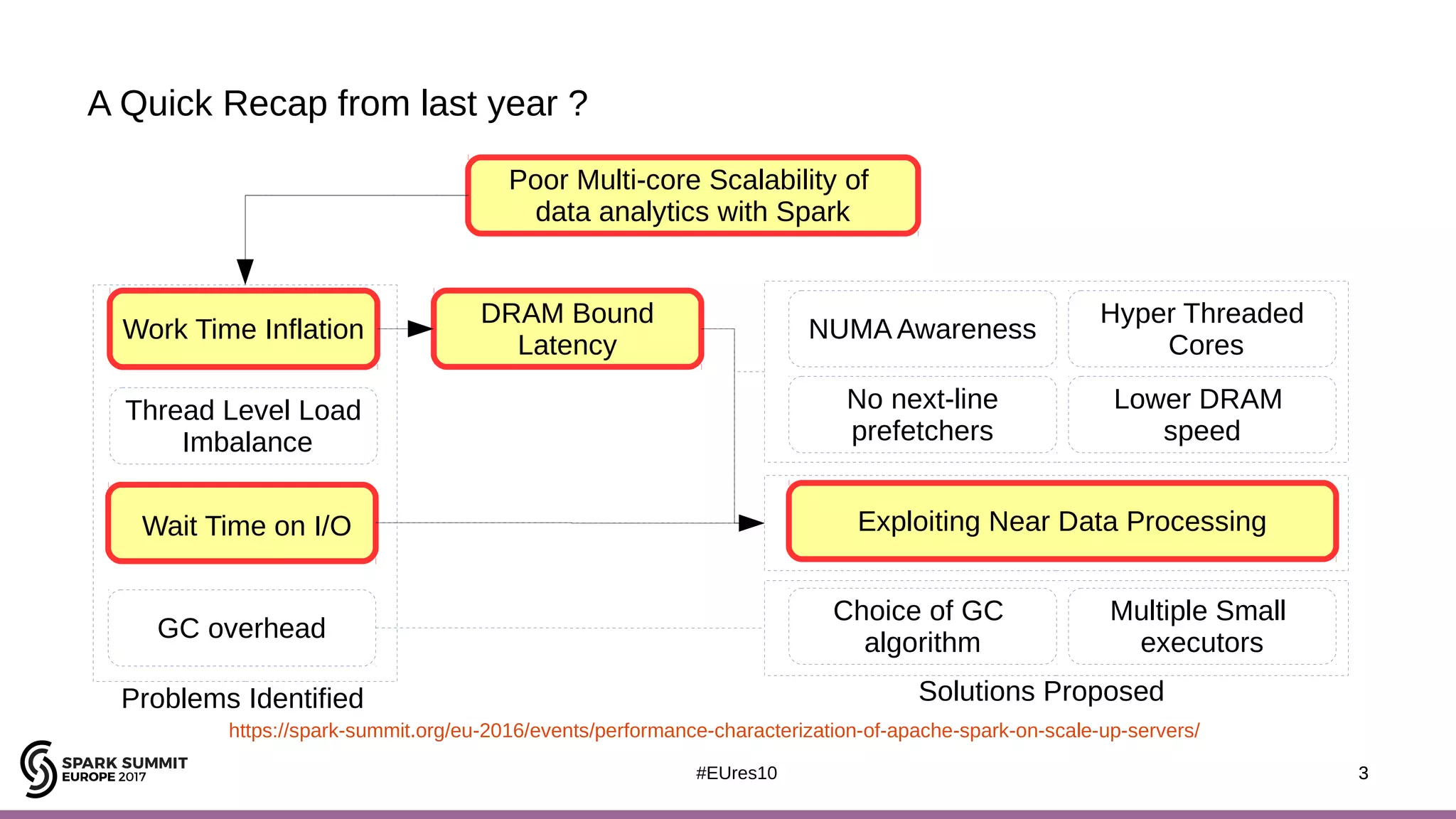
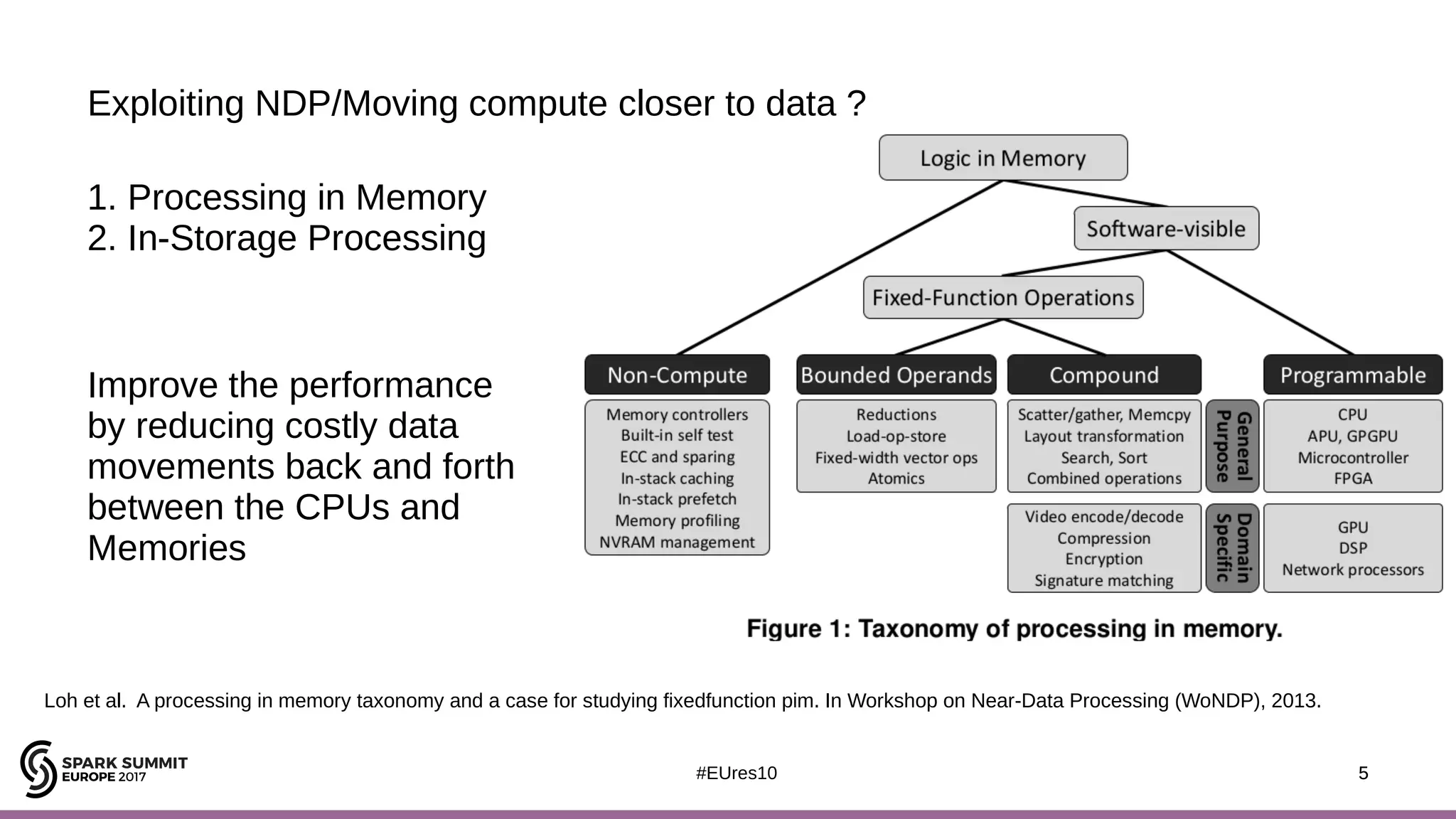
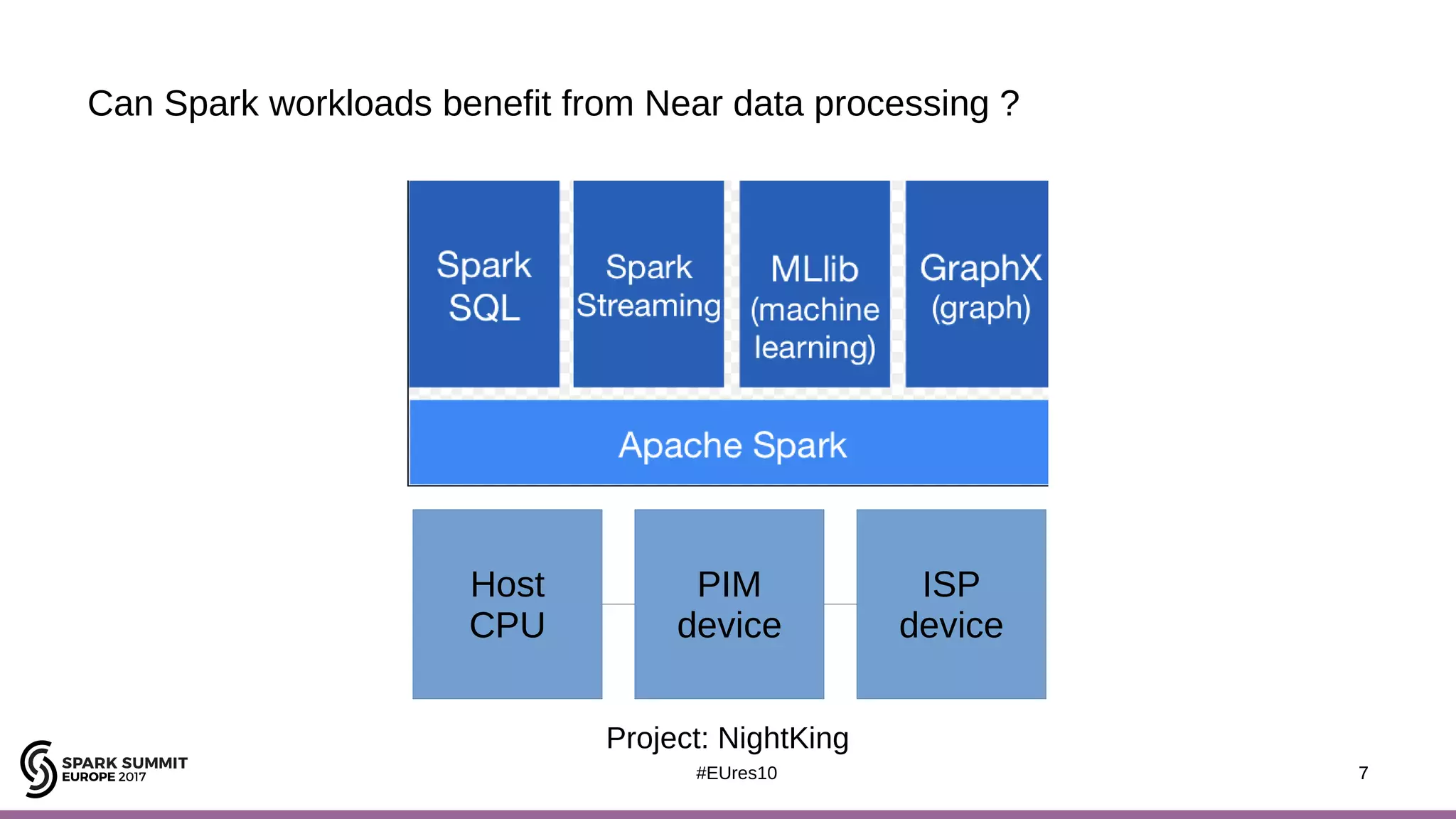
