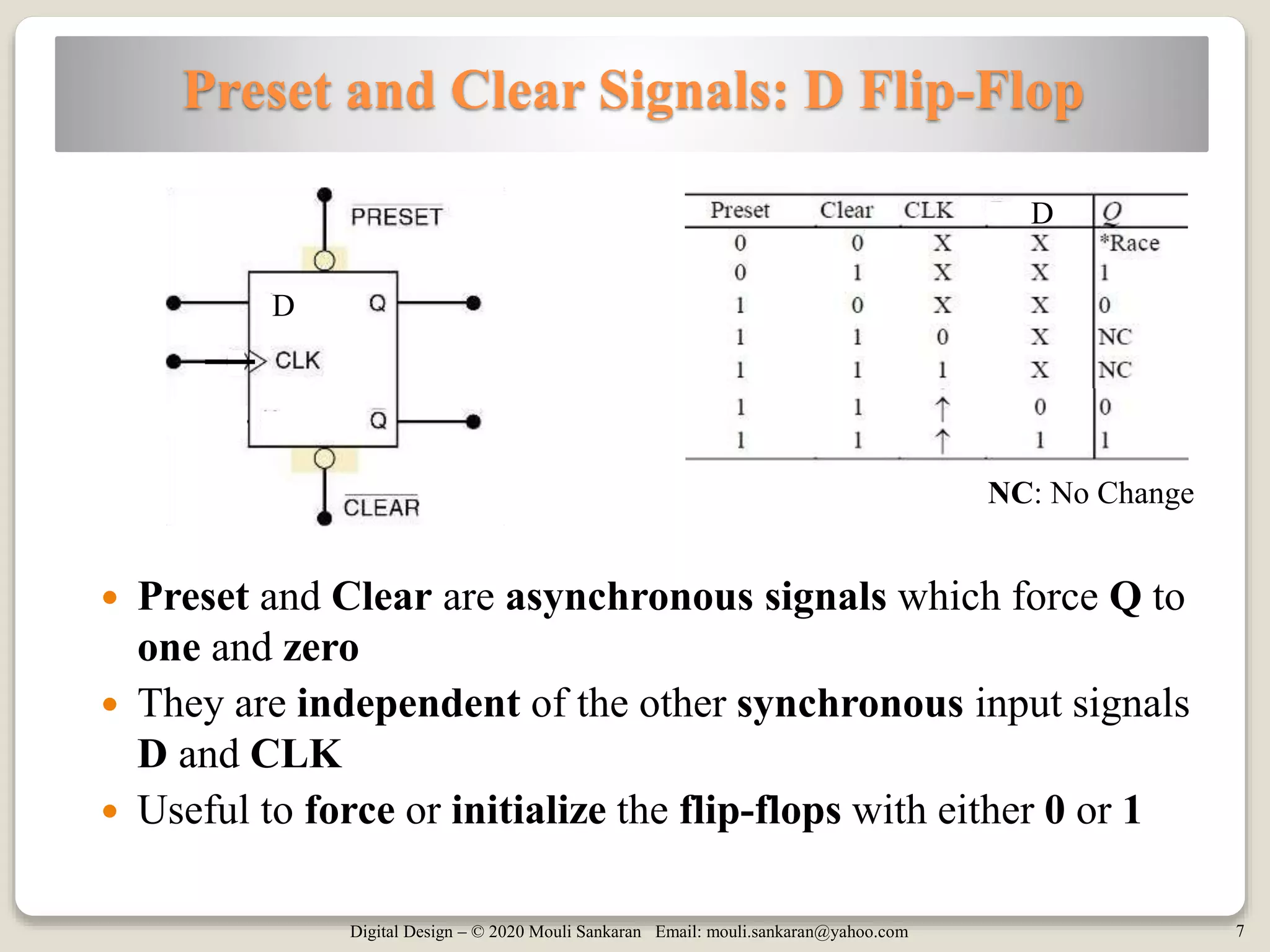
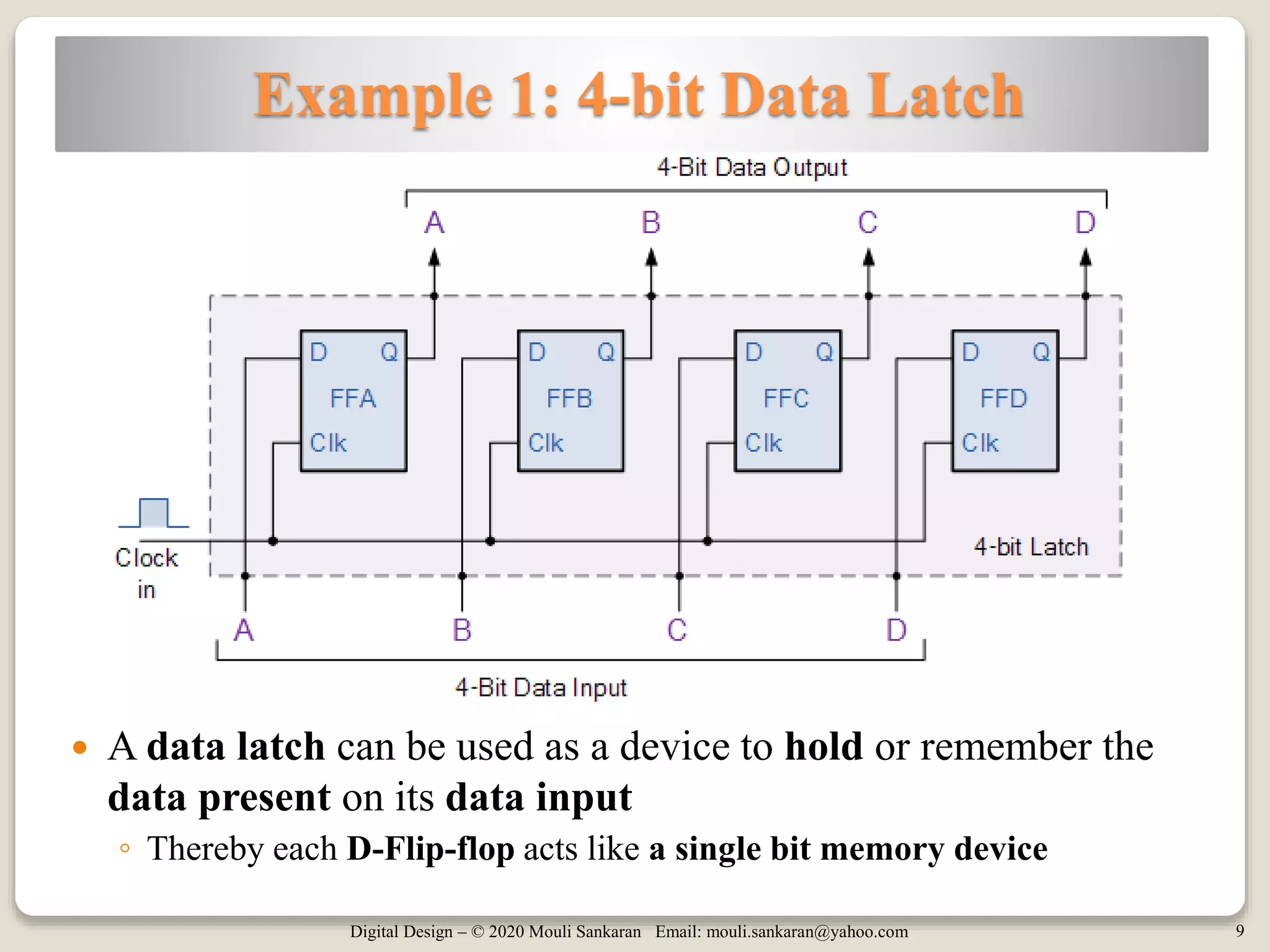
The document discusses the master-slave D flip-flop, focusing on both negative and positive edge triggering, as well as preset and clear implementations. It explains circuits that utilize D flip-flops, such as data latches and edge detection mechanisms. Key aspects include the behavior of preset and clear signals that affect the output independently of other inputs.