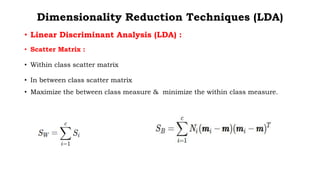
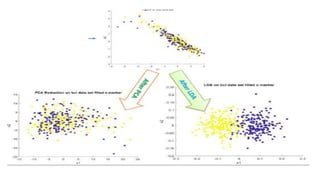
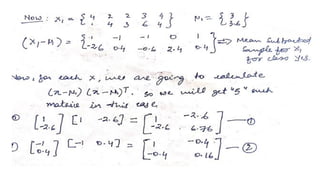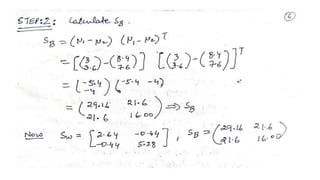Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is a dimensionality reduction technique that projects data onto a lower dimensional space to maximize separation between classes. It works by computing eigenvectors from within-class and between-class scatter matrices to generate a linear transformation of the data. The transformation projects the high-dimensional data onto a new subspace while preserving the separation between classes.