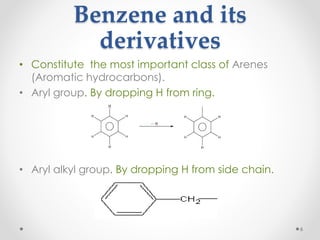
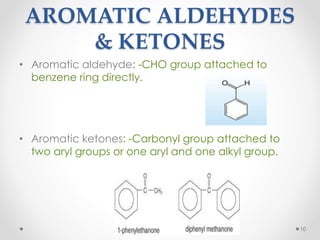
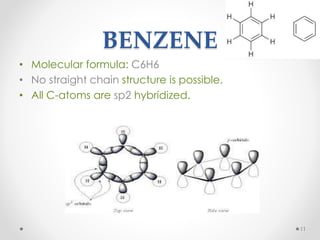
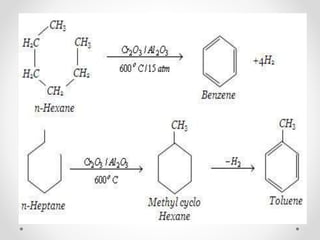
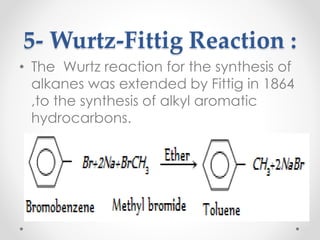
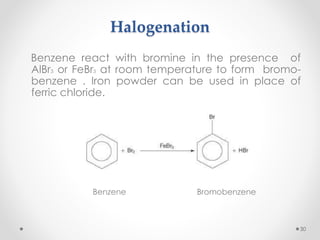
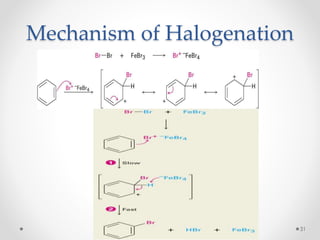
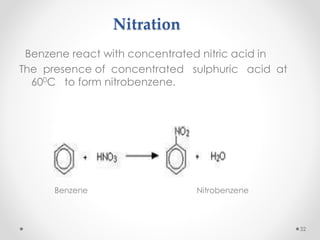
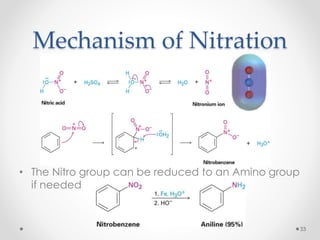
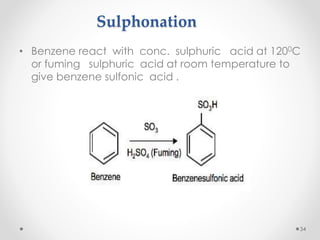
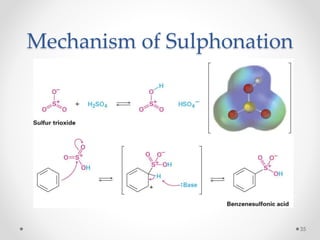
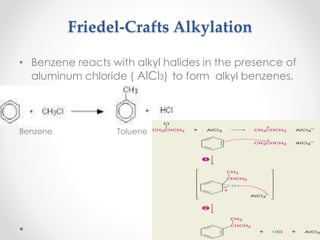
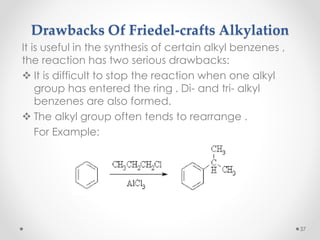
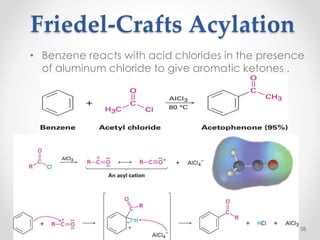
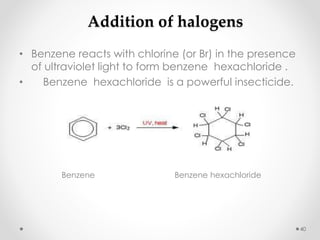
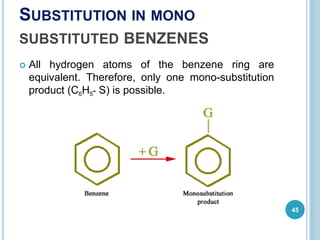
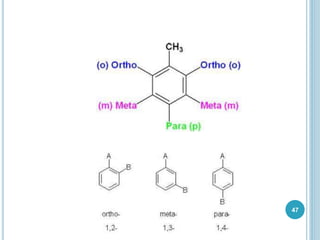
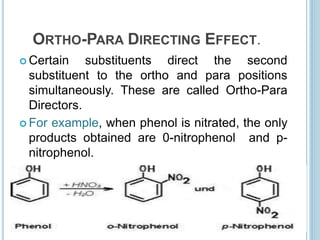
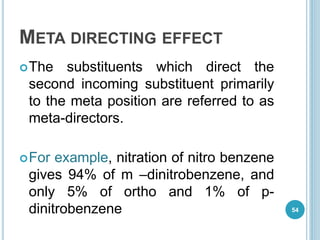
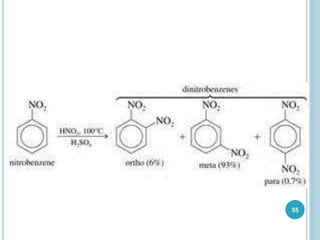
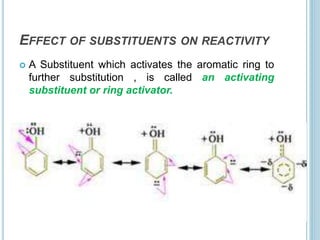
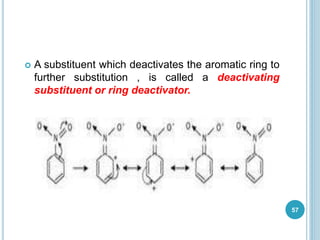
Kekulé had a dream in which he envisioned snakes grasping their own tails and forming rings, inspiring his hypothesis that carbon atoms in benzene are arranged in a ring structure with alternating single and double bonds. This ring structure explains benzene's stability and resistance to addition reactions compared to open-chain alkenes. Aromatic compounds are named for many originally having pleasant aromas, though the term now refers to chemical stability conferred by conjugated planar ring structures like benzene that allow for resonance. These compounds are important industrially as precursors to dyes, drugs, polymers, and other chemicals.