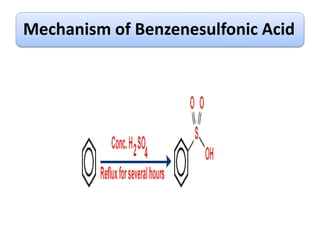
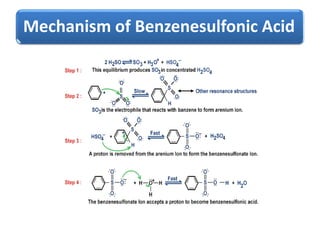
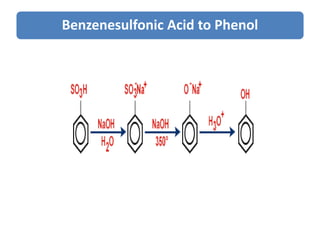
The document discusses the mechanism of sulfonation of benzene to form benzenesulfonic acid. It involves the formation of sulfur trioxide as the electrophile, which attacks the benzene ring to form an intermediate stabilized by resonance. This intermediate then loses a proton in the presence of a base to form benzenesulfonate ion, which is protonated to yield benzenesulfonic acid. Benzenesulfonic acid can be converted to phenol through a reaction with sodium hydroxide involving addition-elimination with sulfite ion as the leaving group.