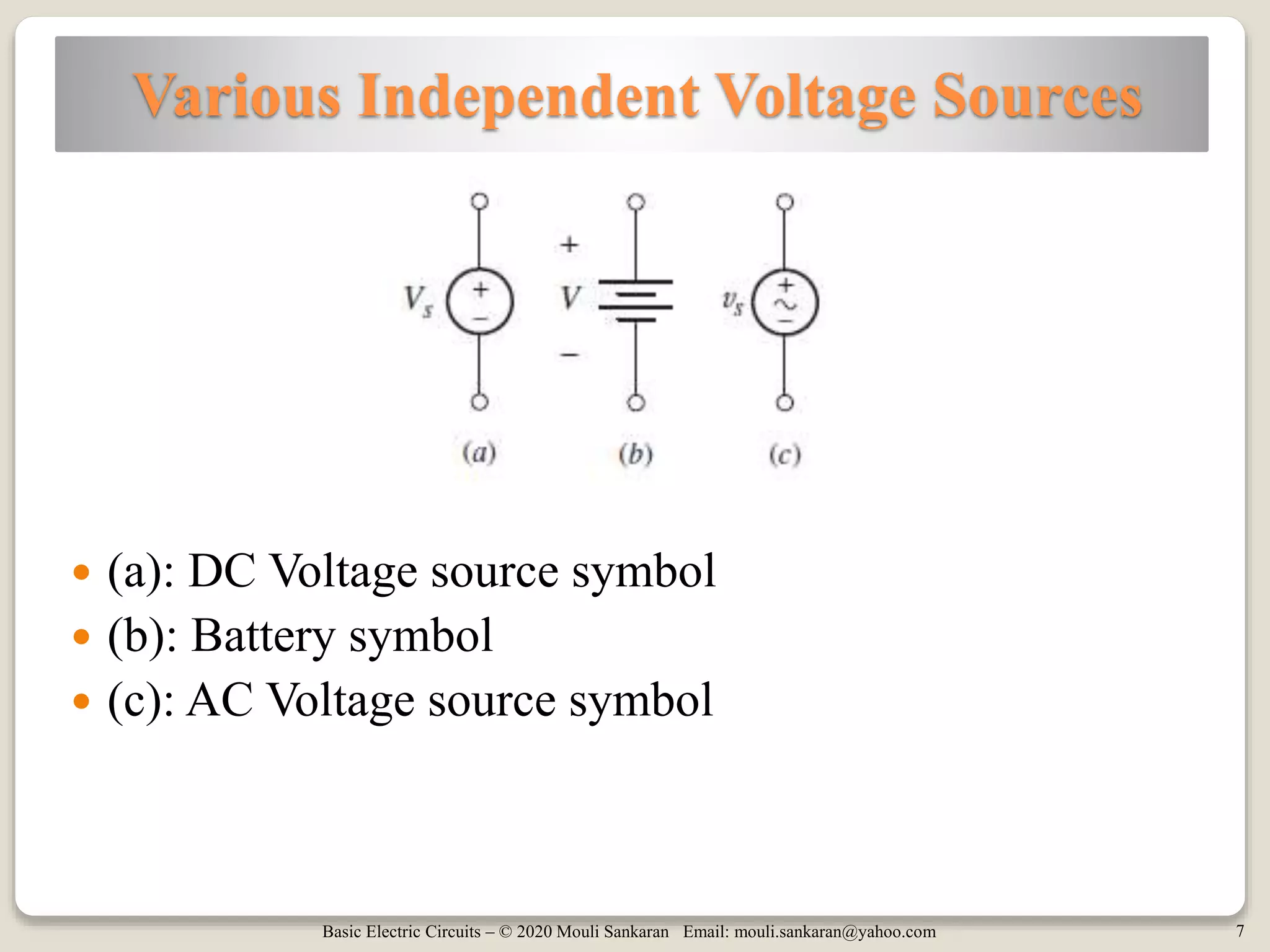
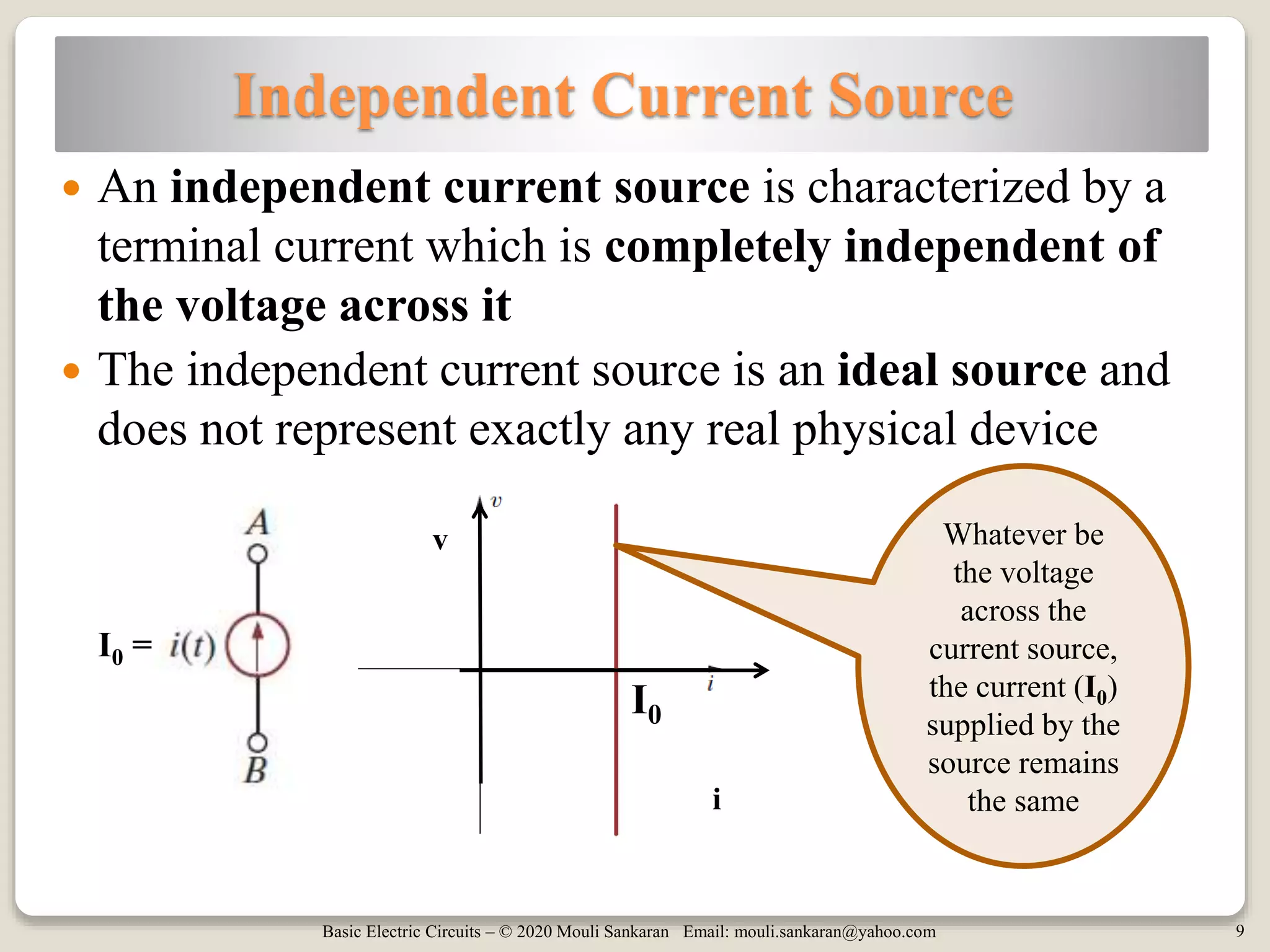
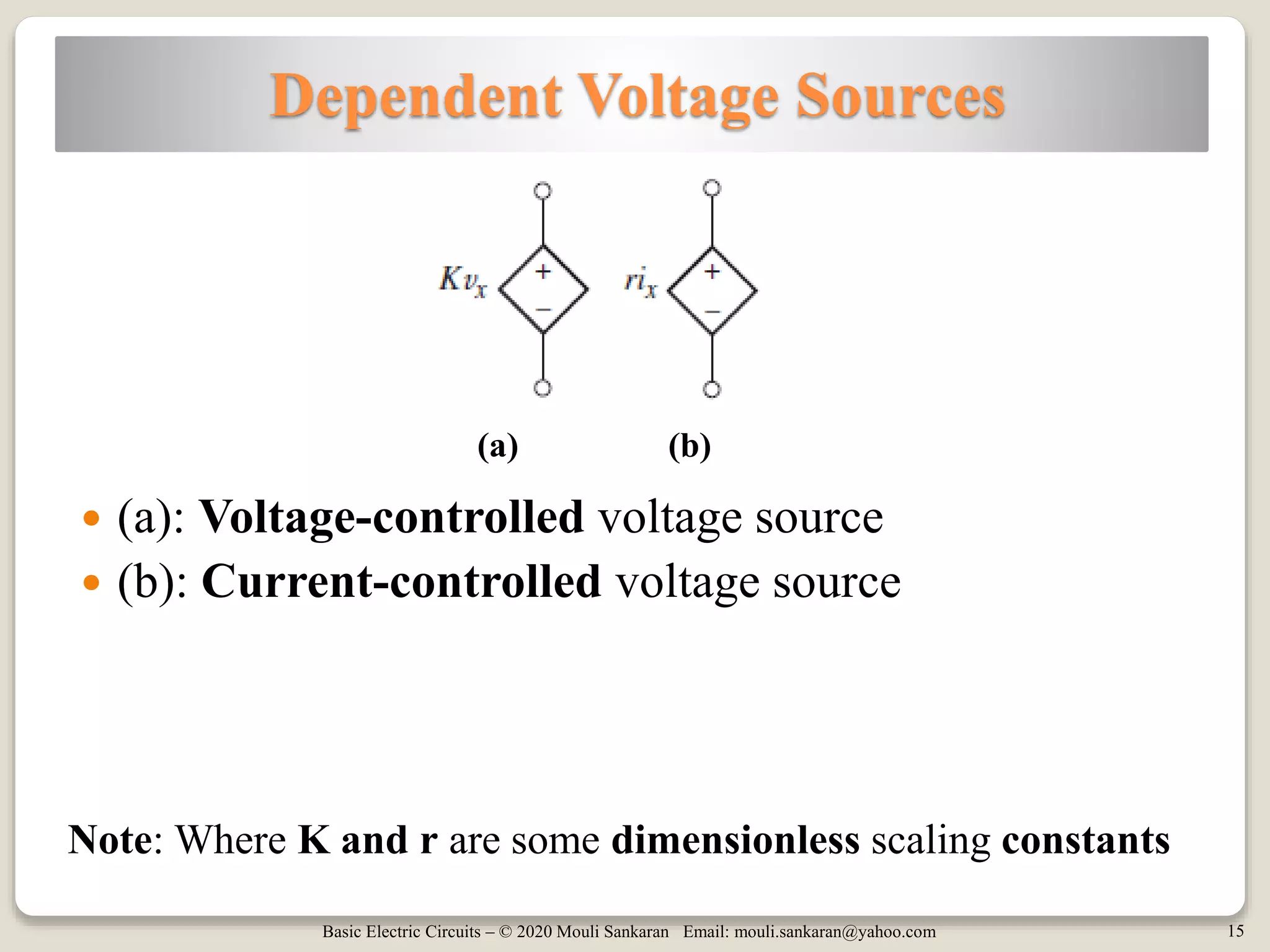