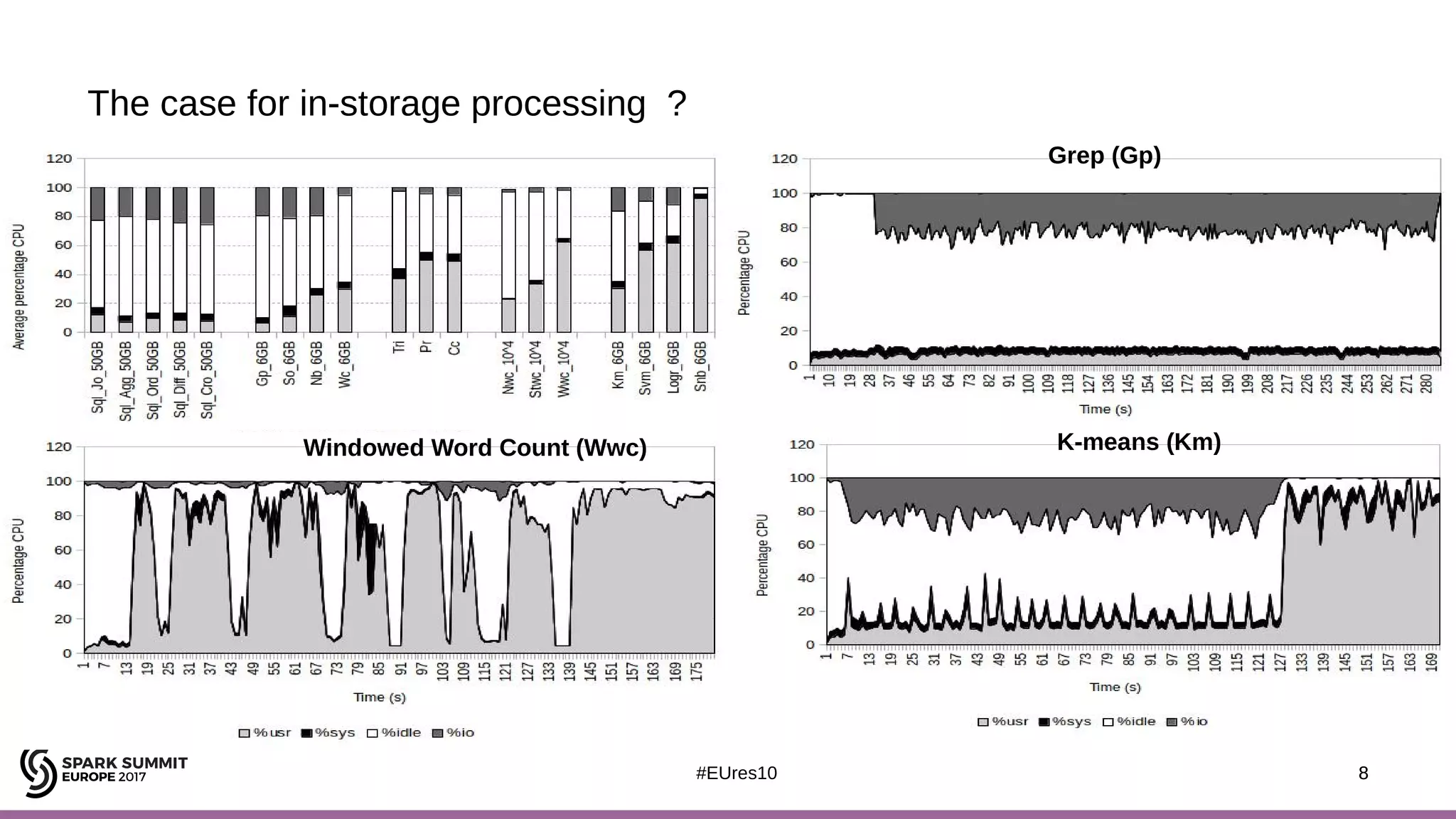
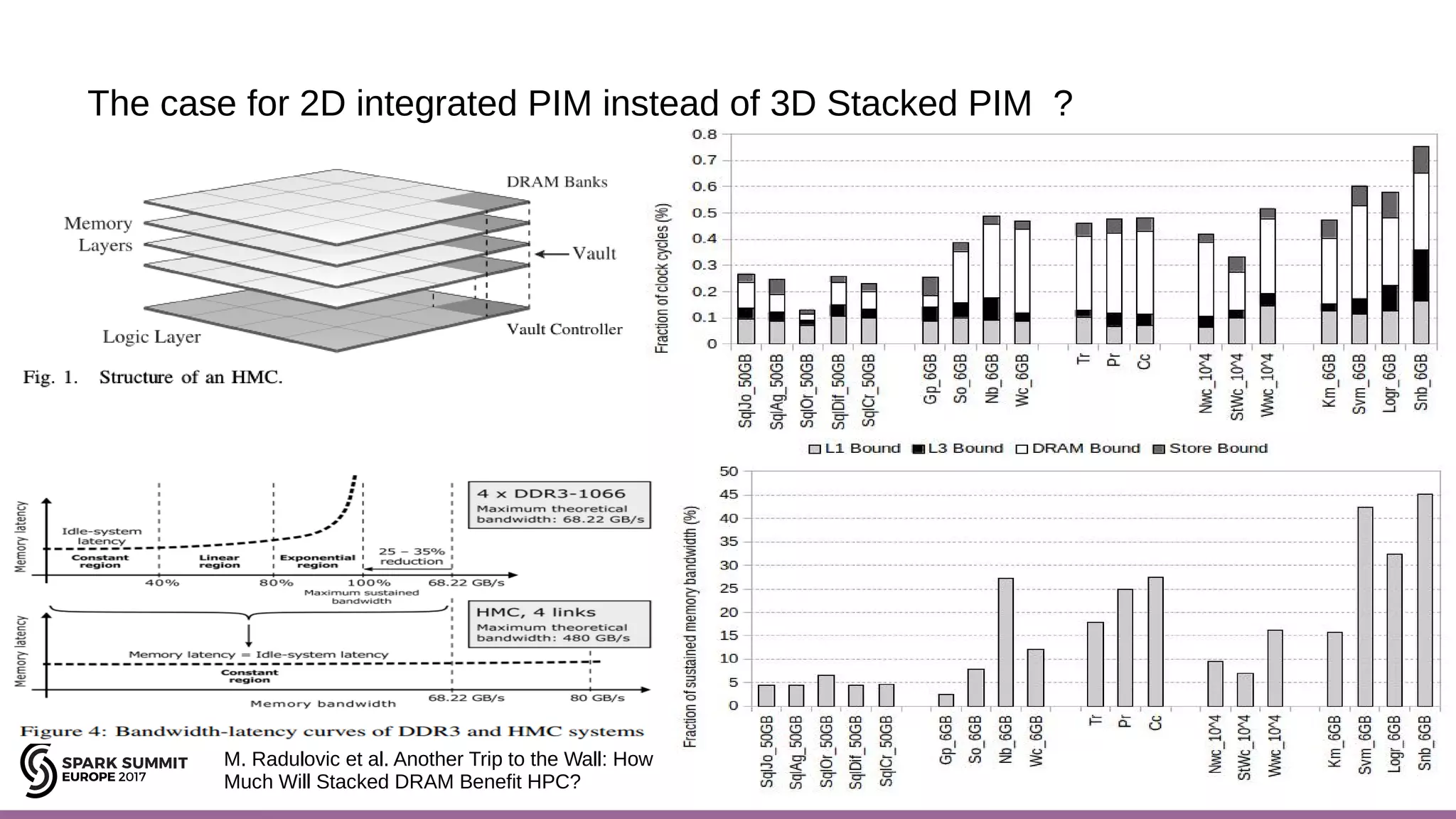
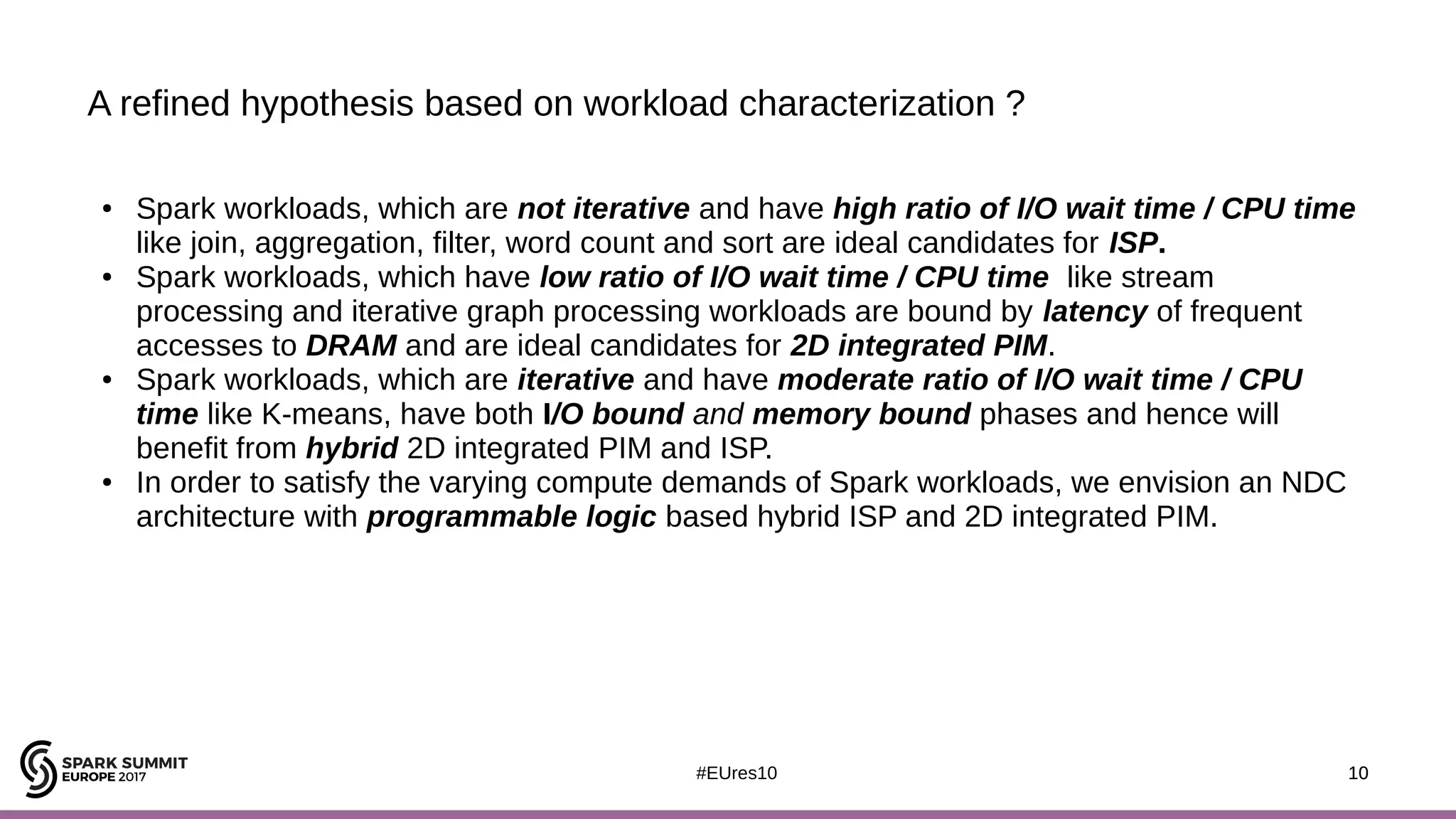
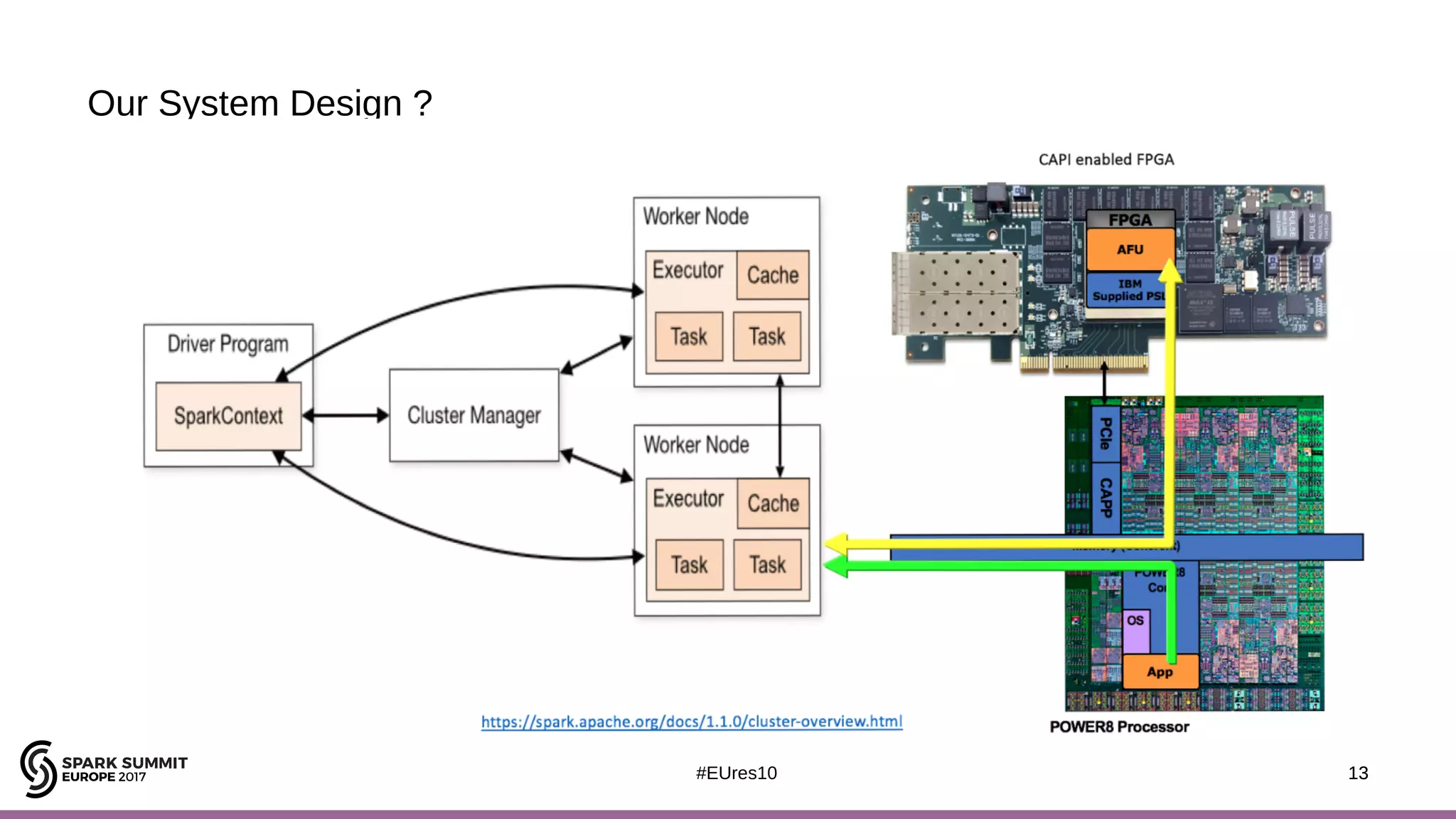
