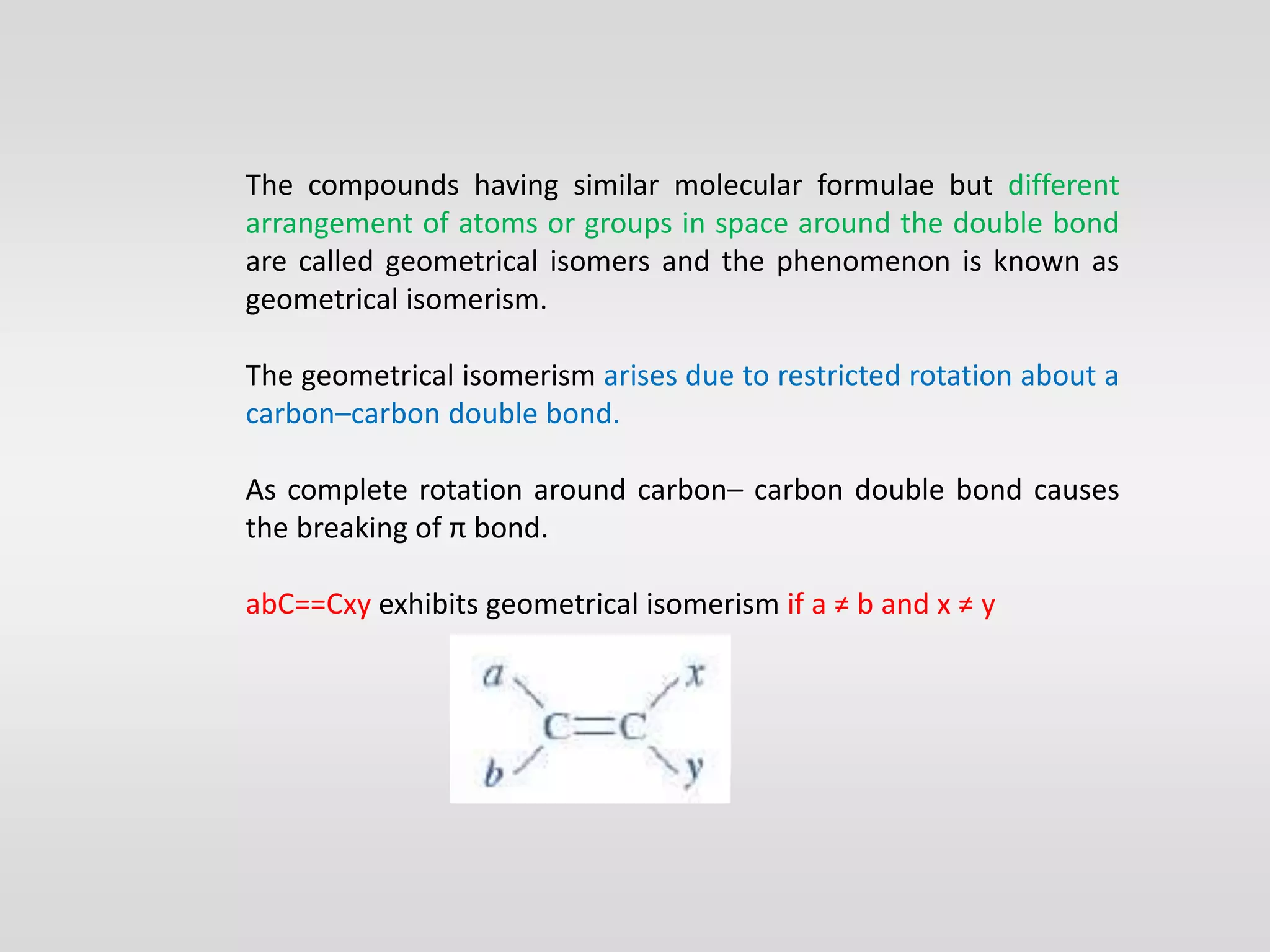
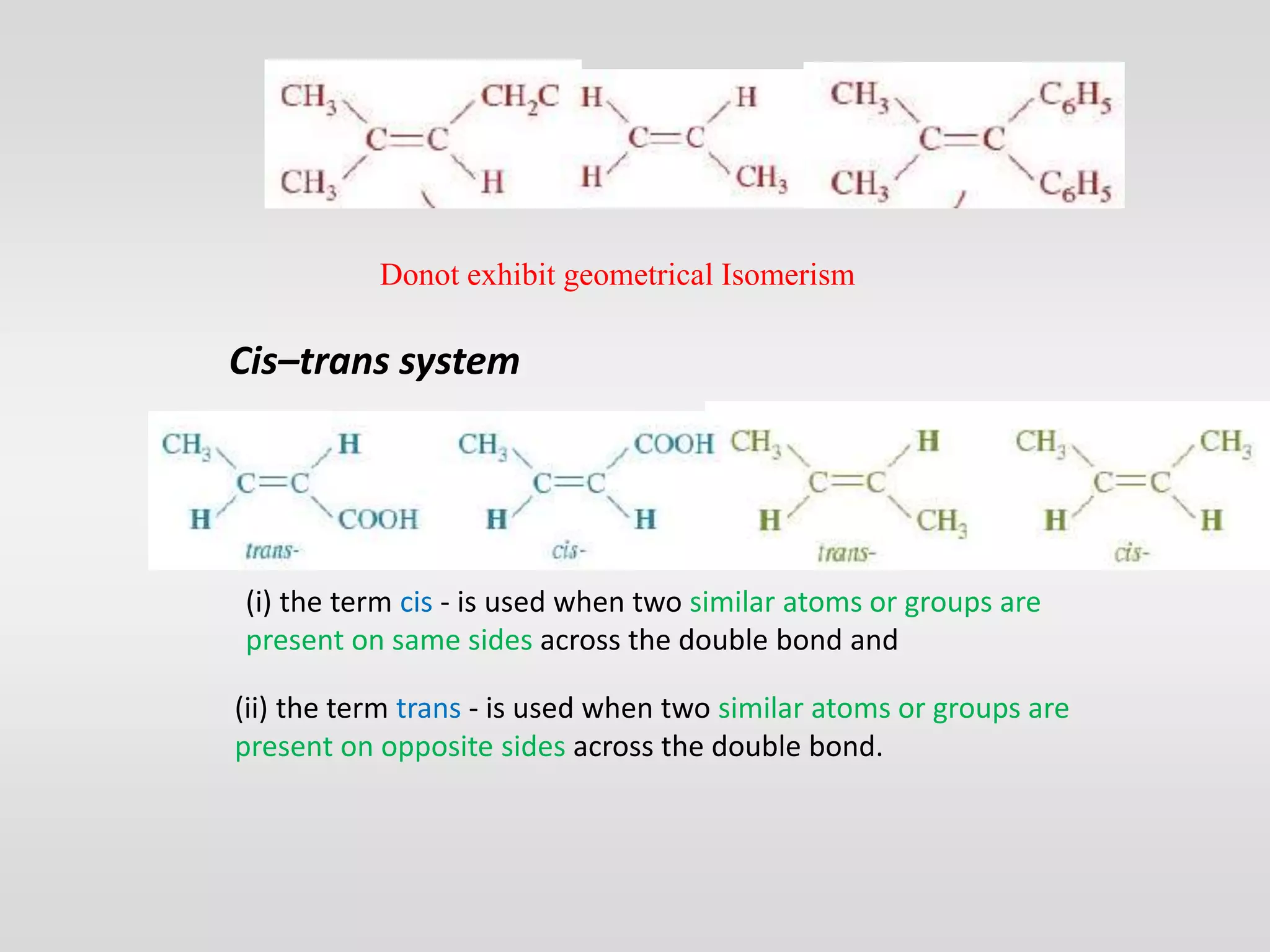
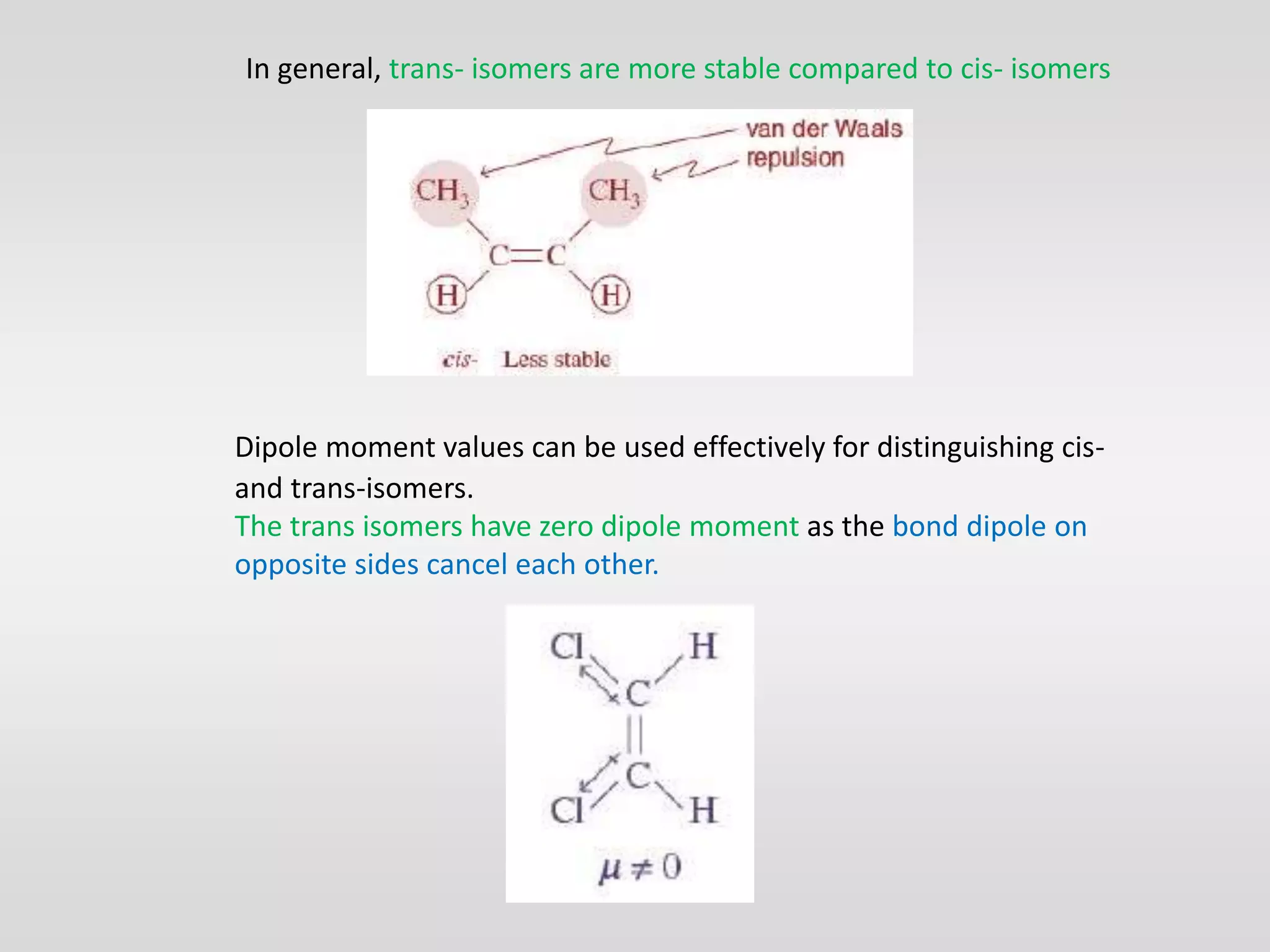
