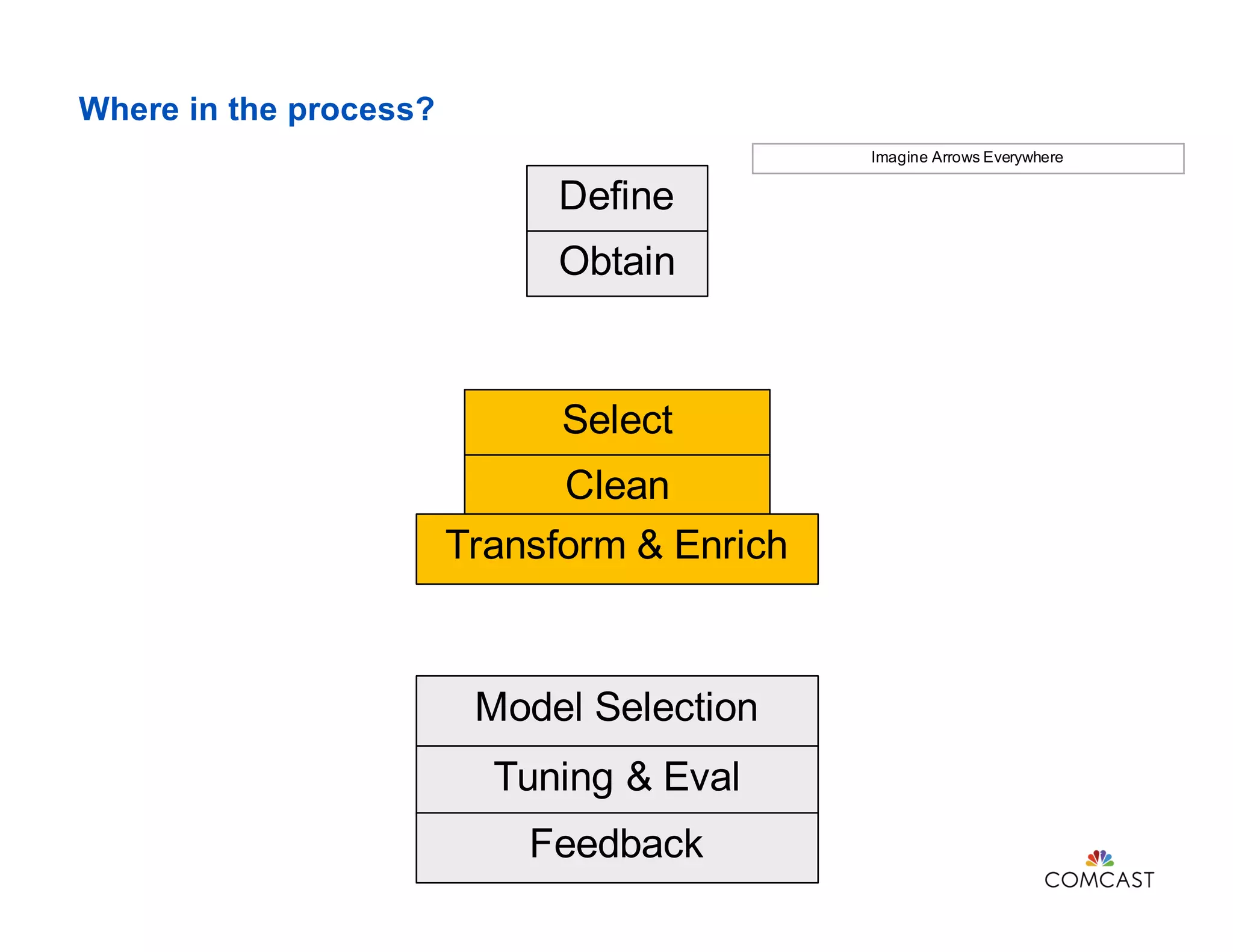
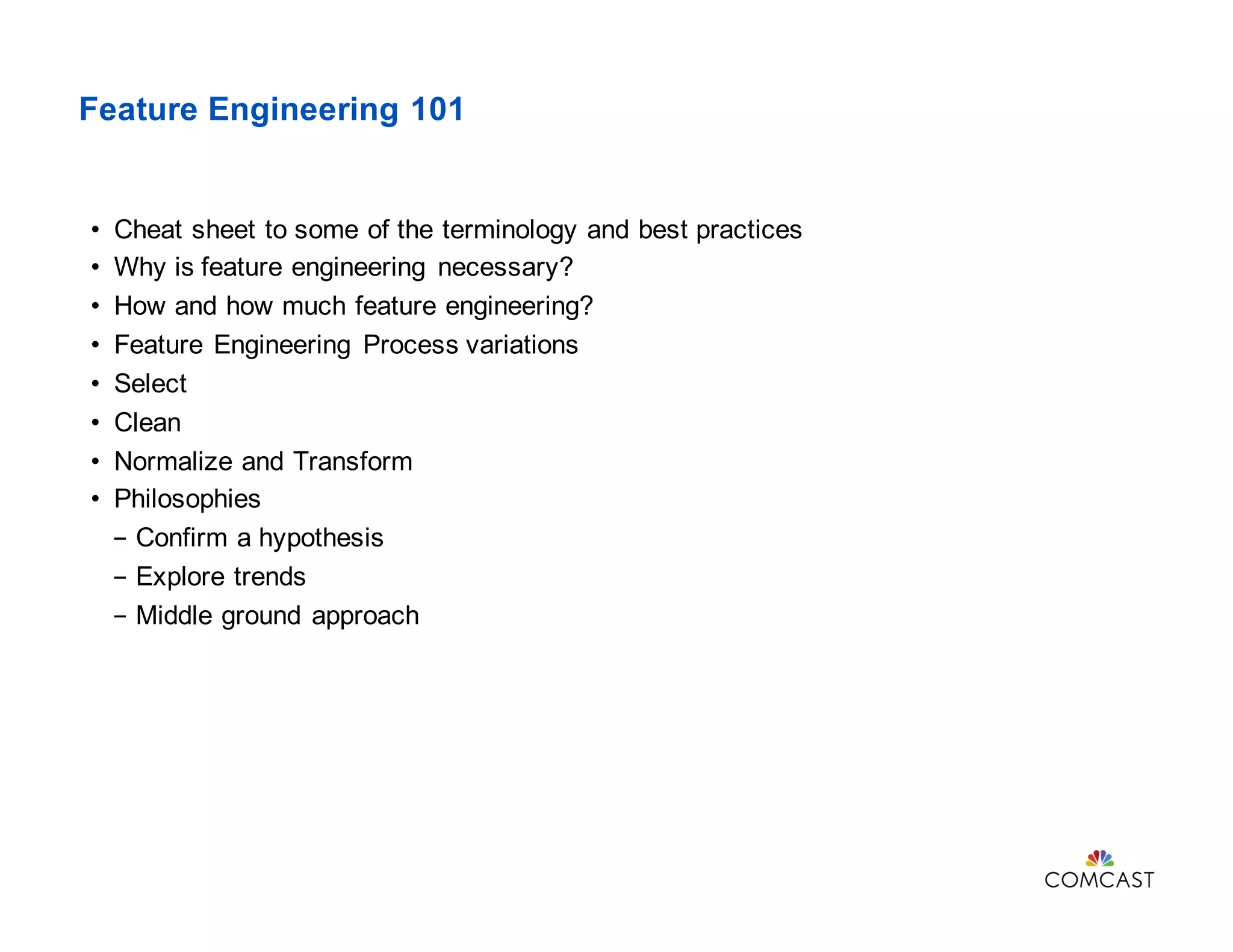
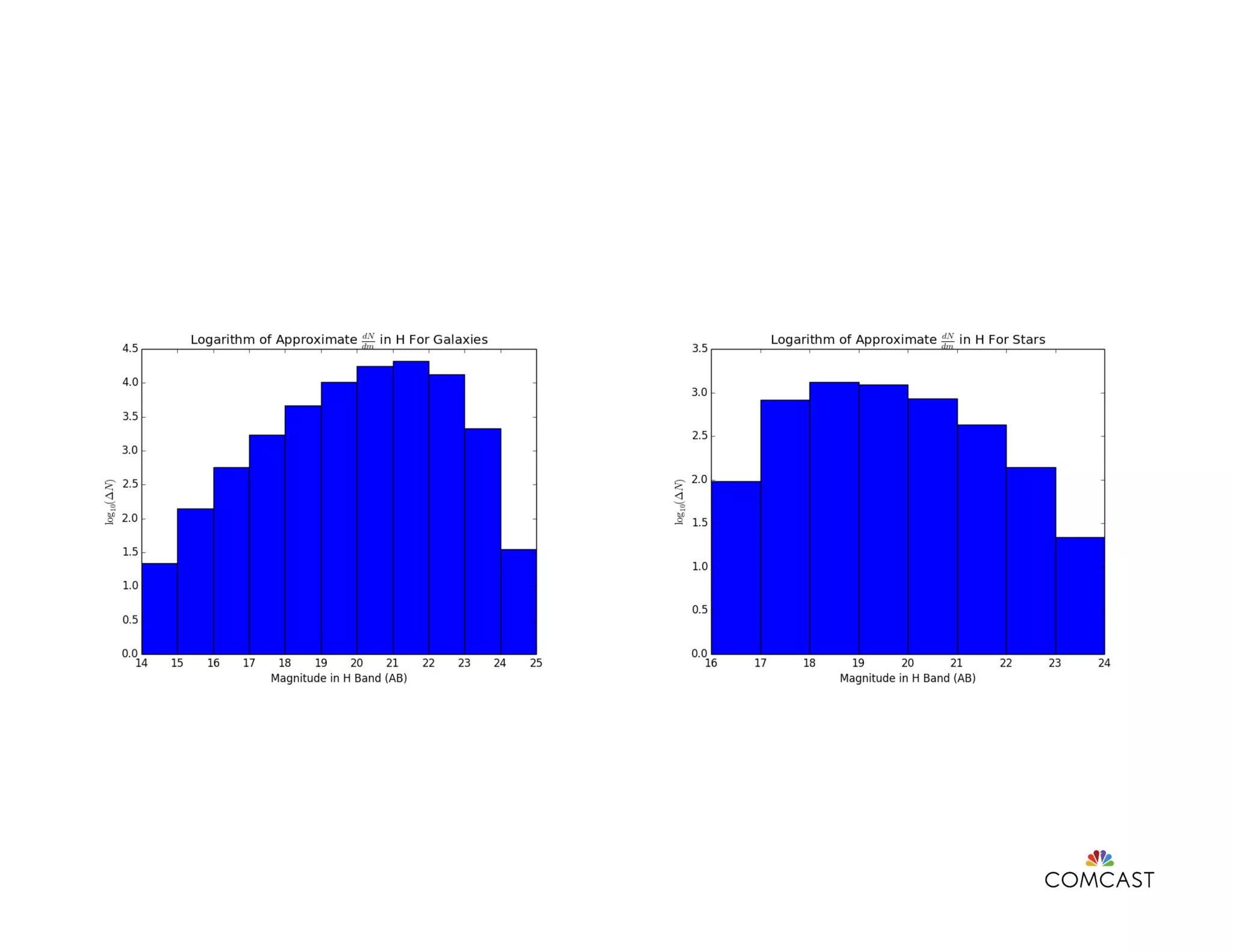
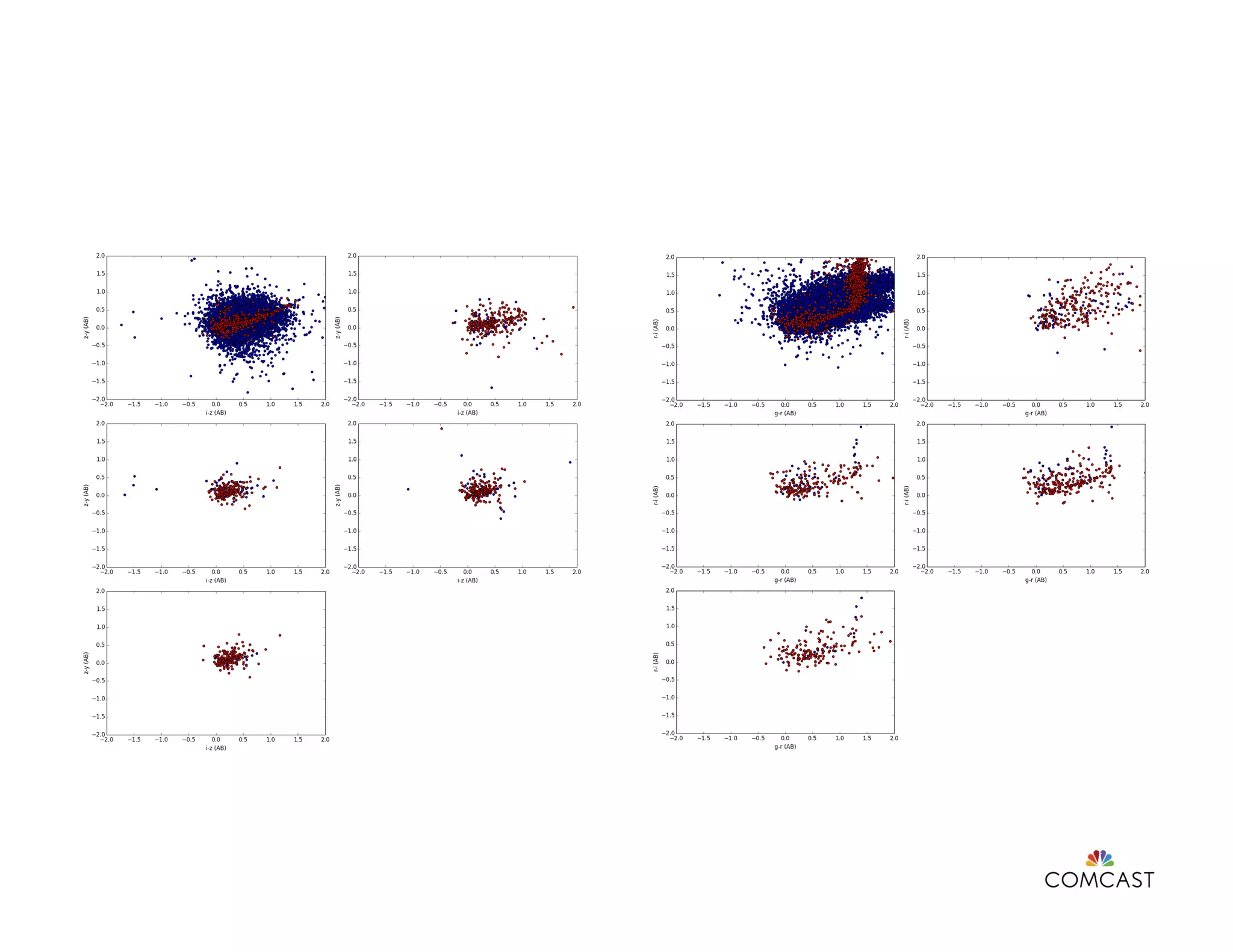
This document discusses feature engineering in data science, particularly in the context of machine learning at Comcast. It covers various processes involved in feature engineering such as selecting, cleaning, transforming, and enriching data, as well as methodologies for handling categorical and numerical variables. Additionally, it highlights the importance of domain knowledge, statistical correlation, and the challenges of dimensionality in optimizing machine learning models.