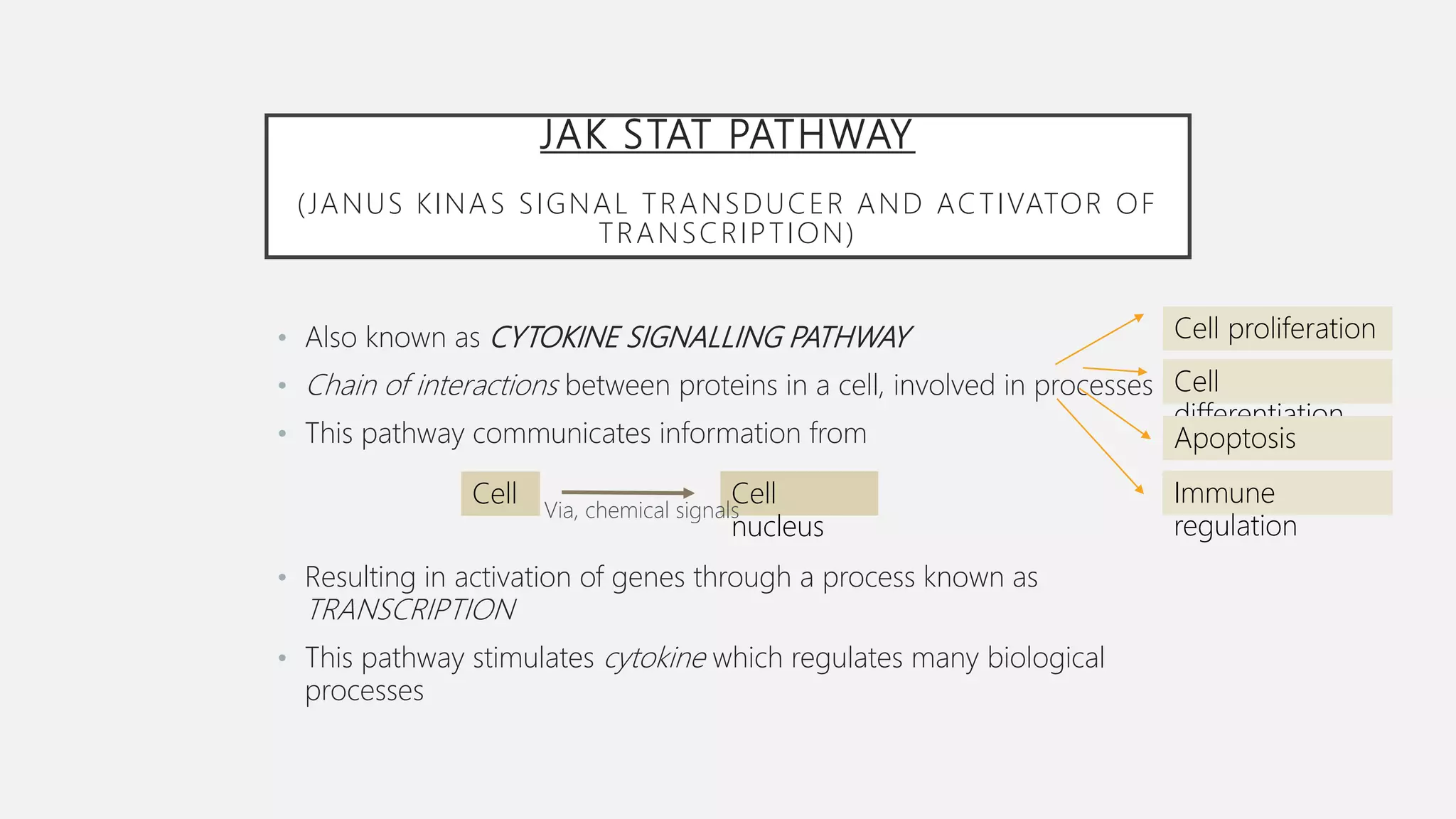
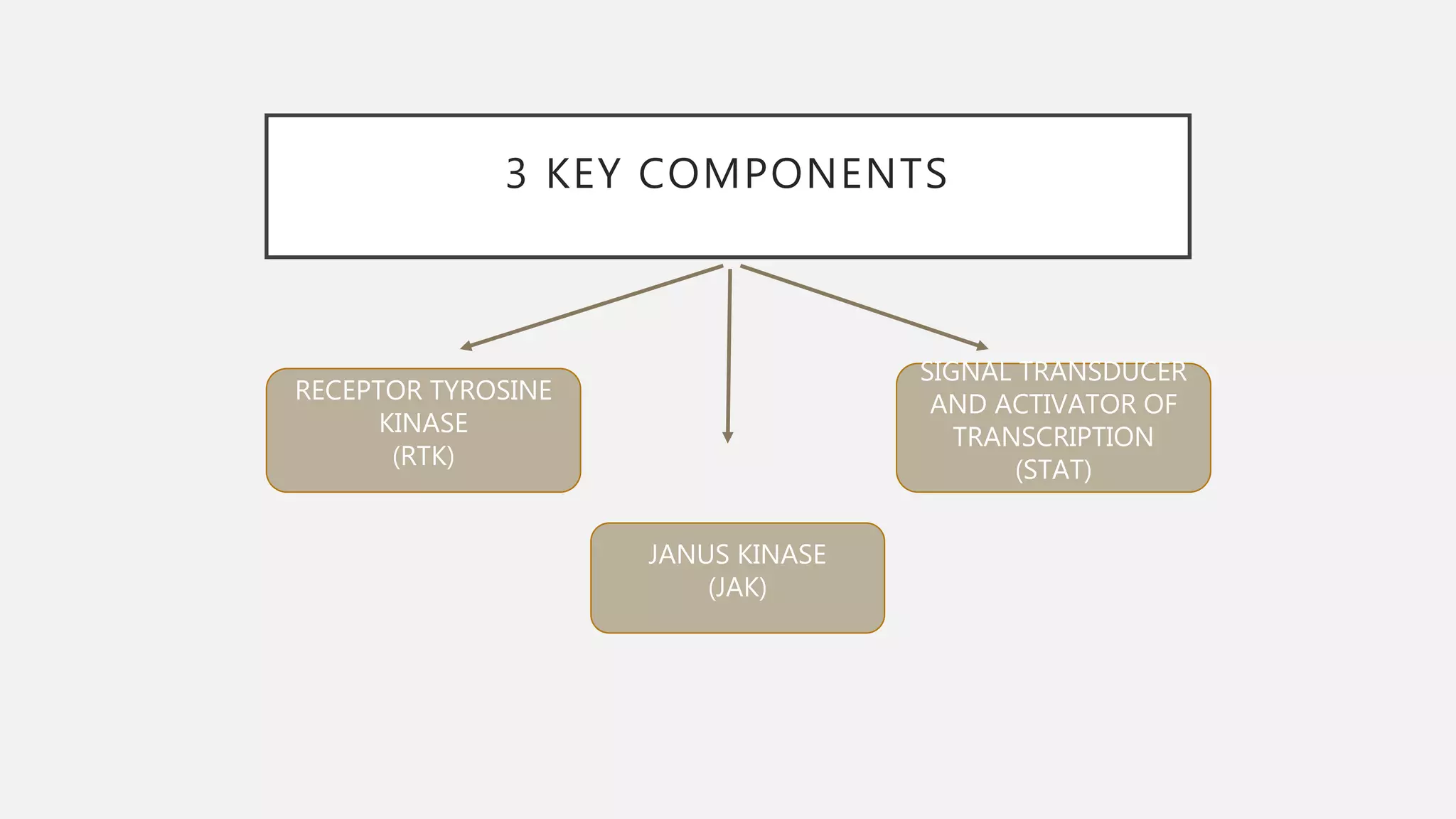
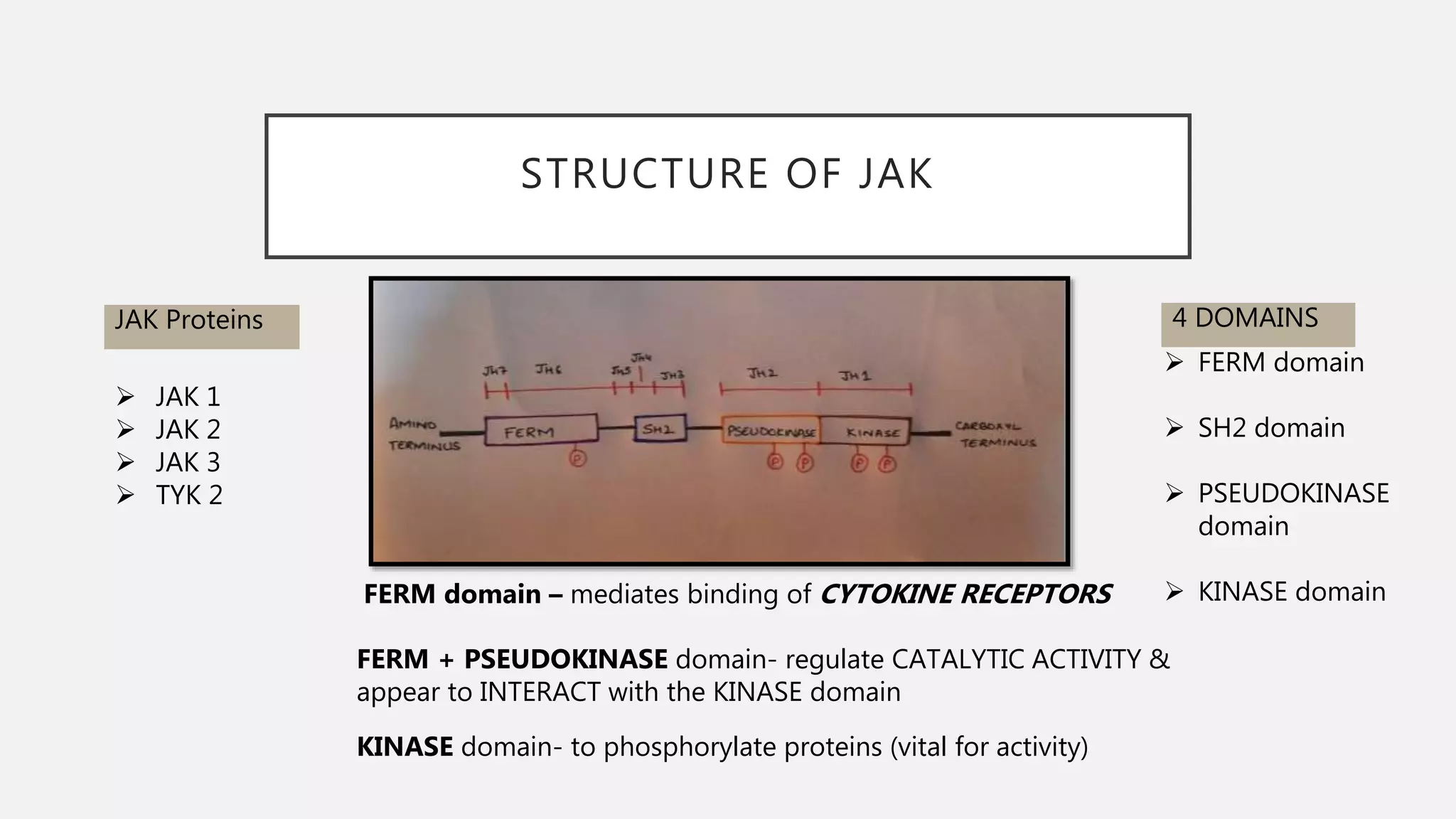
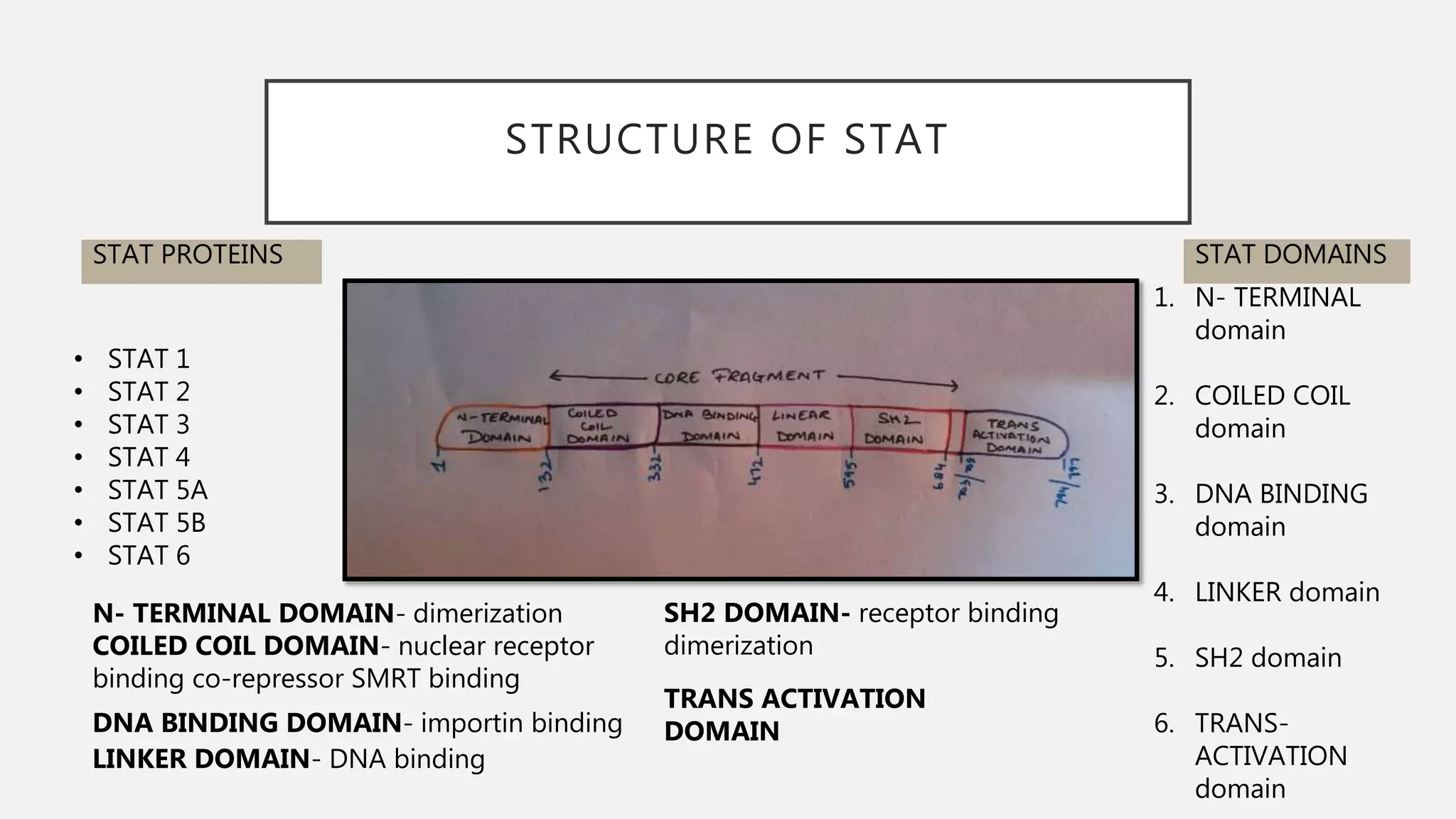