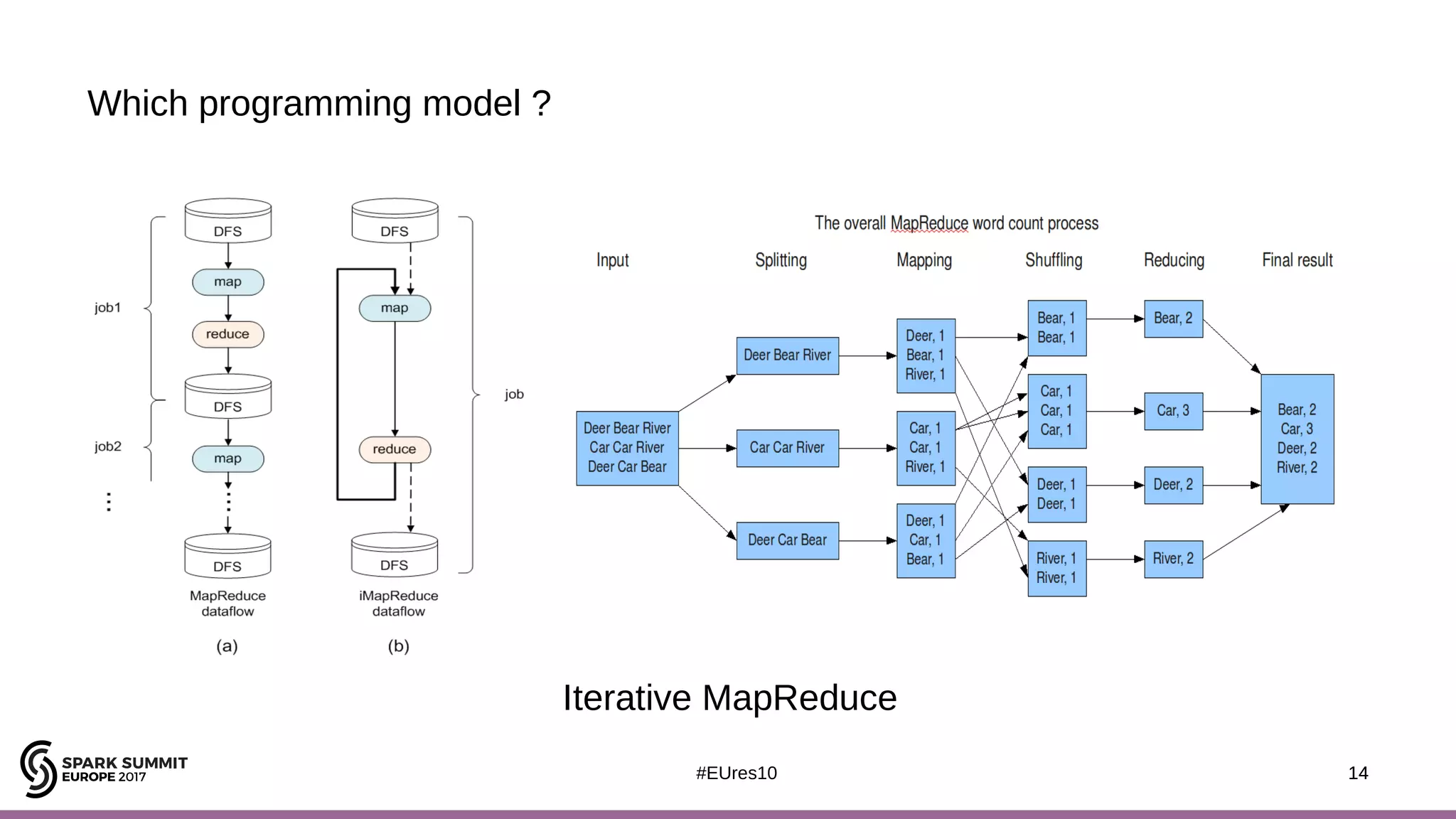
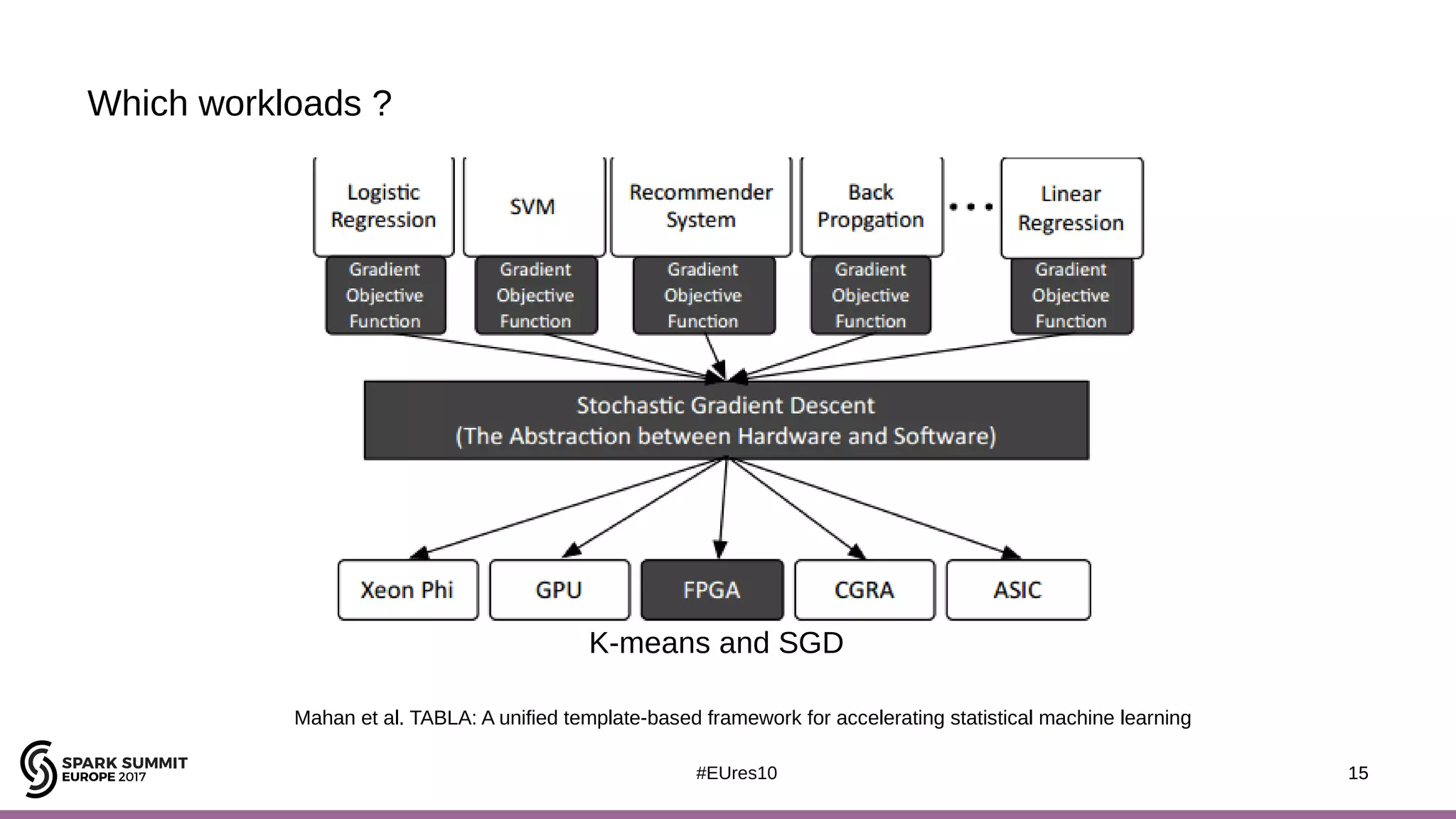
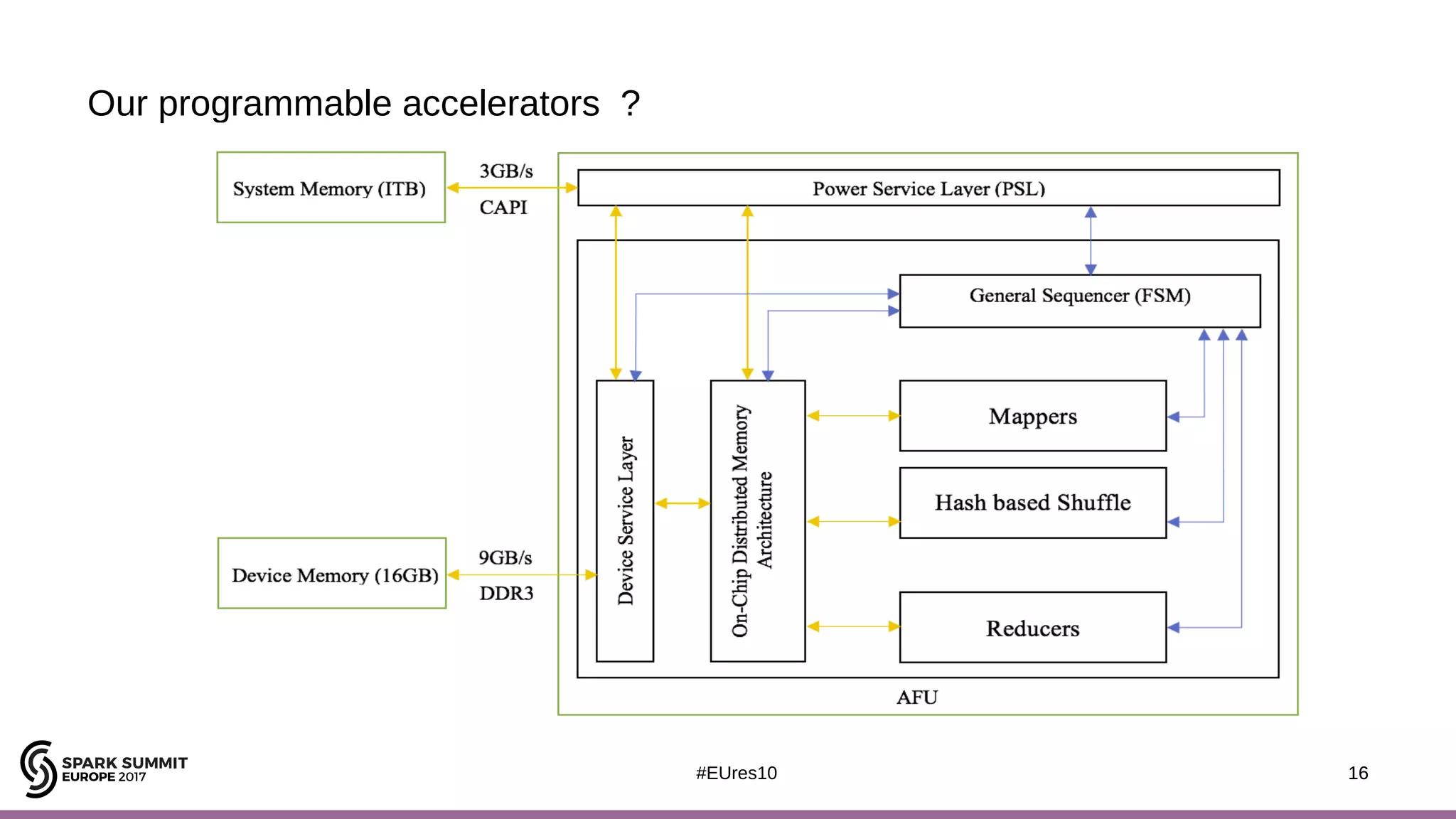
