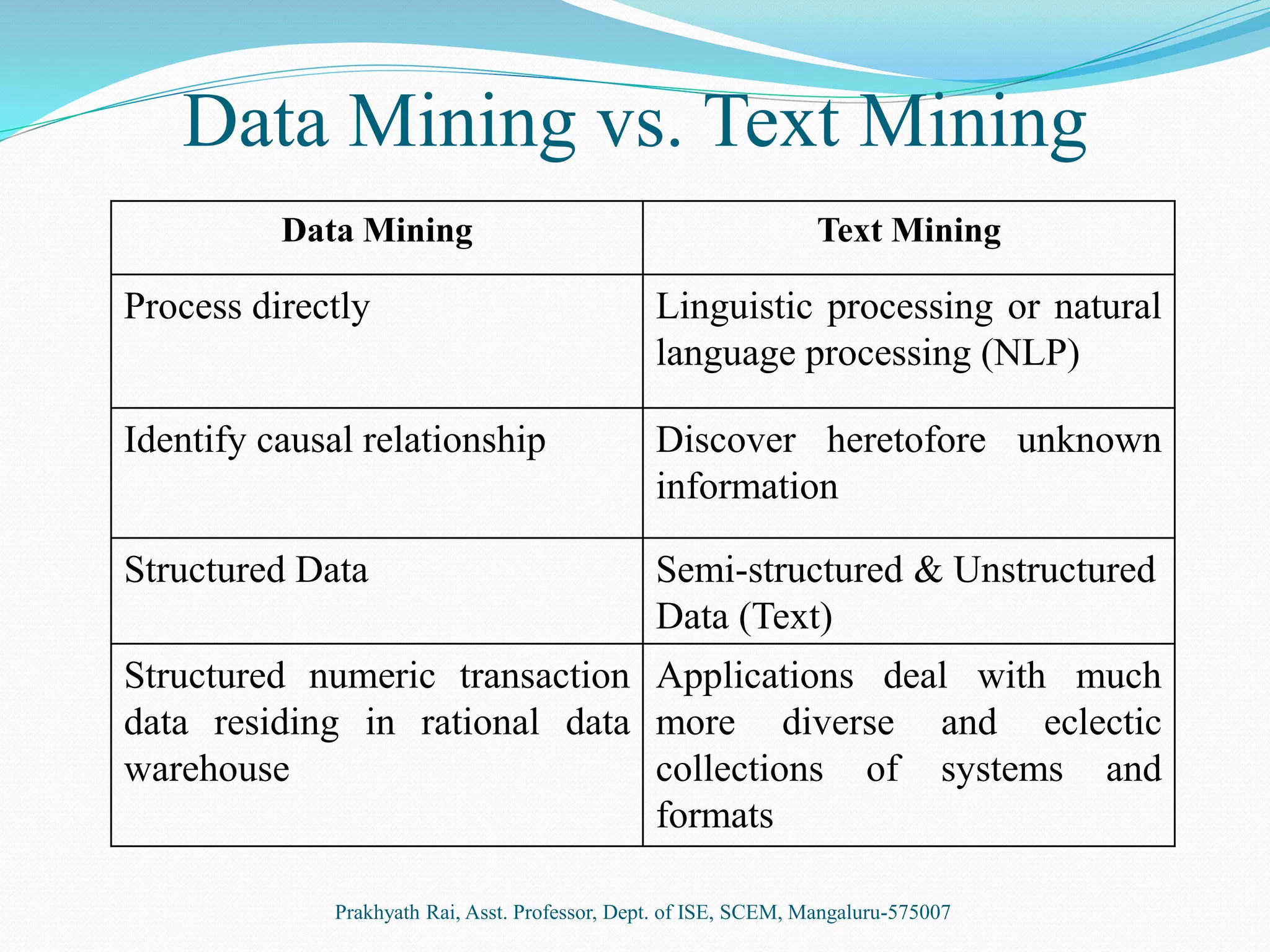
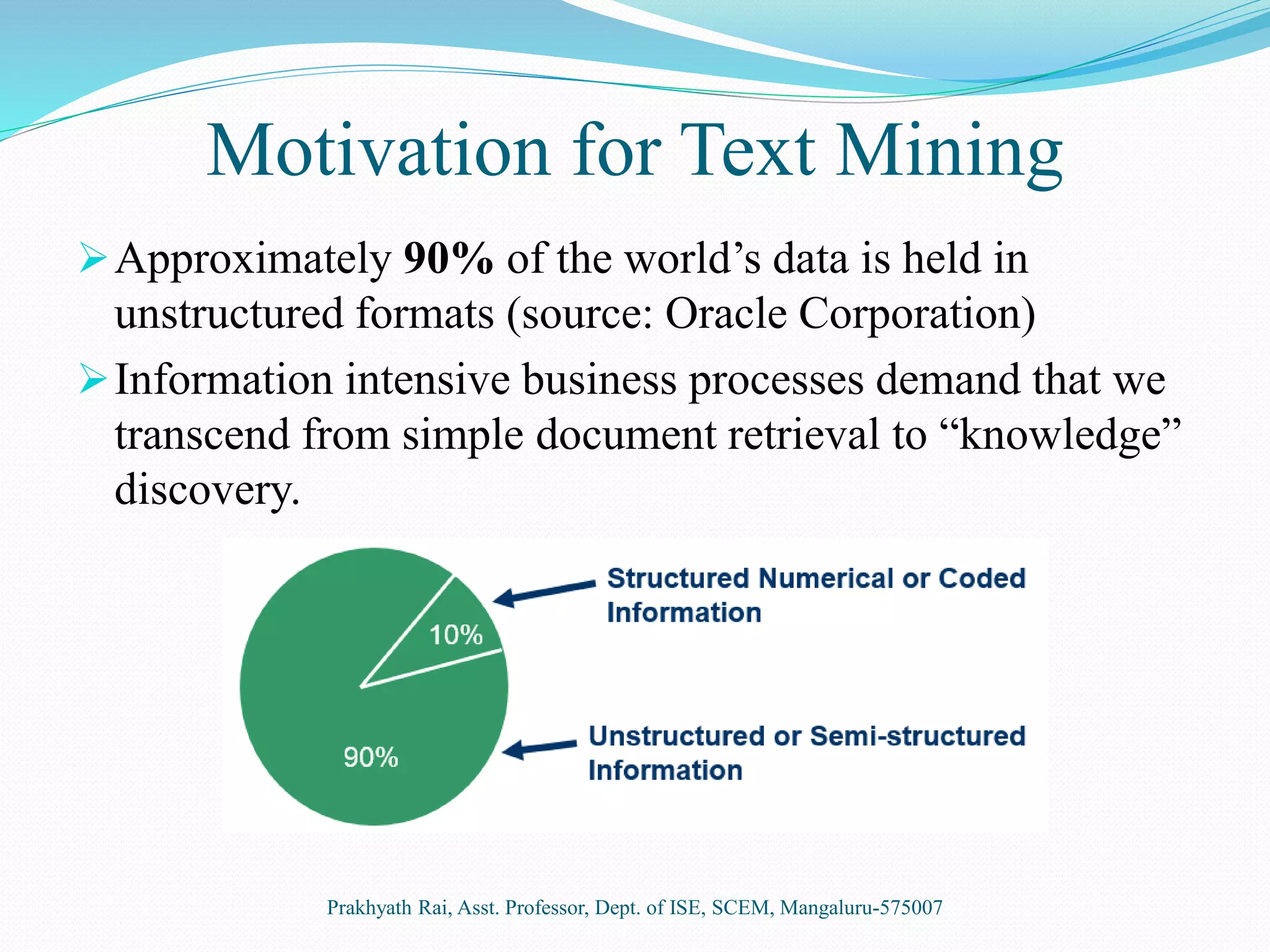
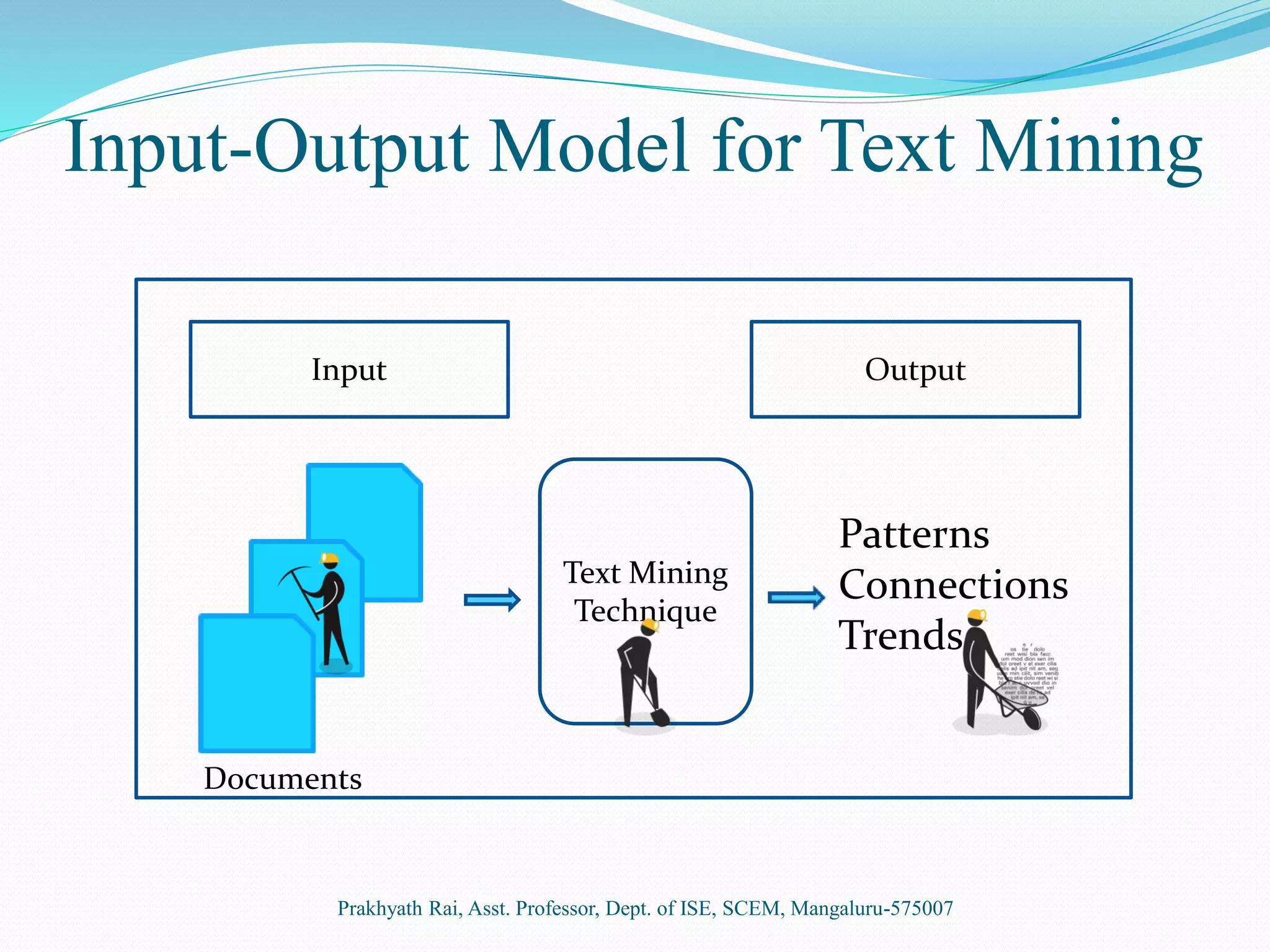
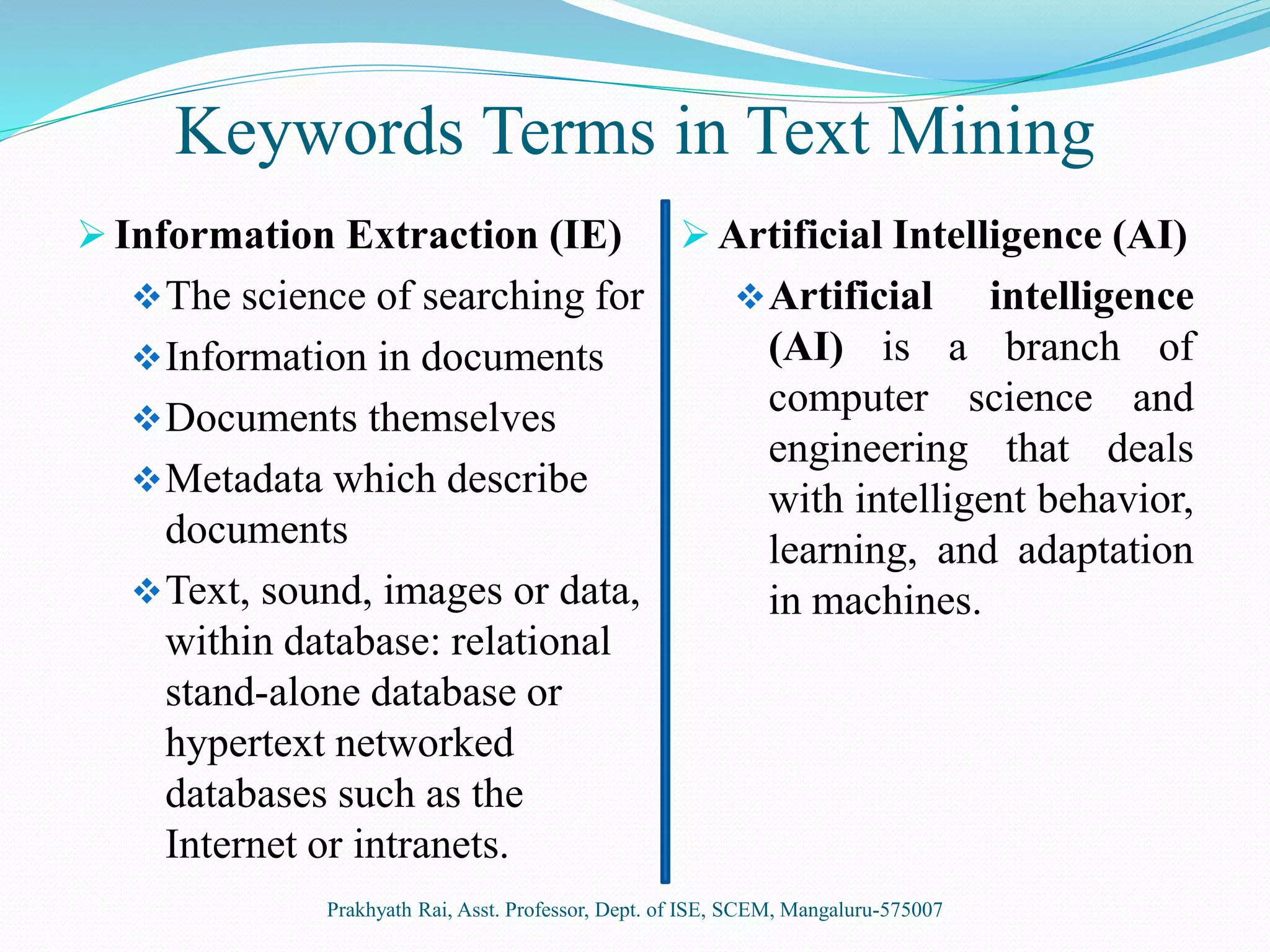
This document presents an overview of text mining. It discusses how text mining differs from data mining in that it involves natural language processing of unstructured or semi-structured text data rather than structured numeric data. The key steps of text mining include pre-processing text, applying techniques