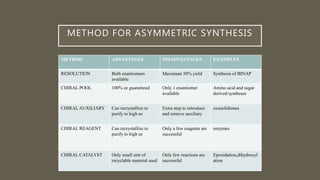
This document discusses different methods of asymmetric synthesis, which is a type of chemical reaction that produces unequal amounts of stereoisomeric products. It describes three main approaches: using a chiral starting material from natural sources (chiral pool synthesis), introducing chirality with an auxiliary group that is later removed (chiral auxiliaries), and using a chiral catalyst or reagent (external asymmetric induction). Examples of each method are provided. The document also summarizes several ways to separate enantiomers, such as preferential crystallization, biochemical separation, and forming diastereomers.

![INTRODUCTION[1]
• Asymmetric synthesis or Stereo selective synthesis chemical reaction (or
reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are
formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereo isomeric
(enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.
• Production of a specific enantiomer from achiral compound or racemic
mixture
• More simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favours the
formation of chiral molecules in unequal amounts.
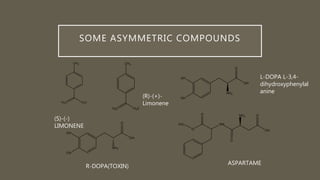
• The smells of orange and lemon differ in being the left- and righthanded
versions of the same molecule,
• Limonene. (R)-(+)-Limonene smells rounded and orangey whereas (S)-(–)-
limonene is sharp and lemony.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymetricsynthesis-210513074922/85/Asymmetric-synthesis-chemistry-presentation-2021-2-320.jpg)
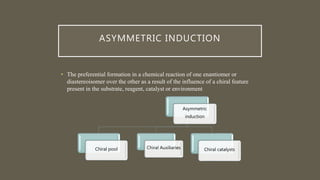
![DIFFERENT
APPROACHES[3]
Chiral pool synthesis - Internal asymmetric
induction: chiral center bound to the reaction
center used Chiral pool synthesis
Chiral auxiliaries - Relayed asymmetric
induction: chirality introduced in separate
step Chiral auxiliaries
Chiral reagents, Chiral catalysts and chiral
ligands - External asymmetric induction:
chiral information at transition state](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymetricsynthesis-210513074922/85/Asymmetric-synthesis-chemistry-presentation-2021-6-320.jpg)



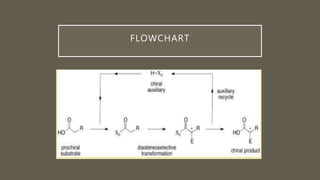
![ASYMETRIC SYNTHESIS USING CHIRAL
AUXILARY[ 2 ]
• The product of a Diels–Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and benzyl
acrylate must racemic as both reagents are achiral.
• Chiral auxiliary : amide derived from valine via reaction to give asymmetric
product](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymetricsynthesis-210513074922/85/Asymmetric-synthesis-chemistry-presentation-2021-11-320.jpg)
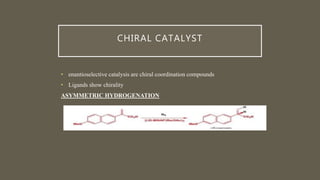
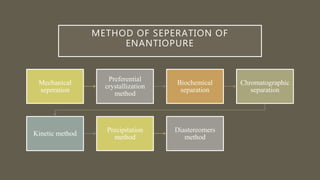
![ENATIOPURE SEPARATION AND STEREO
SELECTIVE SYNTHESIS[ 4 ]
• An enantiopure drug is a
pharmaceutical that is available in
one specific enantiomeric form. Most
biological molecules (proteins,
sugars, etc.) are present in only one
of many chiral forms, so different
enantiomers of a chiral drug molecule
bind differently (or not at all) to
target receptors.
• Enantioselective synthesis, also called
asymmetric synthesis.
• It is a form of chemical synthesis.
• It is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical
reaction (or reaction sequence) in which
one or more new elements of chirality are
formed in a substrate molecule and which
produces the stereo isomeric
(enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric)
products in unequal amounts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymetricsynthesis-210513074922/85/Asymmetric-synthesis-chemistry-presentation-2021-14-320.jpg)