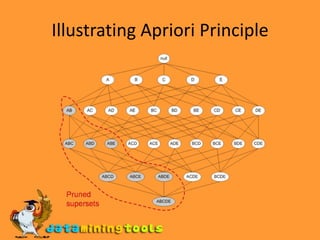
Association analysis is used to uncover relationships between data items by identifying frequent patterns and association rules. The Apriori algorithm is a two-step process used for association rule mining: 1) find frequent itemsets that satisfy a minimum support threshold, and 2) generate strong association rules from the frequent itemsets that meet minimum support and confidence thresholds. Practical issues like level of data aggregation and appropriate support/confidence levels must be considered.