like summarization, classification, clustering and information extraction, and analyzing the results. Some common applications of text mining are market trend analysis and filtering of spam emails. While text mining allows extraction of information from diverse sources, it requires initial learning systems and suitable programs for knowledge discovery.








![References
[1] R Baeza-Yates and B Ribeiro-Neto. “Modern Information Retrieval”, ACM
Press, New York, 1999.
[2] Ning Zhong, Yuefeng Li and T. Grance, “Effective Pattern Discovery for Text
Mining,” IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, Vol. 24, No. 1,
January 2012.
[3] Raymond J Mooney and Un Yong Nahm, “ Text Mining with Information
Extraction”, Proceedings of the 4th International MIDP Colloquium, pages 141-
160, Van Schaik Pub., South Africa, 2005.
[4] M E Califf and R J Mooney, “Relational Learning of Pattern-Match Rules for
Information Extraction”, Proceedings of the 16th National Conference on Artificial
Intelligence (AAAI-99), pages 328-334, Orlando, FL, July 1999.
[5] D Freitag and N Kushmerick, “Boosted Wrapper Induction”, Proceedings of
the 17th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2000), pages 577-
583, Austin, TX, July 2000.
Prakhyath Rai, Asst. Professor, Dept. of ISE, SCEM, Mangaluru-575007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontotextmining-170204032538/75/Text-MIning-13-2048.jpg)

