Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times




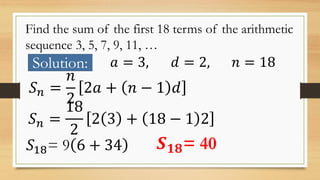



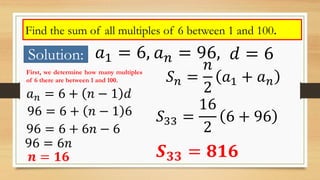

The document outlines objectives for Grade 10 mathematics focused on arithmetic series, including definitions and methods for calculating the sum of n terms. It provides formulae for the sum of terms in an arithmetic sequence and includes worked examples for various sequences, demonstrating how to find partial sums. Key examples include finding the sums of sequences like 50, 47, 44 and the first 30 natural numbers.









