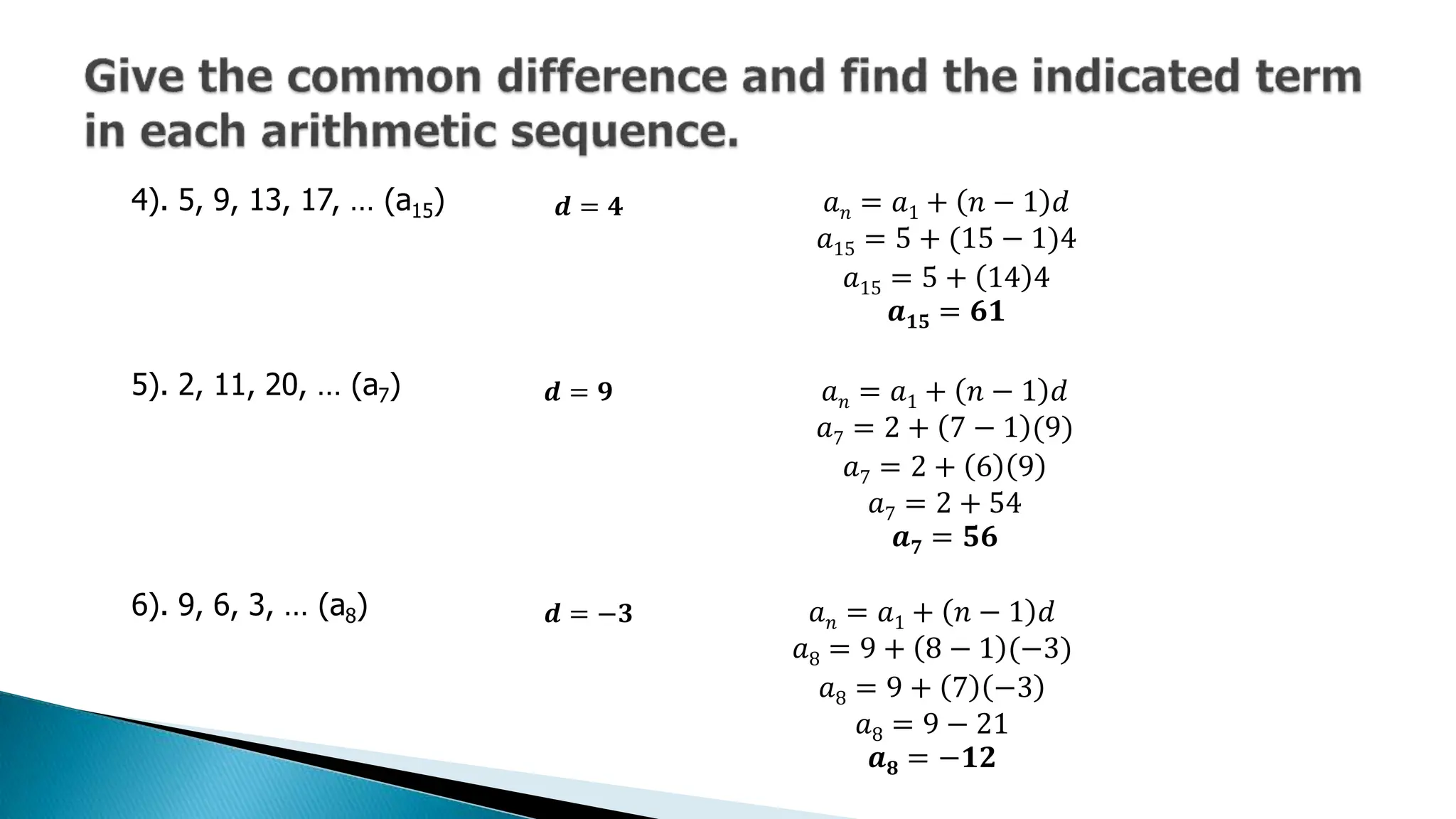
The document discusses arithmetic sequences, detailing how to find terms based on a common difference and the first term. It provides examples to illustrate finding specific terms and generating formulas for the nth term of a sequence. Additionally, it explores inserting arithmetic means between two numbers and calculating the sum of finite sequences.
































![𝑆𝑛=
𝑛
2
2𝑎1 + 𝑛 − 1 𝑑
S𝑛 =
𝑛[2𝑎1 + 𝑛 − 1 𝑑]
2
S𝑛 =
𝑛(𝑎1 + 𝑎𝑛)
2
A SERIES represents the sum of the terms of a sequence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-arithmetic-sequences-240711125928-854f9d8c/75/2-Arithmetic-Sequhgtfwsfedddddences-pptx-34-2048.jpg)



![4. How many terms of the arithmetic sequence 20, 18, 16,…
must be added so that the sum will be -100?
−100 =
𝑛[2 20 + 𝑛 − 1 − 2]
2
𝑎1 = 20 𝑑 = −2 𝑛 = 25 S𝑛 = −100
−200 = 𝑛(40 − 2𝑛 + 2)
𝒏 = 𝟐𝟓
S𝑛 =
𝑛[2𝑎1 + 𝑛 − 1 𝑑]
2
−200 = 42𝑛 − 2𝑛2
42𝑛 − 2𝑛2 + 200 = 0
−𝑛2 + 21𝑛 + 100 = 0
𝑛2 − 21𝑛 − 100 = 0
𝑛 − 25 𝑛 + 4 = 0
𝒏 = −𝟒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-arithmetic-sequences-240711125928-854f9d8c/75/2-Arithmetic-Sequhgtfwsfedddddences-pptx-38-2048.jpg)





