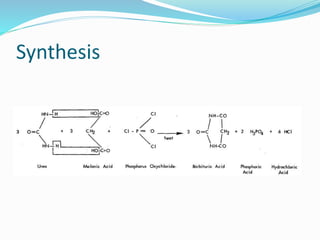
Barbiturates are CNS depressants that were historically used as sedatives and hypnotics. They are synthesized from urea and malonic acid. Barbiturates work by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA, causing neuronal hyperpolarization. They can cause sedation, hypnosis, narcosis, general anesthesia, and even death depending on dosage. Barbiturates are classified based on their duration of action and chemical structure. While formerly widely used, barbiturates have been replaced by safer alternatives due to risks of overdose, tolerance, and drug interactions.