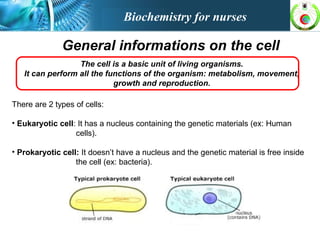
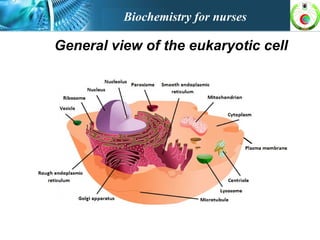
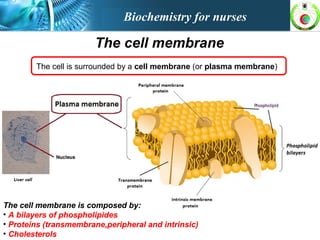
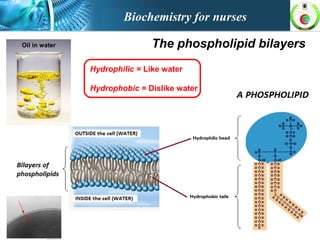
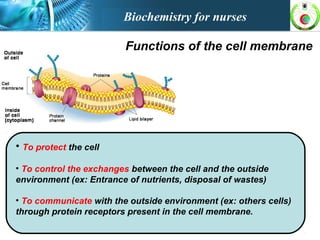
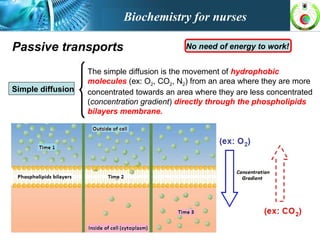
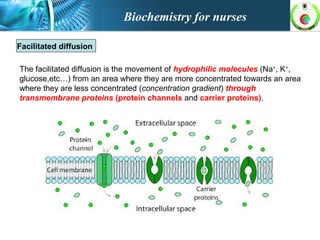
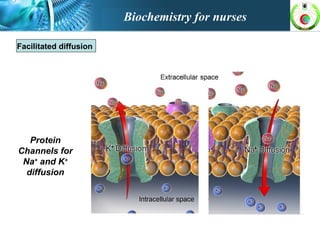
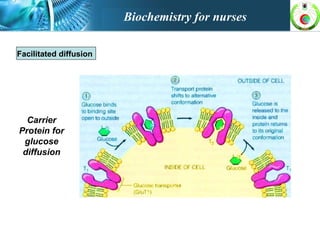
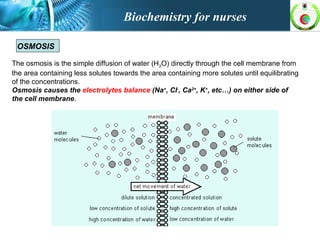
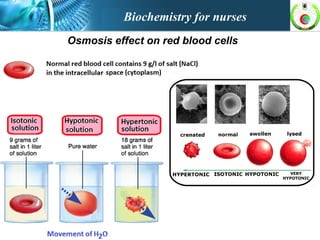
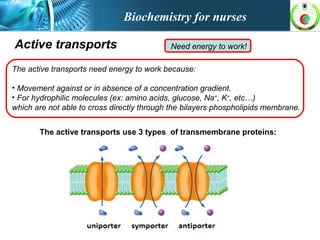
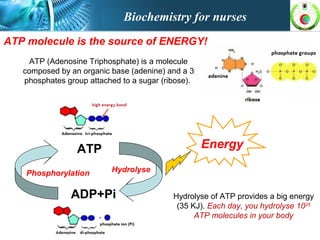
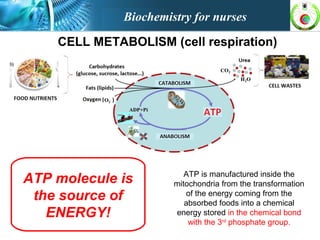
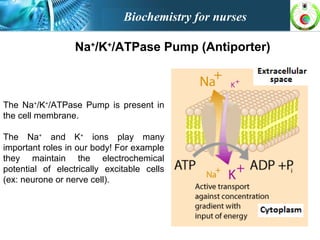
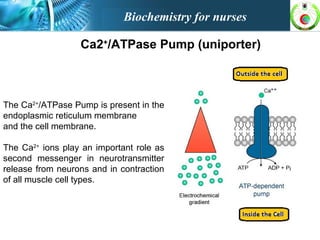
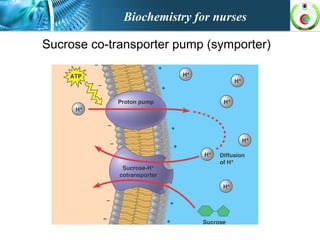
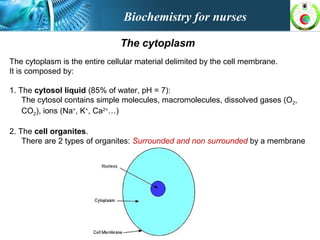
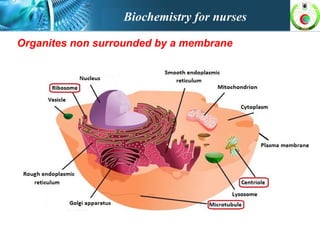
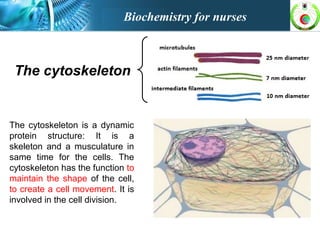
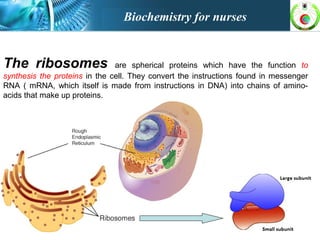
