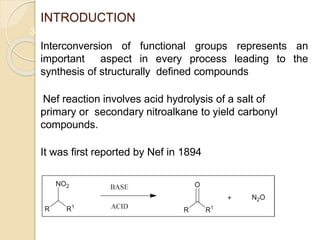
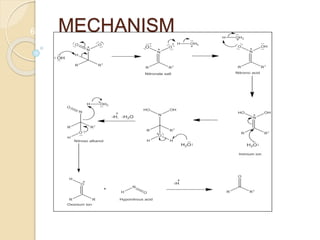
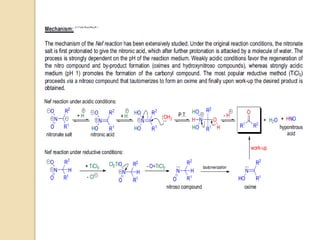
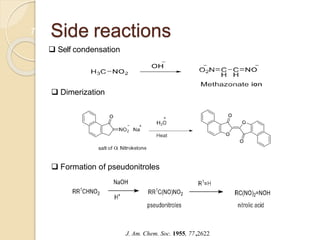
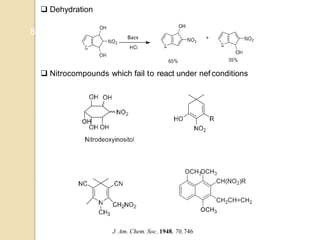
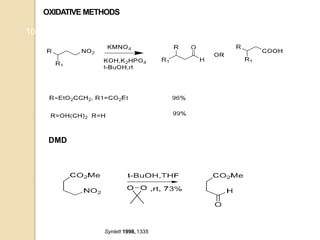
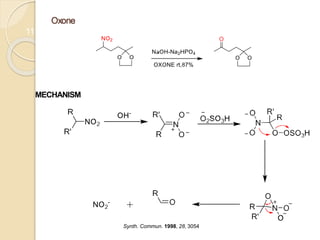
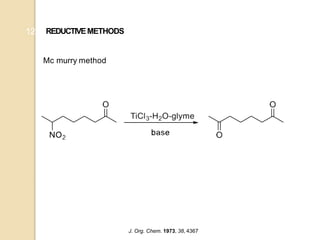
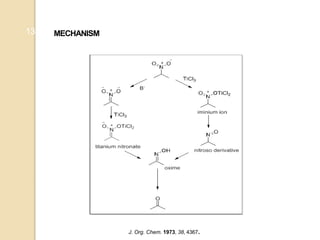
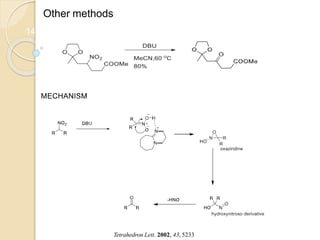
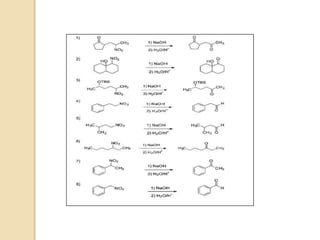
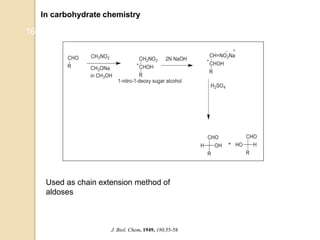
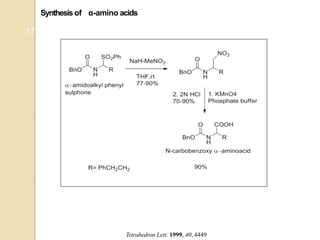
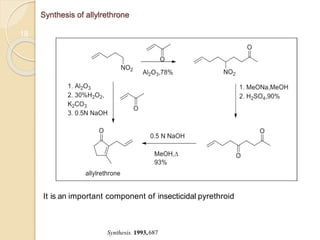
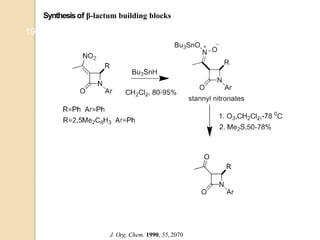
1) The Nef reaction involves the acid hydrolysis of primary or secondary nitroalkane salts, which produces carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes or ketones.
2) The reaction was first reported by J.U. Nef in 1894 and is generally used to convert nitroalkanes into the corresponding carbonyl compounds.
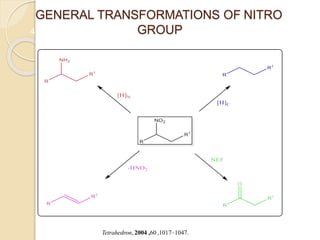
3) Over time, modified Nef reactions have been developed using oxidizing or reducing agents to improve the selectivity and functional group tolerance of the reaction. These allow synthesis of various biologically active compounds.