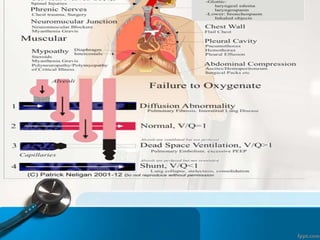
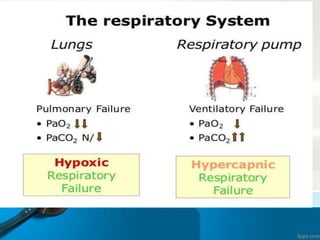
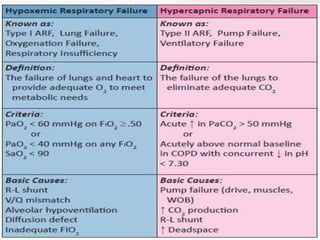
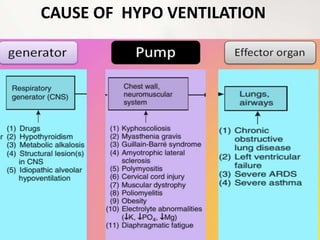
The document defines respiratory failure as a syndrome where the respiratory system fails to meet gas exchange functions, outlining four types: hypoxemic, hypercapnic, peri-operative, and shock. It details the mechanisms, causes, and underlying issues related to each type, including conditions like ventilation/perfusion mismatch, hypoventilation, and shunts. Additionally, it discusses the implications of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in blood, emphasizing the diagnostic significance of the alveolar–arterial gradient in assessing hypoxemia.








![LOW INSPIRED OXYGEN [ PI O2 ]
• Examples-
• A decrease in barometric pressure [e.g. breathing at high
altitude].
• A decrease in FIO2 – accidental [e.g. anesthetist does not
supply enough oxygen or improper installation of oxygen
supply lines or a leak in the breathing circuit].
• P(A-a)O2 normal
• PaCO2 is decreased. This reduction in PaCO2 (hypocapnia) is
due to hyperventilation in response to hypoxemia.
• Peripheral chemoreceptors sense the low arterial PO2 and
initiate an increase in ventilation through their input to the
medullary respiratory centre](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailrefinal-160512112852-240321060436-e3e7fa12/85/respiratoryfailrefinal-1605121128522-ppt-11-320.jpg)


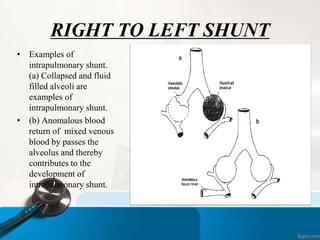
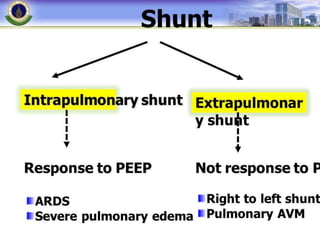
![RIGHT TO LEFT SHUNT
• Congenital abnormalities
• i) intra-cardiac shunt [e.g. Tetralogy of Fallot: ventricular
septal defect + pulmonary artery stenosis]
• ii) intra-pulmonary fistulas [direct communication between a
branch of the pulmonary artery and a pulmonary vein].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailrefinal-160512112852-240321060436-e3e7fa12/85/respiratoryfailrefinal-1605121128522-ppt-14-320.jpg)
![RIGHT TO LEFT SHUNT
• Physiologic shunt: In disease states, a portion of the
cardiac output goes through the regular pulmonary vasculature
but
does not come into contact with alveolar air due to filling of
the alveolar spaces with fluid [e.g. pneumonia, drowning,
pulmonary edema]
• An important diagnostic feature of a shunt
is that the arterial Po2 does not rise to the
normal level when the patient is given 100%
oxygen to breathe.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailrefinal-160512112852-240321060436-e3e7fa12/85/respiratoryfailrefinal-1605121128522-ppt-15-320.jpg)
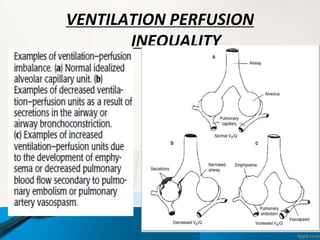
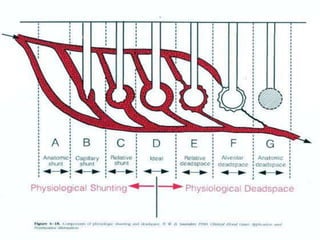
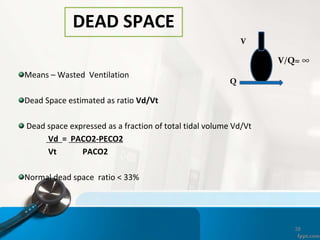
![Ventilation Perfusion ratio VA/Q
The overall V/Q = 0.8 [ ven=4lpm, per=5lpm]
Ranges between 0.3 and 3.0
Upper zone –nondependent area has higher ≥ 1
Lowe zone – dependent area has lower ≤ 1
VP ratio indicates overall respiratory functional
status of lung
V/Q = 0 means ,no ventilation-called SHUNT
V/Q = ∞ means ,no perfusion – called DEAD SPACE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailrefinal-160512112852-240321060436-e3e7fa12/85/respiratoryfailrefinal-1605121128522-ppt-17-320.jpg)












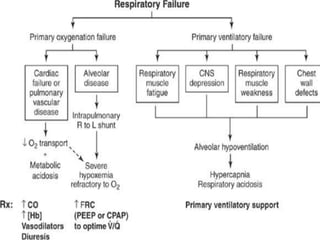
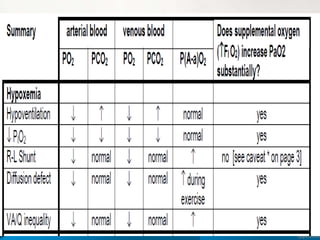



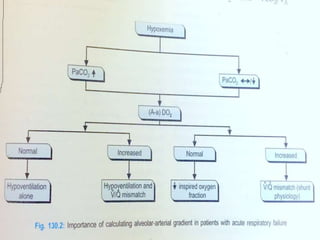
![The Alveolar–arterial gradient ( A–a gradient
is a measure of the difference between
the alveolar concentration (A) of oxygen and
the arterial (a) concentration of oxygen.
It is used in diagnosing the source of hypoxemia.
It helps to assess the integrity of alveolar capillary unit.
For example, in high altitude, the arterial oxygen [[PaO2]]
is low but only because the alveolar oxygen (PAO2) is also
low. However, in states of ventilation perfusion mismatch,
such as pulmonary embolism or right-to-left shunt,
oxygen is not effectively transferred from the alveoli to
the blood which results in elevated A-a gradient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailrefinal-160512112852-240321060436-e3e7fa12/85/respiratoryfailrefinal-1605121128522-ppt-41-320.jpg)