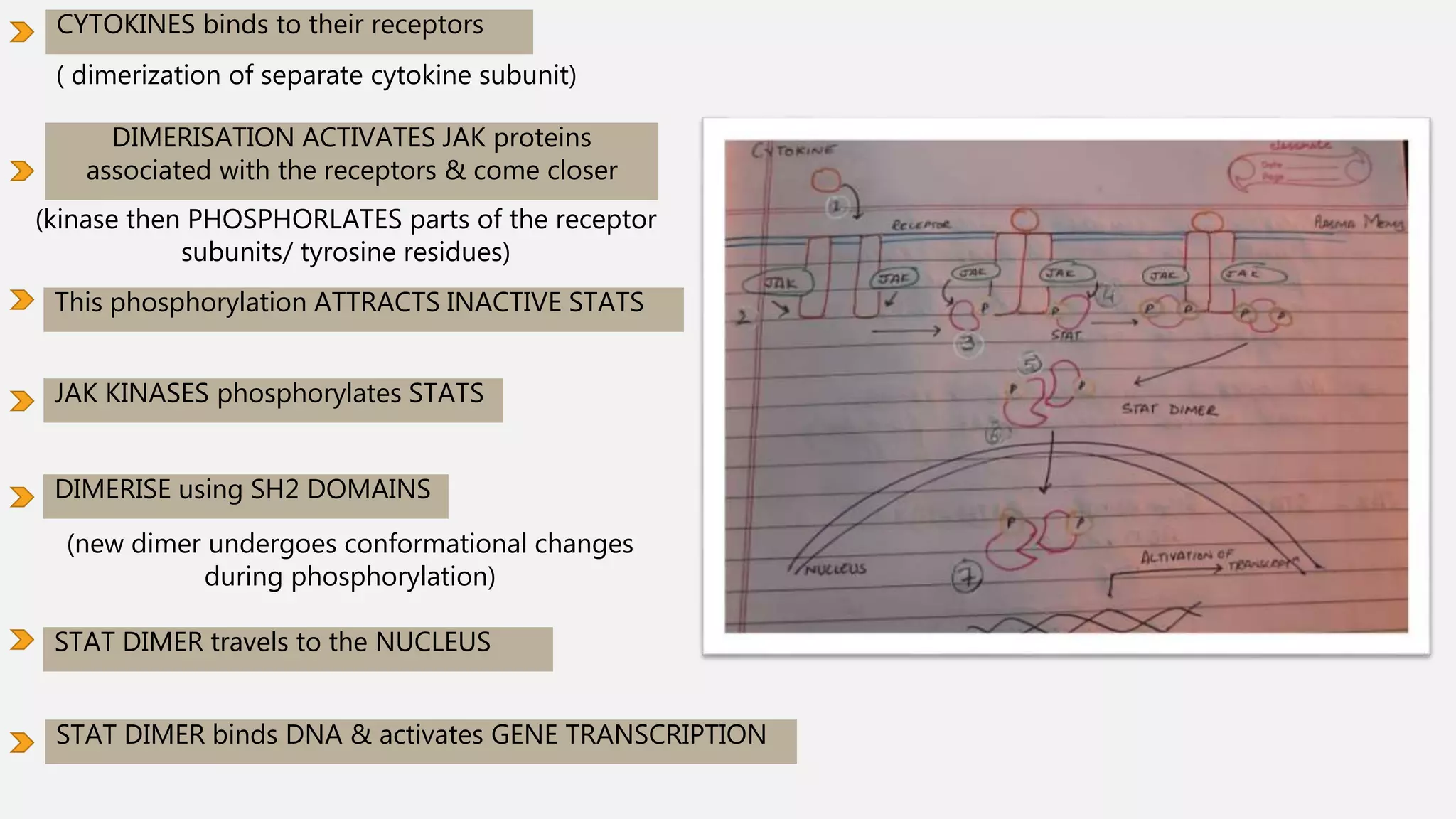
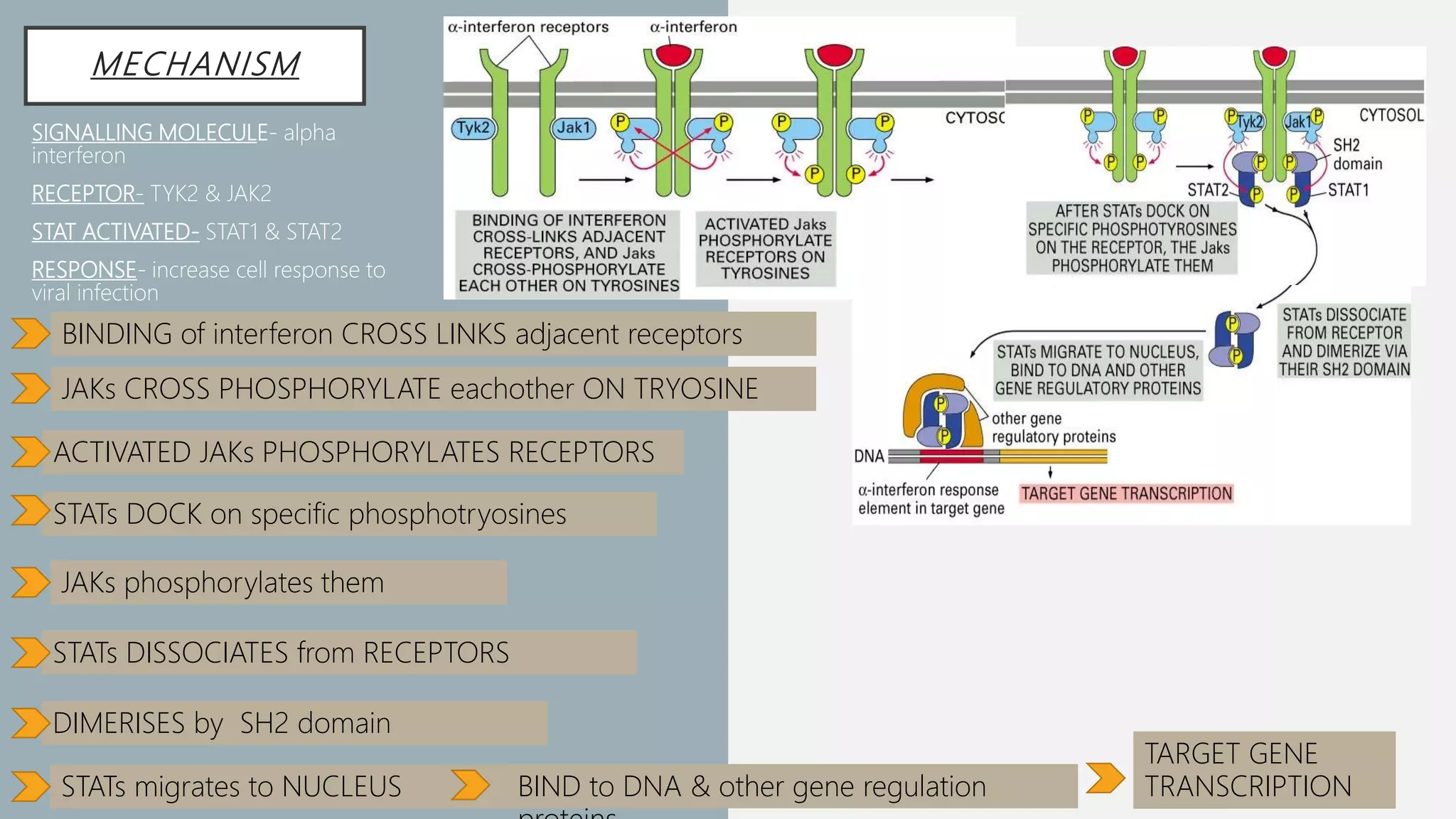
The JAK-STAT pathway is a key cell signaling pathway that communicates information from extracellular signaling molecules called cytokines into the cell nucleus. It involves three main components: Janus kinases (JAKs) that associate with cytokine receptors and become activated by phosphorylation upon cytokine binding, signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) that are phosphorylated by JAKs and then form dimers that translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene expression, and cytokine receptors that dimerize upon cytokine binding to bring associated JAKs together for cross-phosphorylation and activation of the pathway. The JAK-STAT pathway regulates many important cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses by transmitting signals from cytokines and stimulating