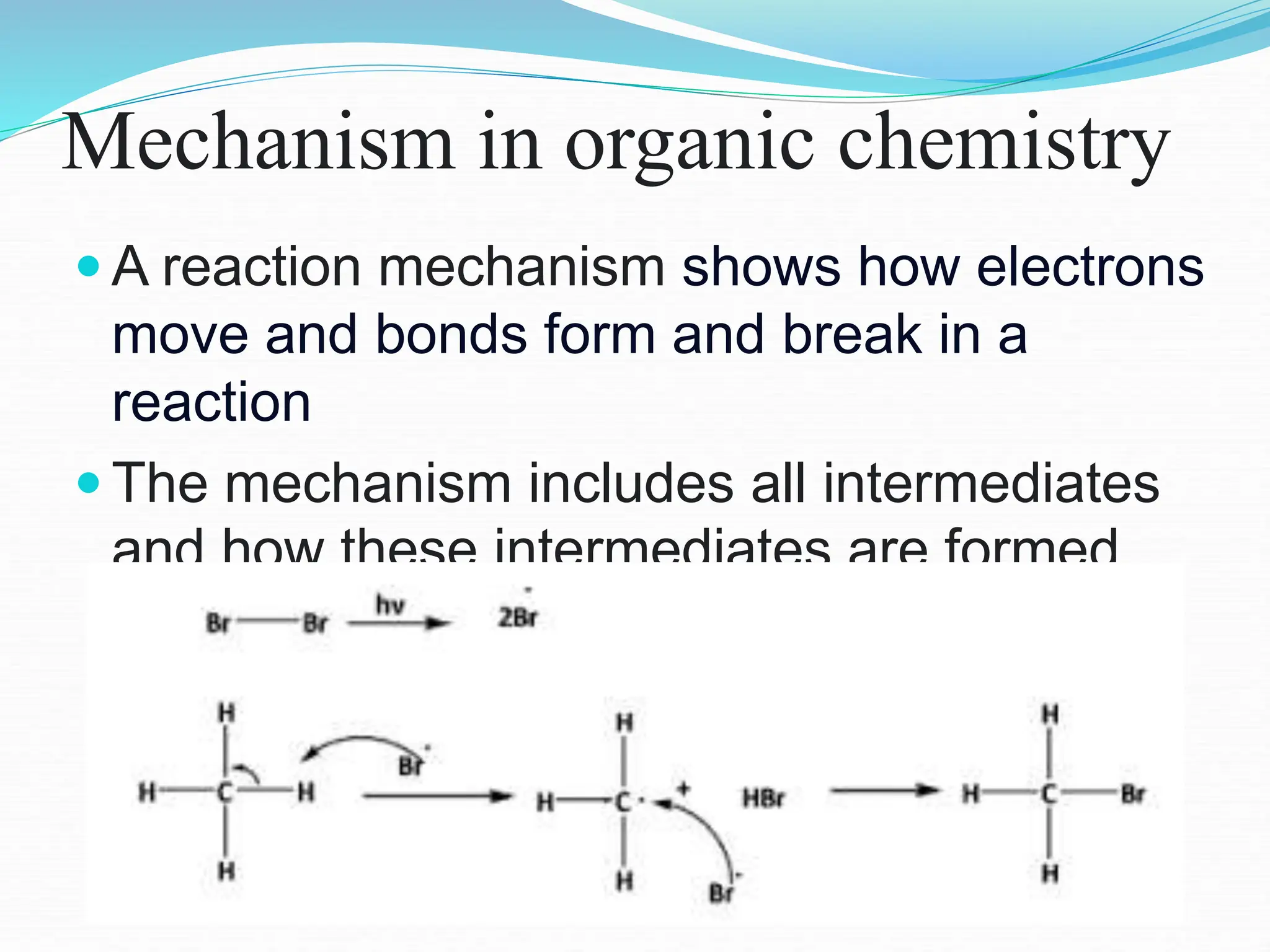
This document discusses various types of organic reaction intermediates. It explains that reaction intermediates are transient chemical species that are formed in one step of a reaction mechanism and consumed in a subsequent step. Common types of intermediates discussed include radicals, carbocations, and carbanions. The document compares the stability of primary, secondary, and tertiary carbocations and carbanions based on factors like inductive effects, hybridization, and resonance. It also provides examples and structures of different organic reaction intermediates.