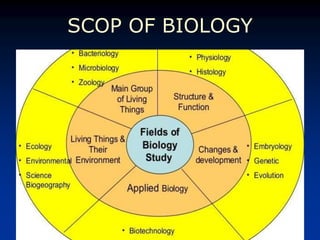
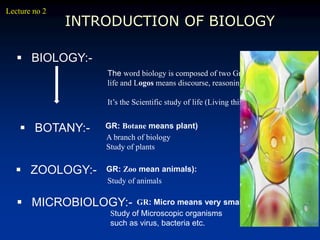
The document provides an overview of science, specifically biology, defining it as the study of life and living organisms through observations and experiments. It describes the characteristics of life, the importance of biology, and various subfields such as zoology, botany, and microbiology. Additionally, it outlines the significance of studying biology in relation to living organisms and their interactions with the environment.