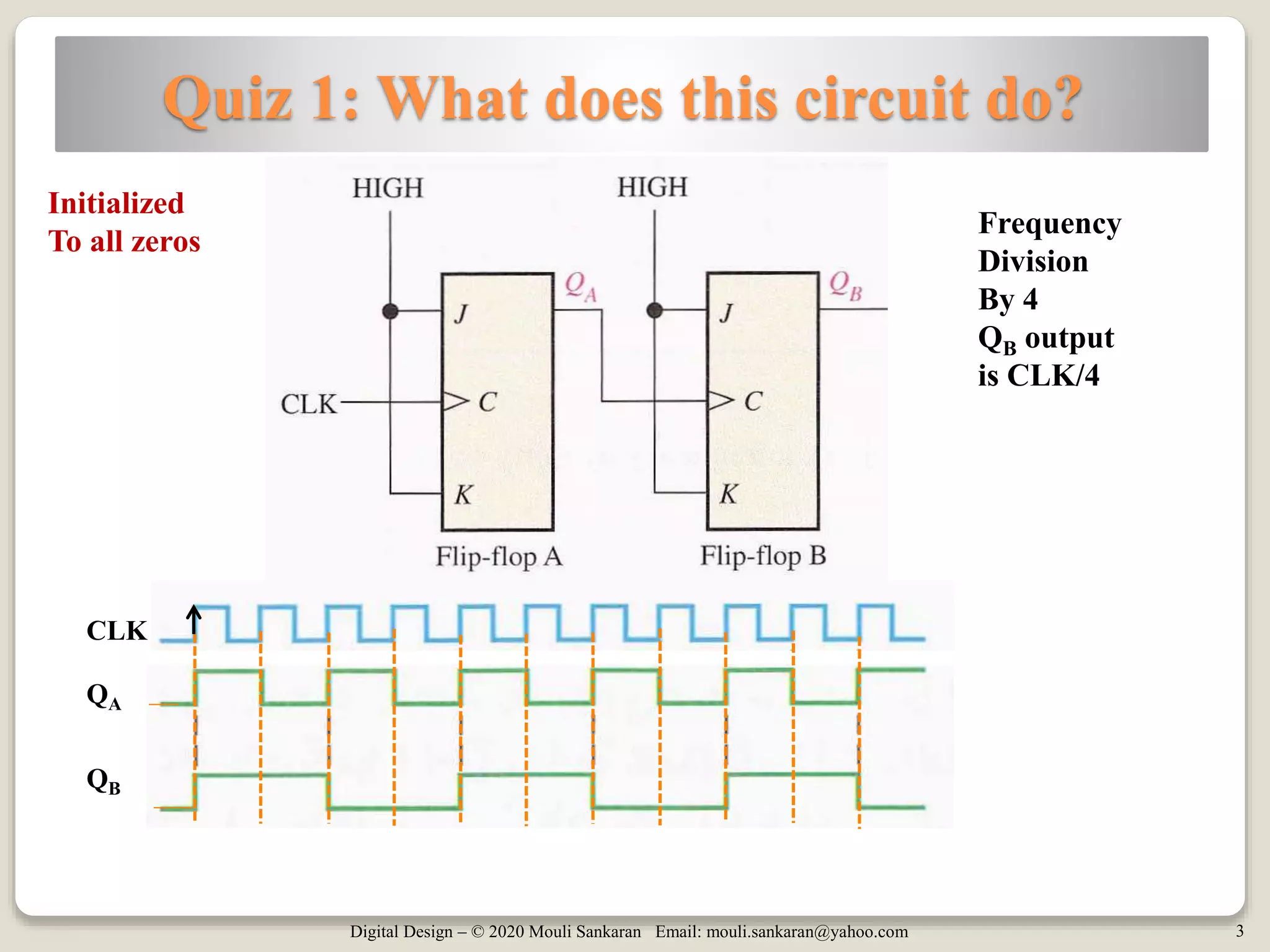
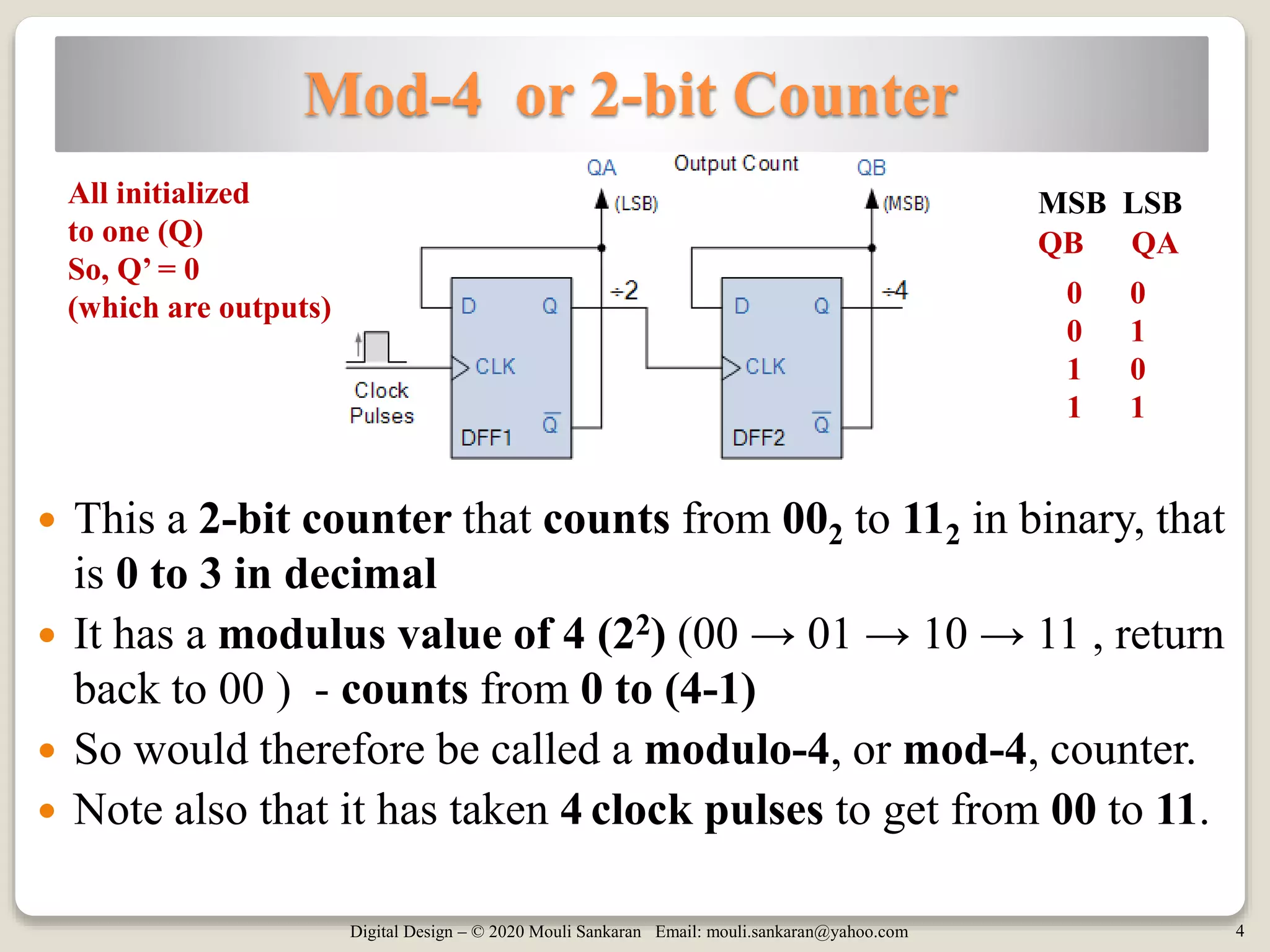
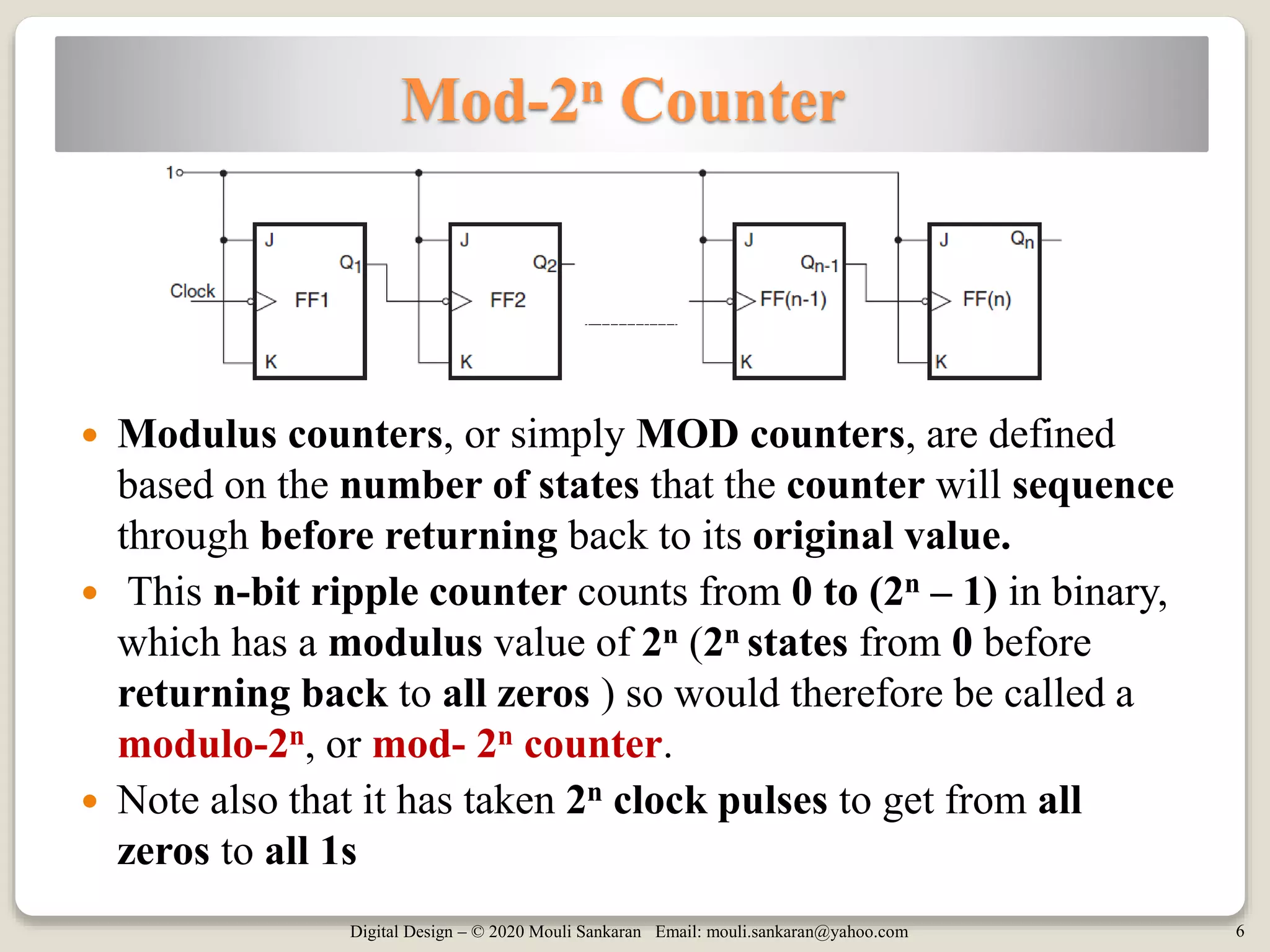