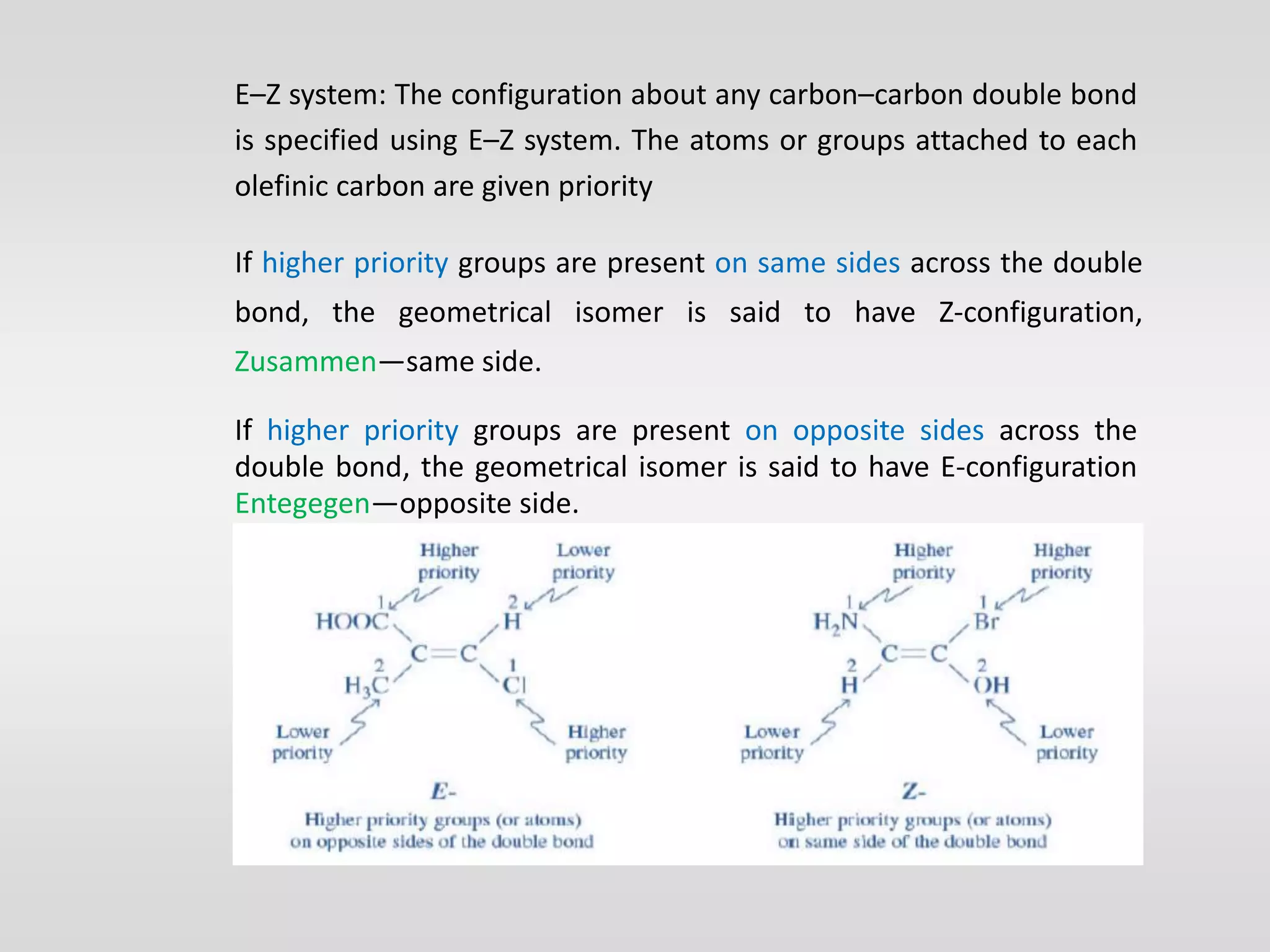
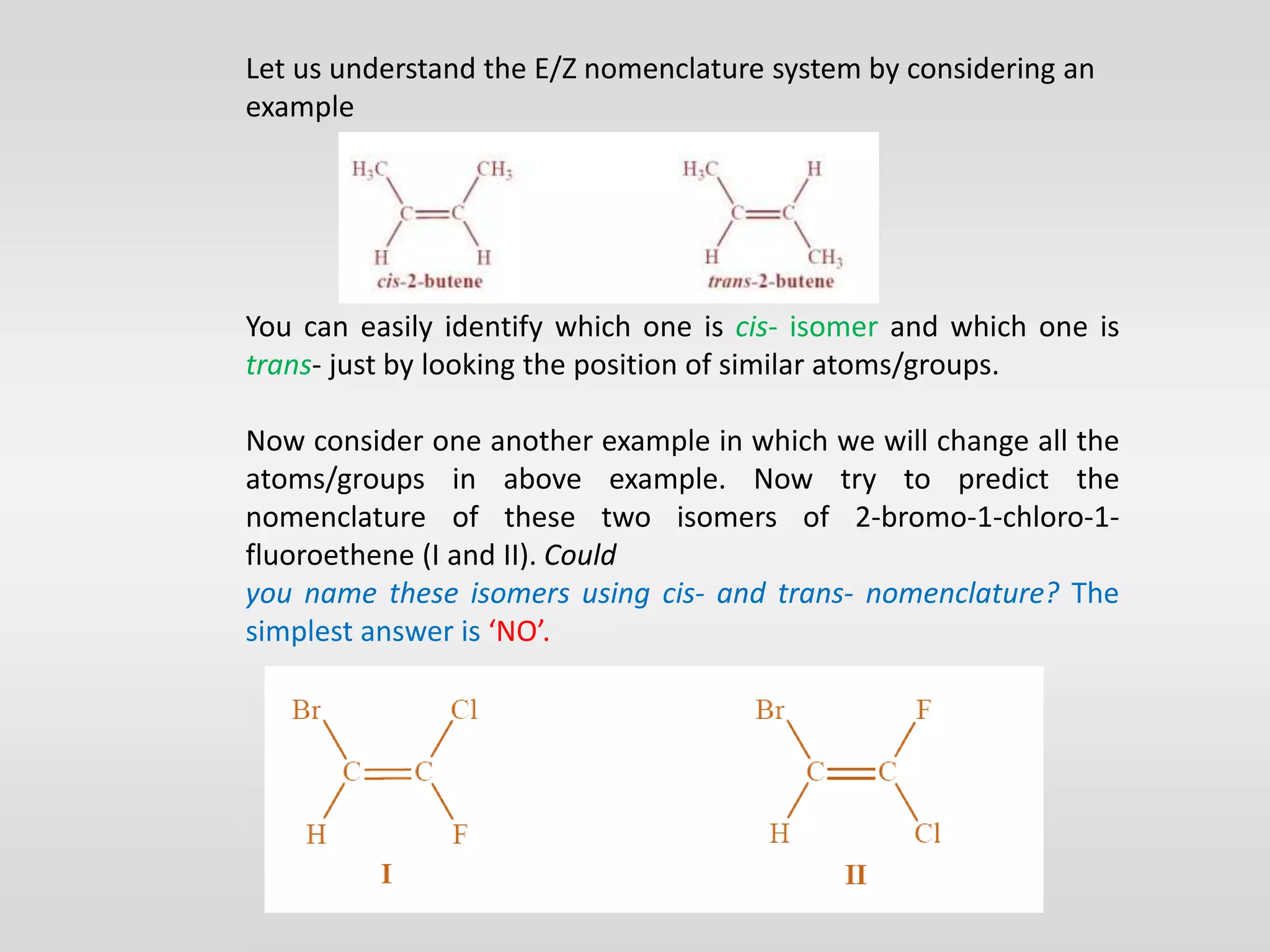
