Embed presentation



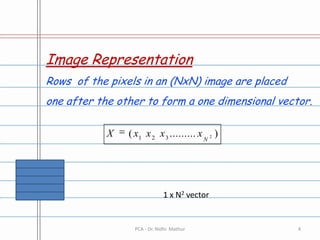





Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a technique used to simplify complex data sets by identifying patterns in the data and expressing it in such a way to highlight similarities and differences. It works by subtracting the mean from the data, calculating the covariance matrix, and determining the eigenvectors and eigenvalues to form a feature vector representing the data in a lower dimensional space. PCA can be used to represent image data as a one dimensional vector by stacking the pixel rows of an image and applying this analysis to multiple images.