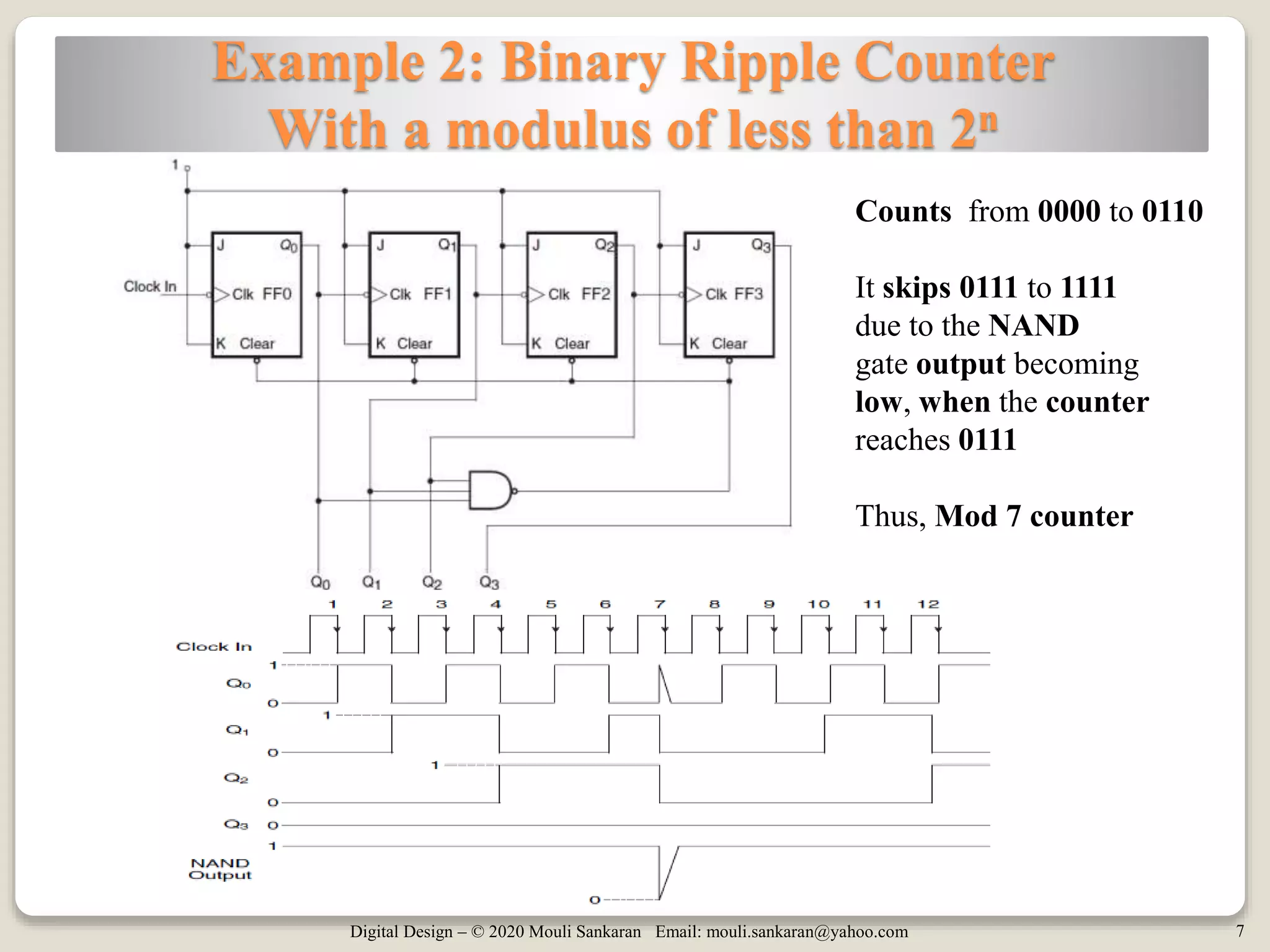
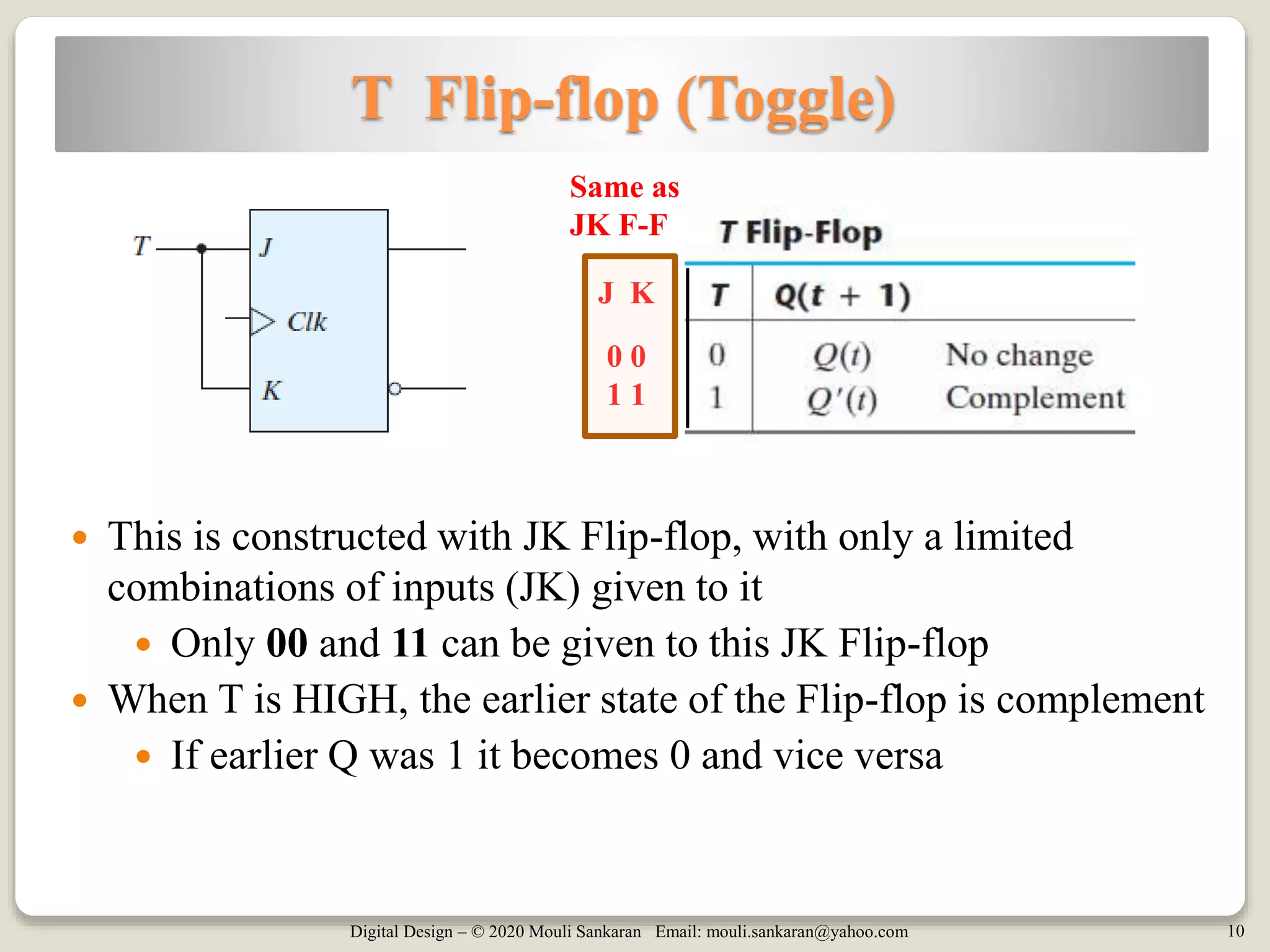
This document discusses various digital logic circuits that use JK flip-flops, including a frequency divider that divides the clock by 4, an n-bit ripple counter that counts from 0 to 2n-1, a ripple counter with a modulus less than 2n, and a 4-bit register. It also describes a T flip-flop, which is constructed from a JK flip-flop and toggles its output each time the input is pulsed high. Examples of different types of counters are provided and their operations explained.