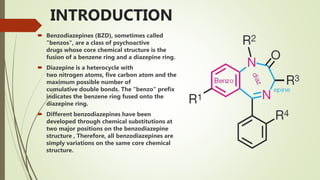
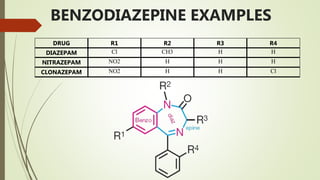
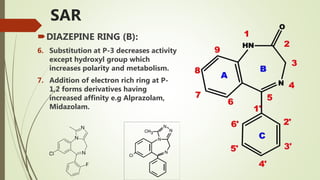
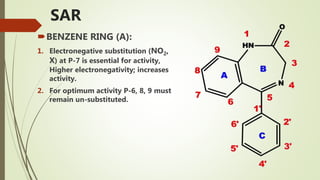
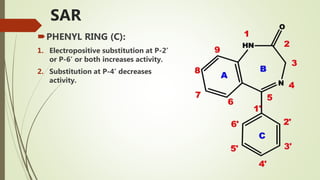
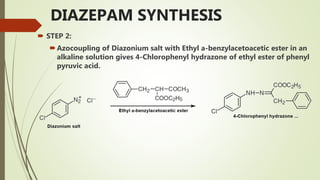
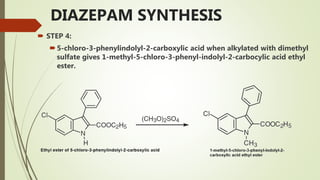
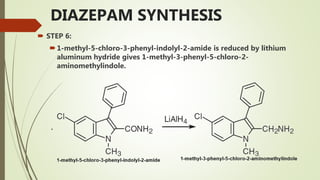
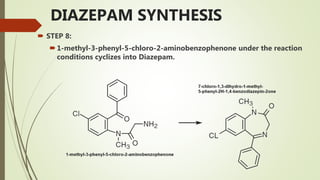
This document summarizes information about benzodiazepines. It discusses their core chemical structure as a fusion of benzene and diazepine rings, with different substitutions leading to different benzodiazepines. It provides examples like diazepam, nitrazepam, and clonazepam. The document outlines the history of benzodiazepines from their synthesis in the 1950s-60s and increasing use as alternatives to barbiturates. It also covers their classification, mechanism of action involving GABA receptors, advantages, structure-activity relationships, and indications like alcohol withdrawal, anxiety, and insomnia.