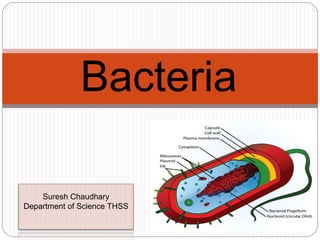
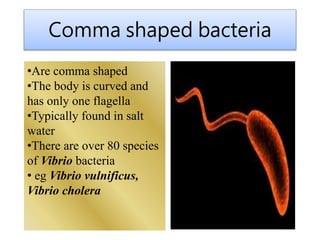
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that come in a variety of shapes and live in many environments. They were first observed by Van Leeuwenhoek in 1676 and named by Ehrenberg in 1828. Bacteria are prokaryotic, lacking organelles like nuclei, and reproduce through binary fission. There are four main types - rod-shaped bacilli like E. coli, spherical cocci like streptococci, spiral-shaped spirilla, and comma-shaped vibrios like V. cholerae. Bacteria can be helpful by increasing soil fertility, aiding digestion, and creating antibiotics, but can also be harmful as pathogens causing diseases or by contaminating food.