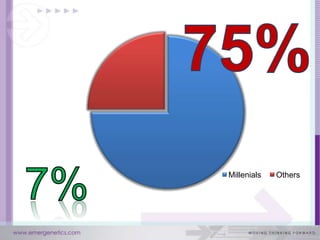
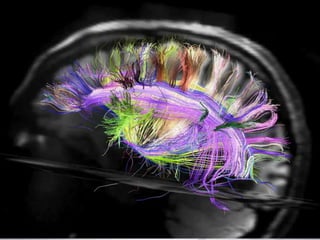
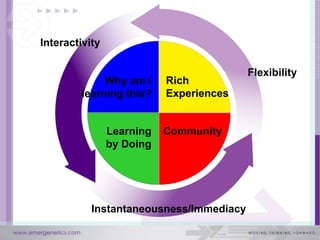
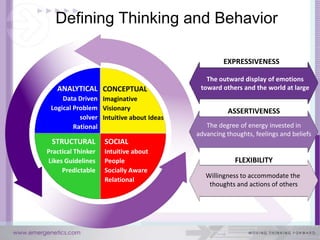
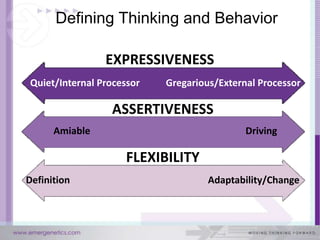
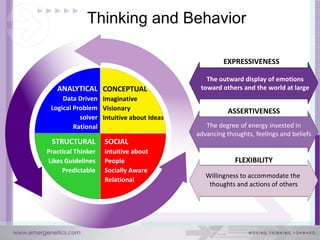
The document discusses how the brain and learning have changed with new technologies. It addresses how learning needs to be relevant, efficient, applied, and connective. Modern learners want rich experiences, flexibility, community, instant results, and interactivity. Effective learning involves problem solving, results, and flexibility. It also examines different thinking styles and how to design learning to accommodate different learners.