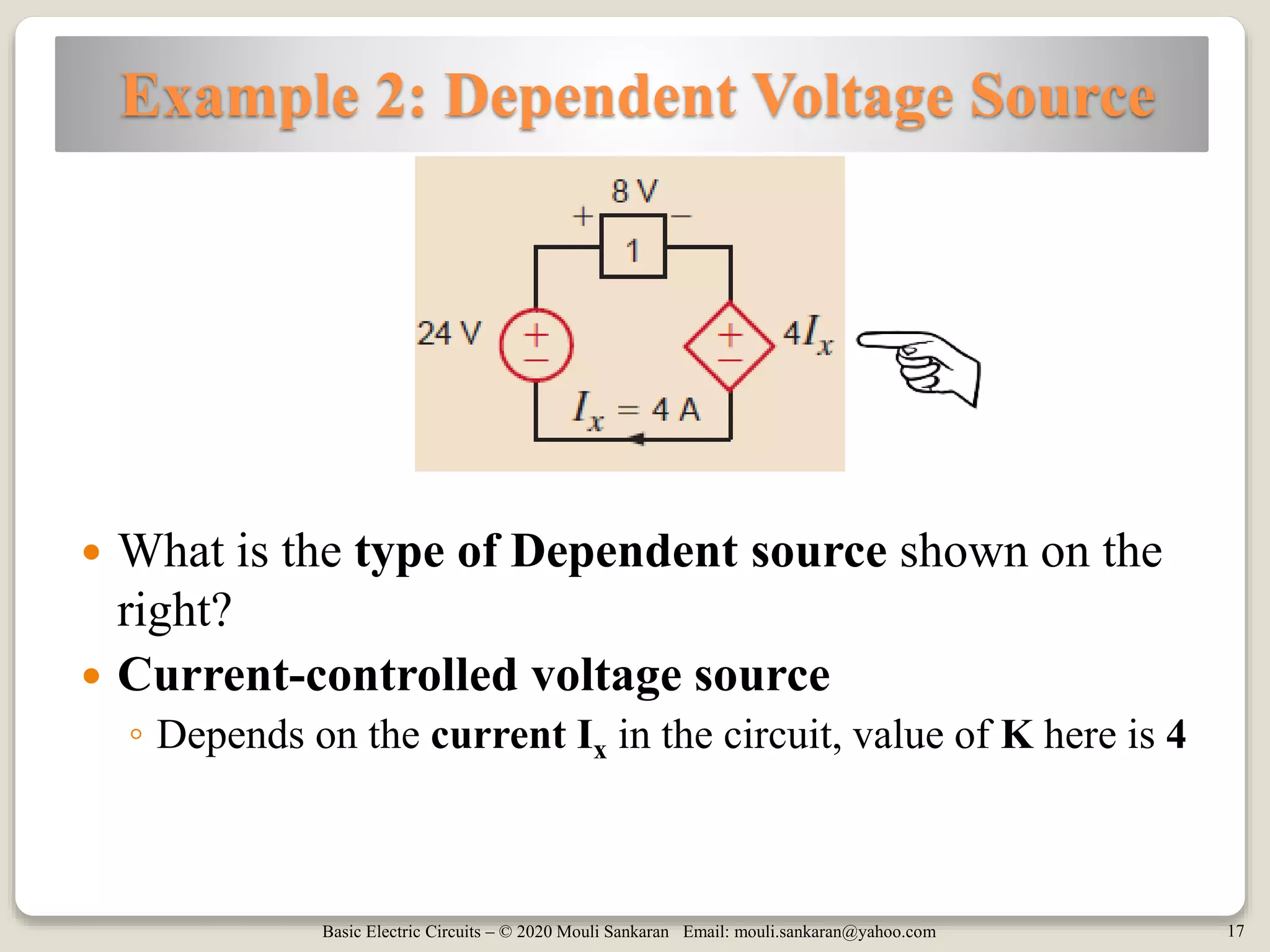
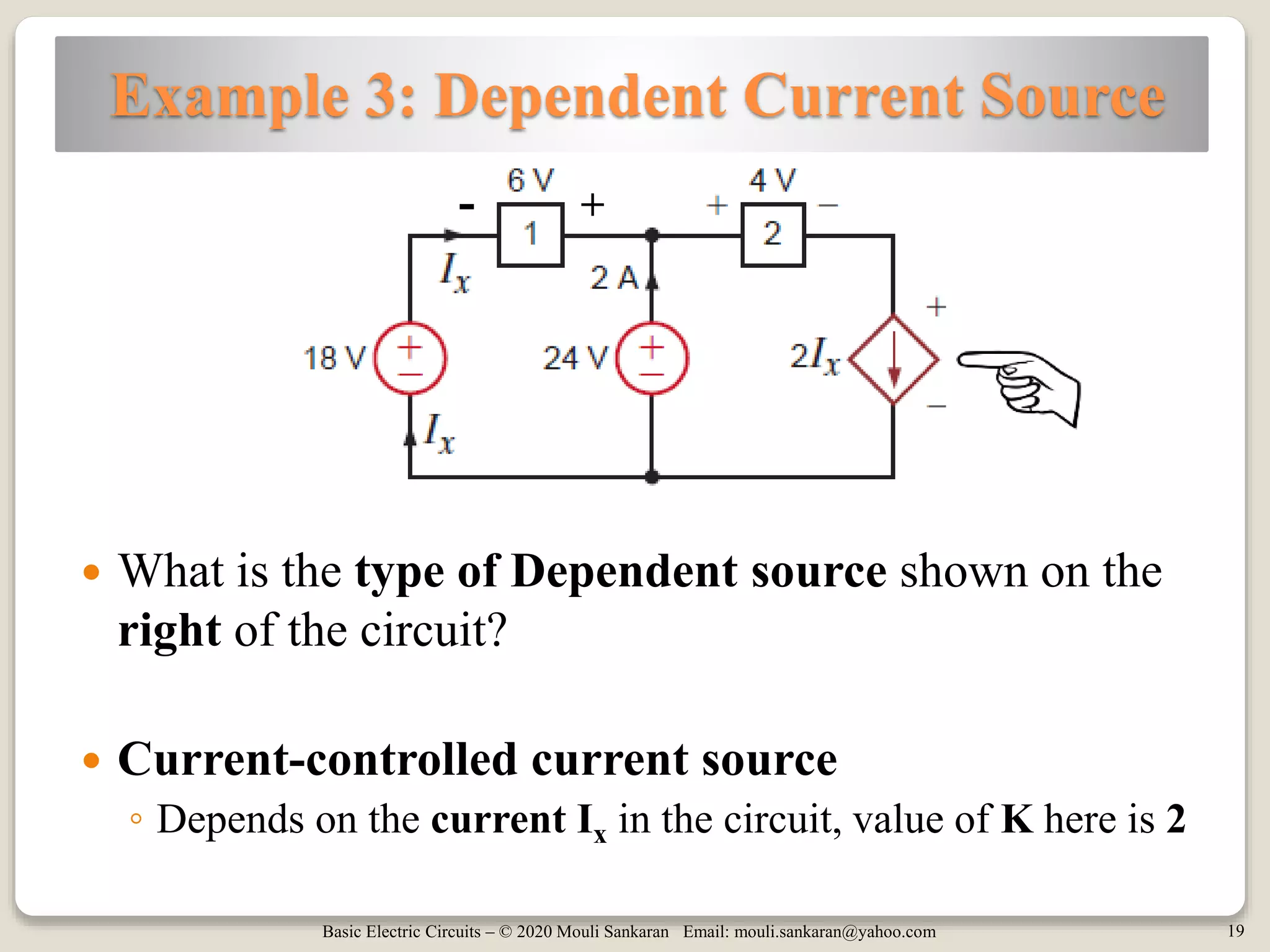
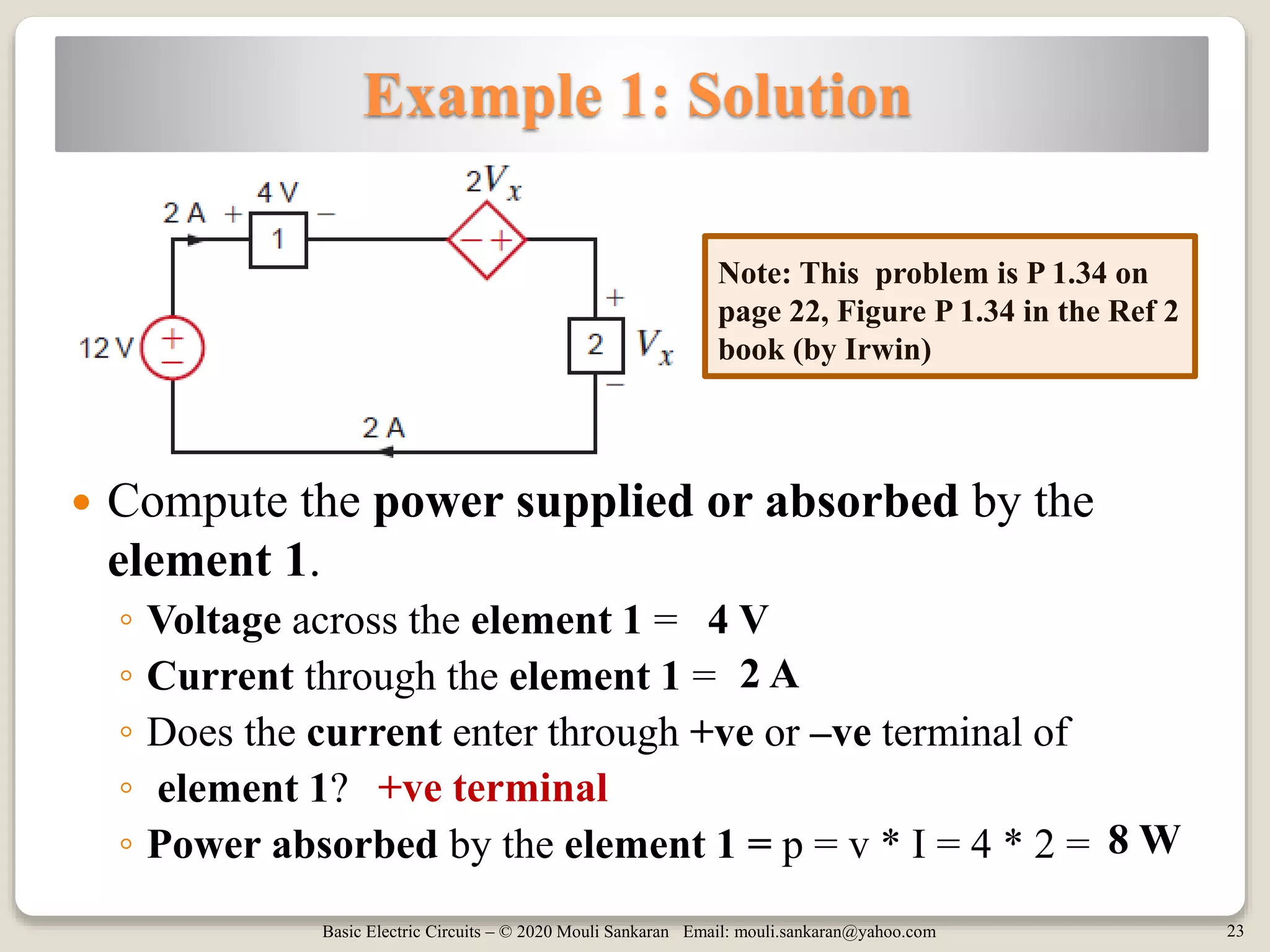
The document provides a comprehensive overview of basic electric circuit concepts, including simple circuit elements and various types of independent and dependent sources. It elaborates on independent voltage and current sources, their characteristics, and includes example problems and homework assignments focusing on circuit analysis. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of dependent sources in modeling electronic circuit behavior.