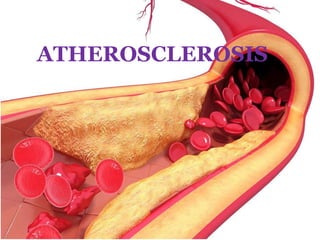
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the thickening of artery walls due to fatty materials, leading to restricted blood flow and potential complications such as heart disease and stroke. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and an unhealthy diet, while prevention focuses on lifestyle changes. Treatments involve lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical procedures to manage symptoms and reduce risks.