Barbiturates are a class of drugs that act as central nervous system depressants and were one of the first intravenous anesthetic agents used clinically, with thiopental and methohexital being two examples that are ultra short-acting and can be used for anesthetic induction. Barbiturates work by enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the brain and have a variety of clinical uses but also potential adverse effects like respiratory depression if overdosed.



![STRUCTURE
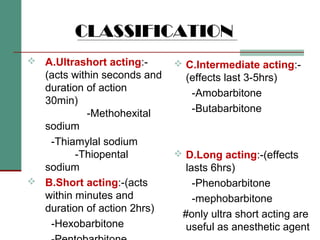
Oxybarbiturates
Thiobarbiturates
THIOPENTONE:5-ethyl,5[methyl,butyl]2-thiobarbiturate
METHOHEXITONE:1-methyl-5-allyl5[methyl,pentynyl]
2-oxybarbiturate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barbiturates-120826112622-phpapp01/85/Barbiturates-5-320.jpg)





