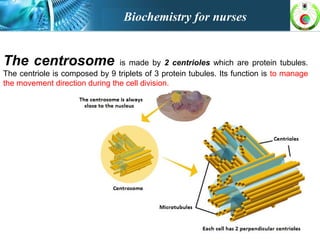
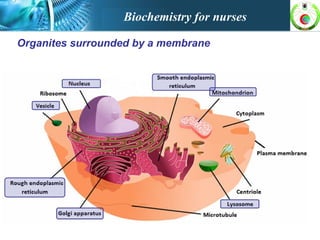
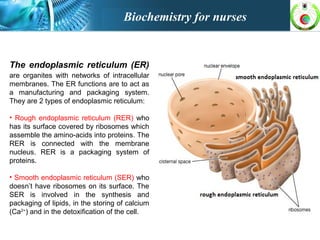
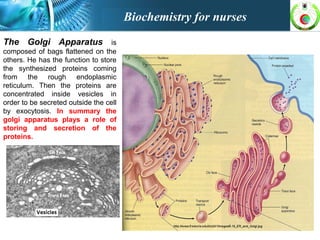
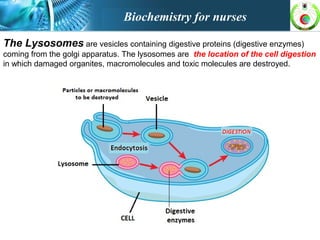
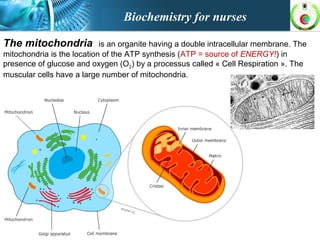
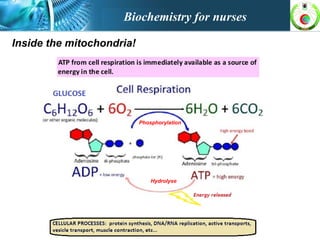
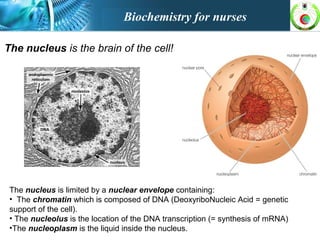
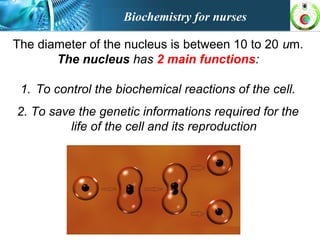
This document provides an overview of cell biology for nurses. It describes the basic components and functions of eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, and nucleus. Specifically, it discusses the structure and roles of the phospholipid bilayer, membrane transport mechanisms like passive diffusion and active transport via pumps, the cytoskeleton, ribosomes, mitochondria which generate energy in the form of ATP, and other organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.