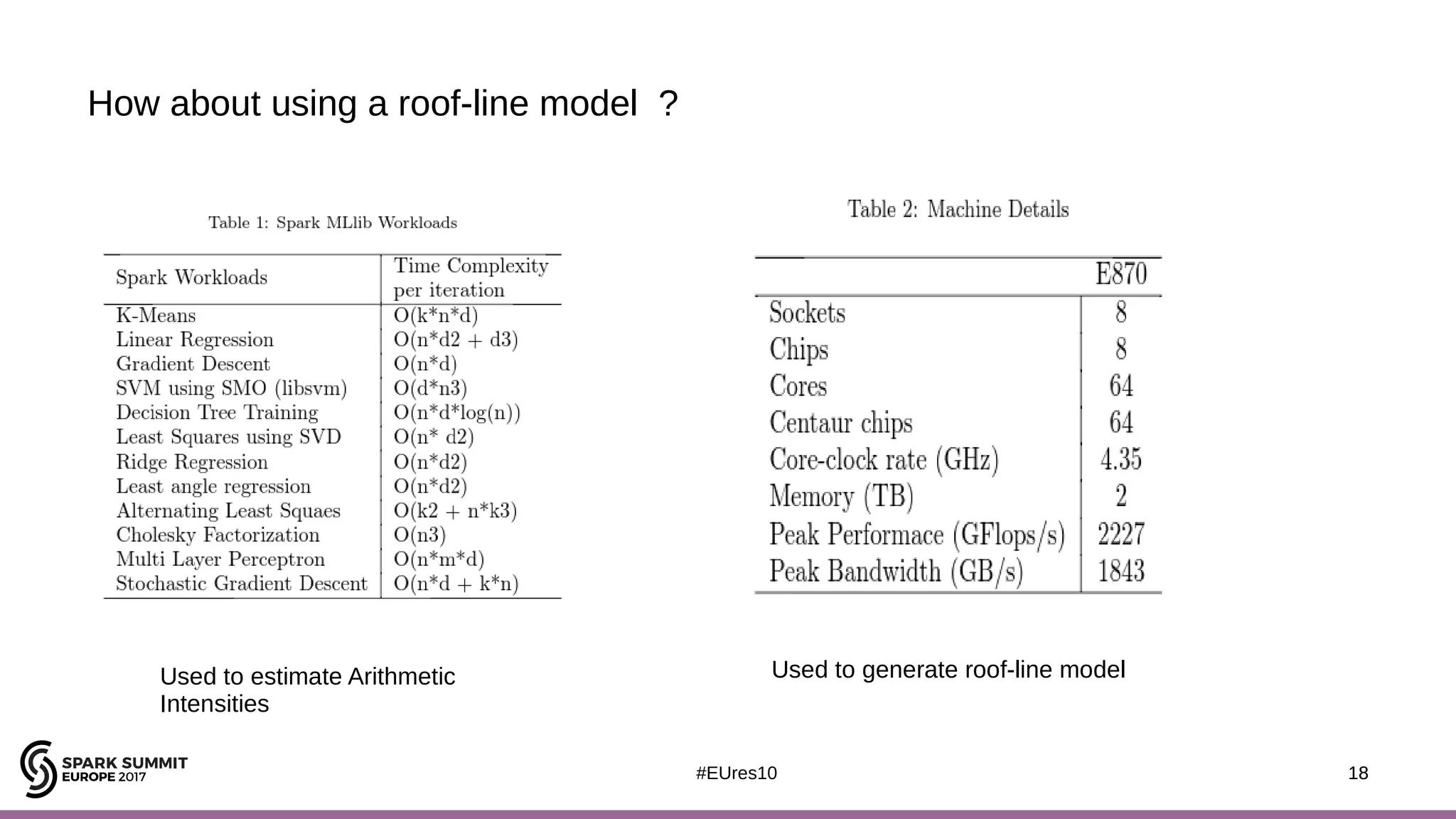
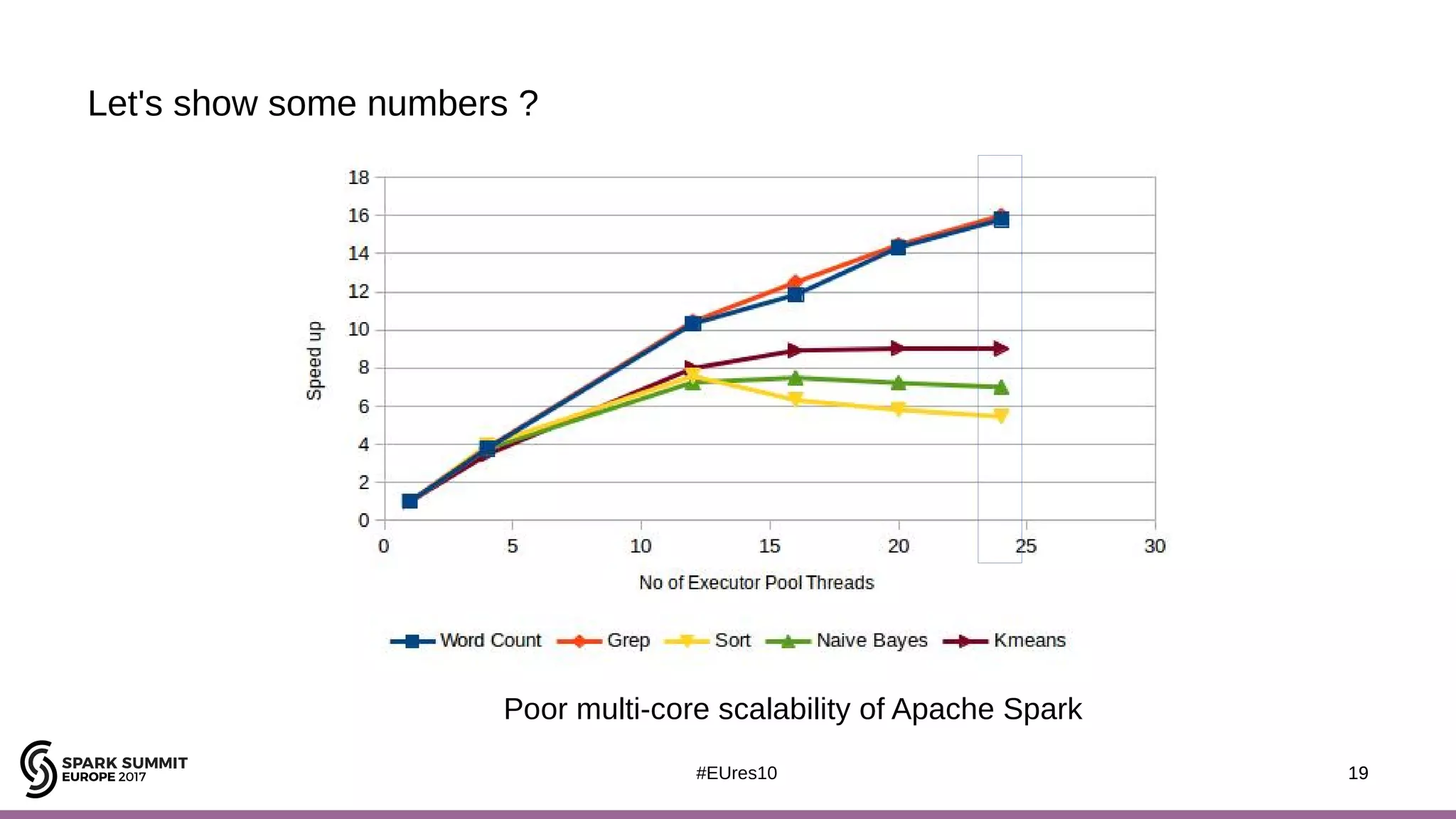
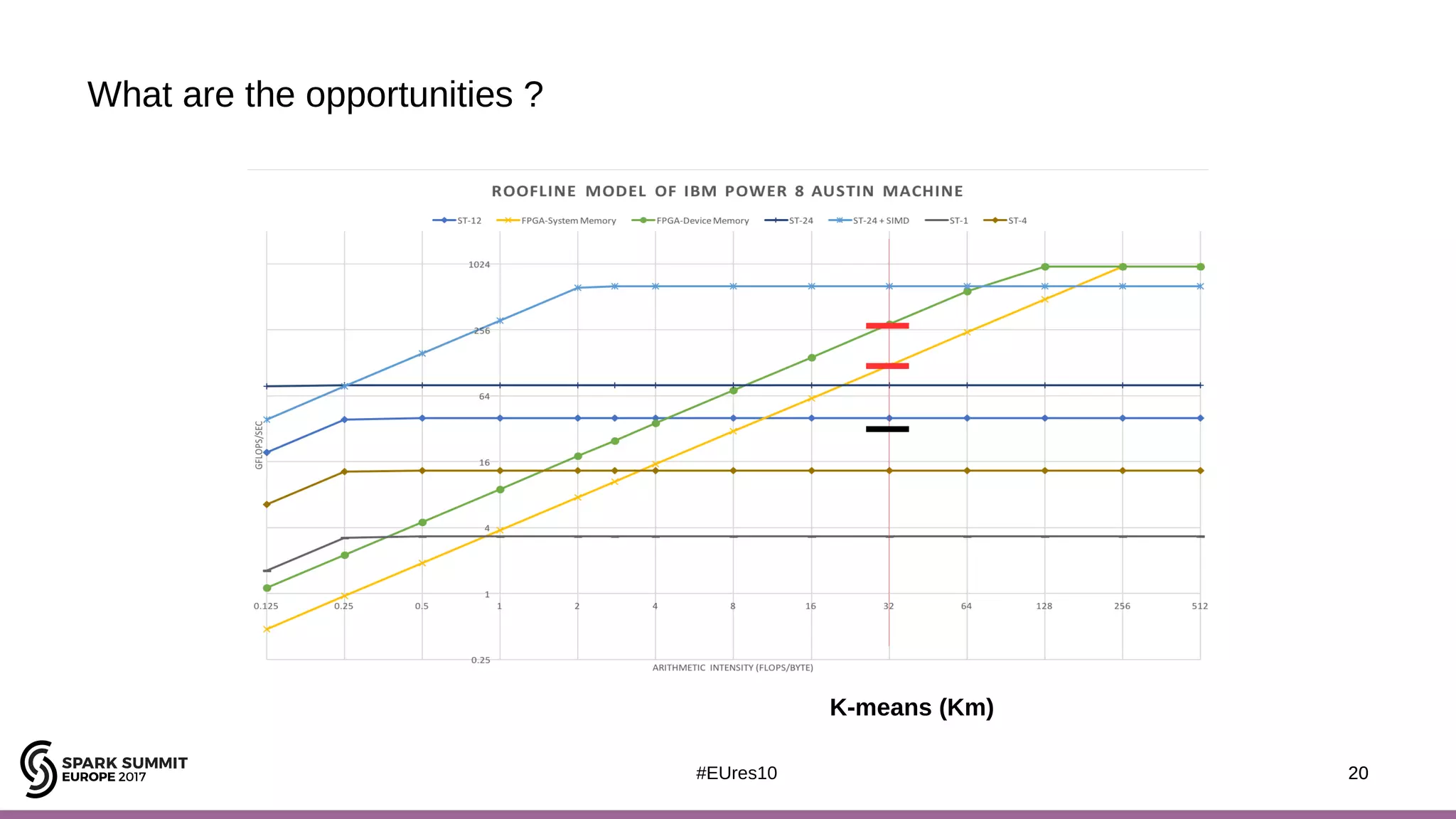
The document discusses opportunities for improving Apache Spark performance using near data computing architectures. It proposes exploiting in-storage processing and 2D integrated processing-in-memory to reduce data movement between CPUs and memory. Certain Spark workloads like joins and aggregations that are I/O bound would benefit from in-storage processing, while iterative workloads are more suited for 2D integrated processing-in-memory. The document outlines a system design using FPGAs to emulate these architectures for evaluating Spark machine learning workloads like k-means clustering.