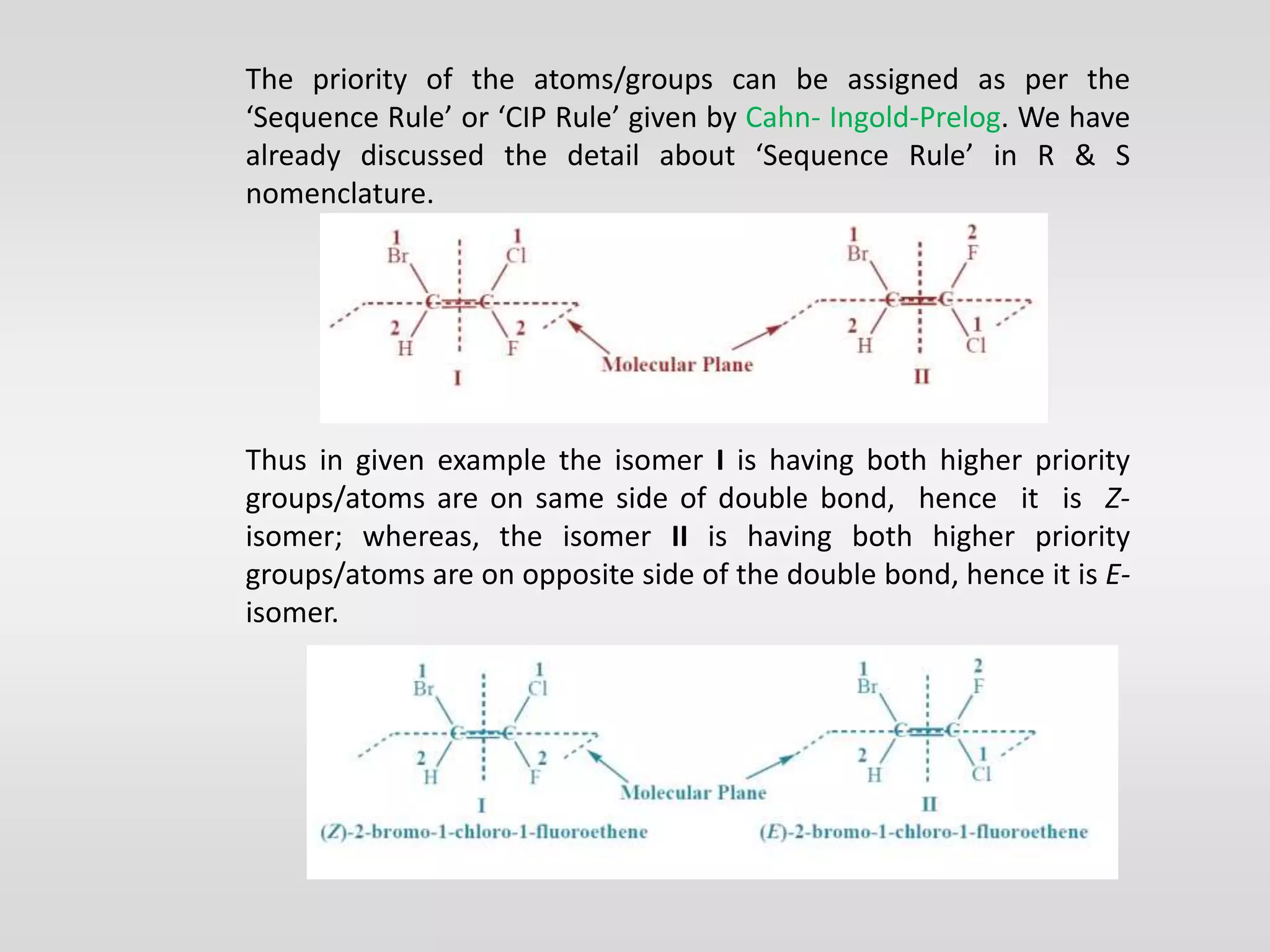
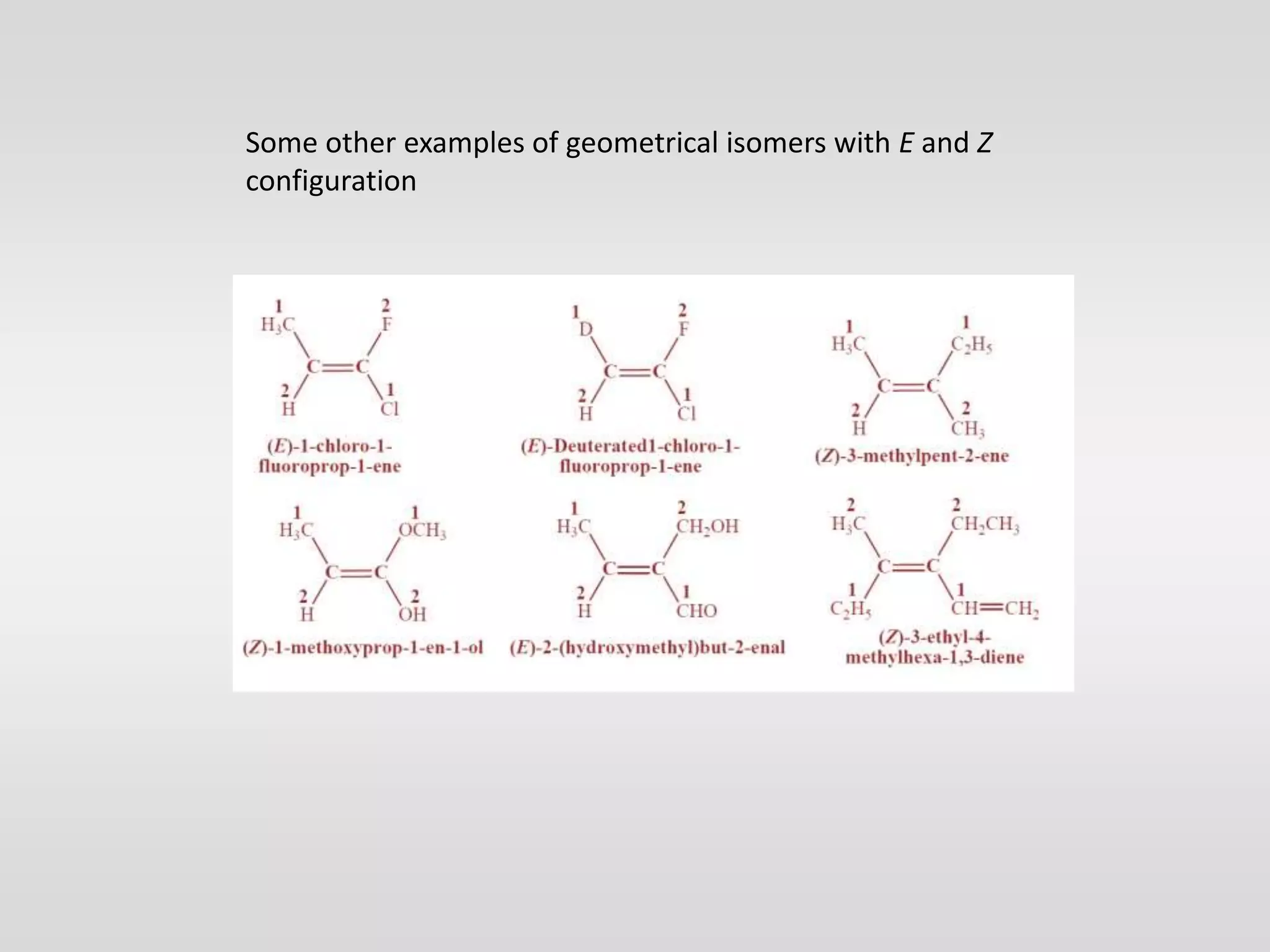
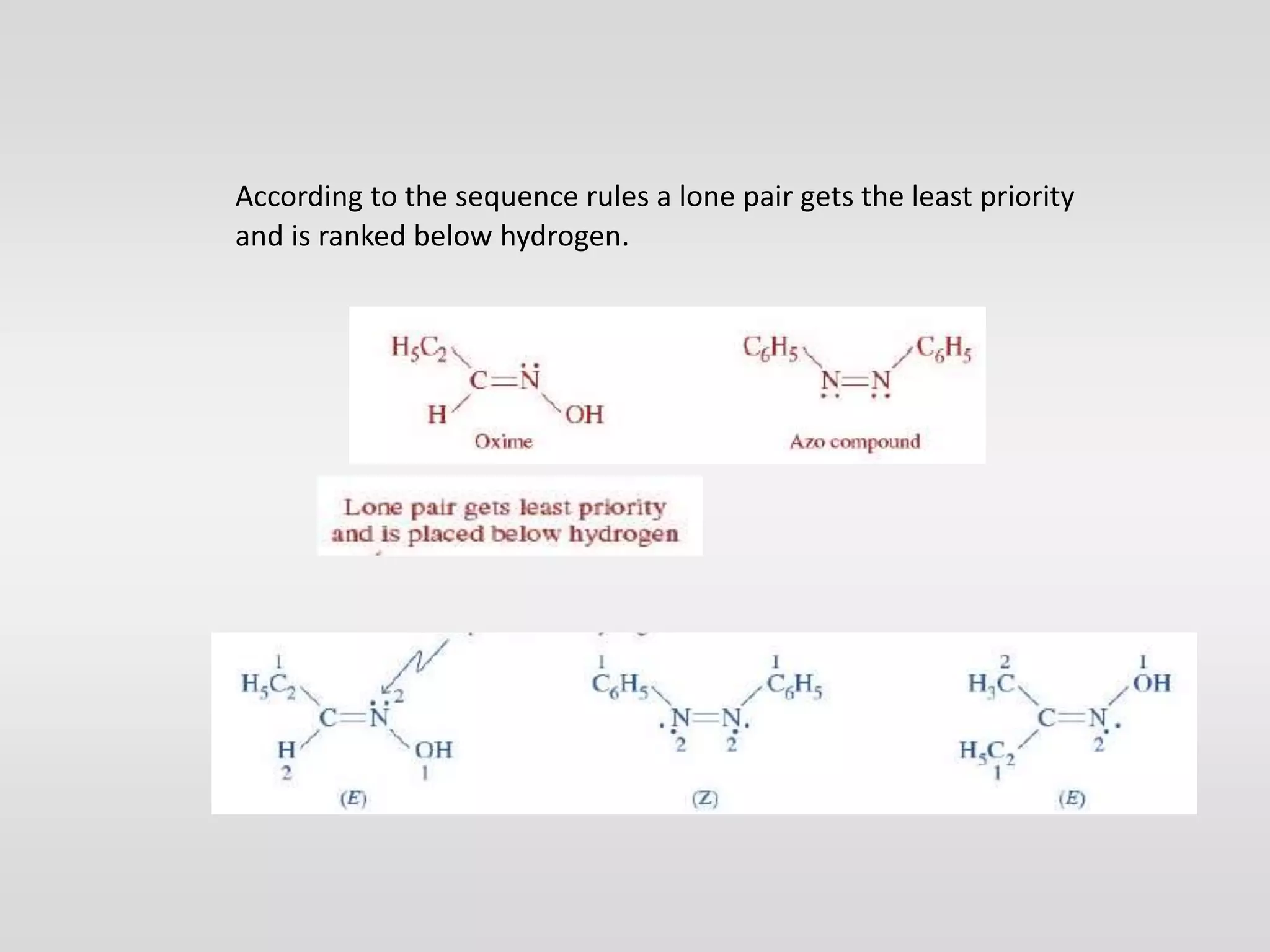
Geometrical isomers have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements around a double bond, resulting from restricted rotation that breaks π bonds. The cis-trans nomenclature is limited to molecules with identical groups, while the e/z system provides a more general naming method based on the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules for the relative positions of different substituents. In the e/z system, isomers are categorized as z (same side) or e (opposite side) based on the placement of higher priority groups around the double bond.