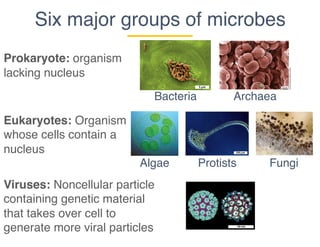
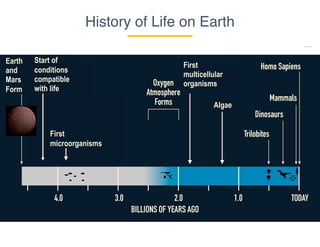
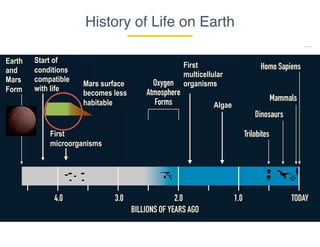
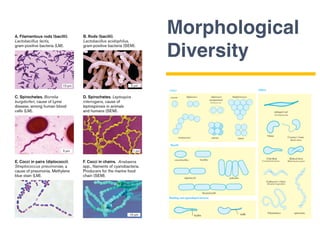
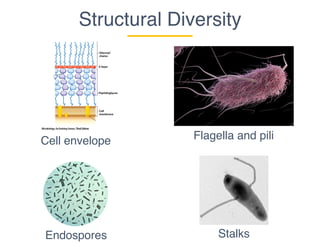
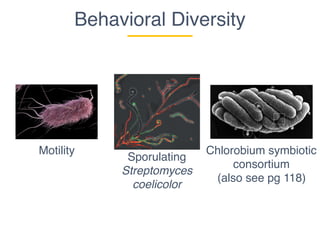
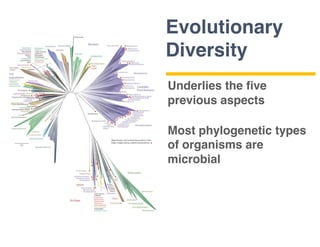
This document provides an introduction to microbial diversity. It defines microbes as small living organisms that require a microscope to be seen, including six major groups: bacteria, archaea, algae, protists, fungi, and viruses. The document discusses the morphological, metabolic, ecological, behavioral, and evolutionary diversity of microbes and provides some examples, such as different cell structures, means of obtaining energy like photosynthesis, and habitats like the human gut and acid mine drainage. It notes that microbes play critical roles in biogeochemical cycles, multicellular life, agriculture, and human health.