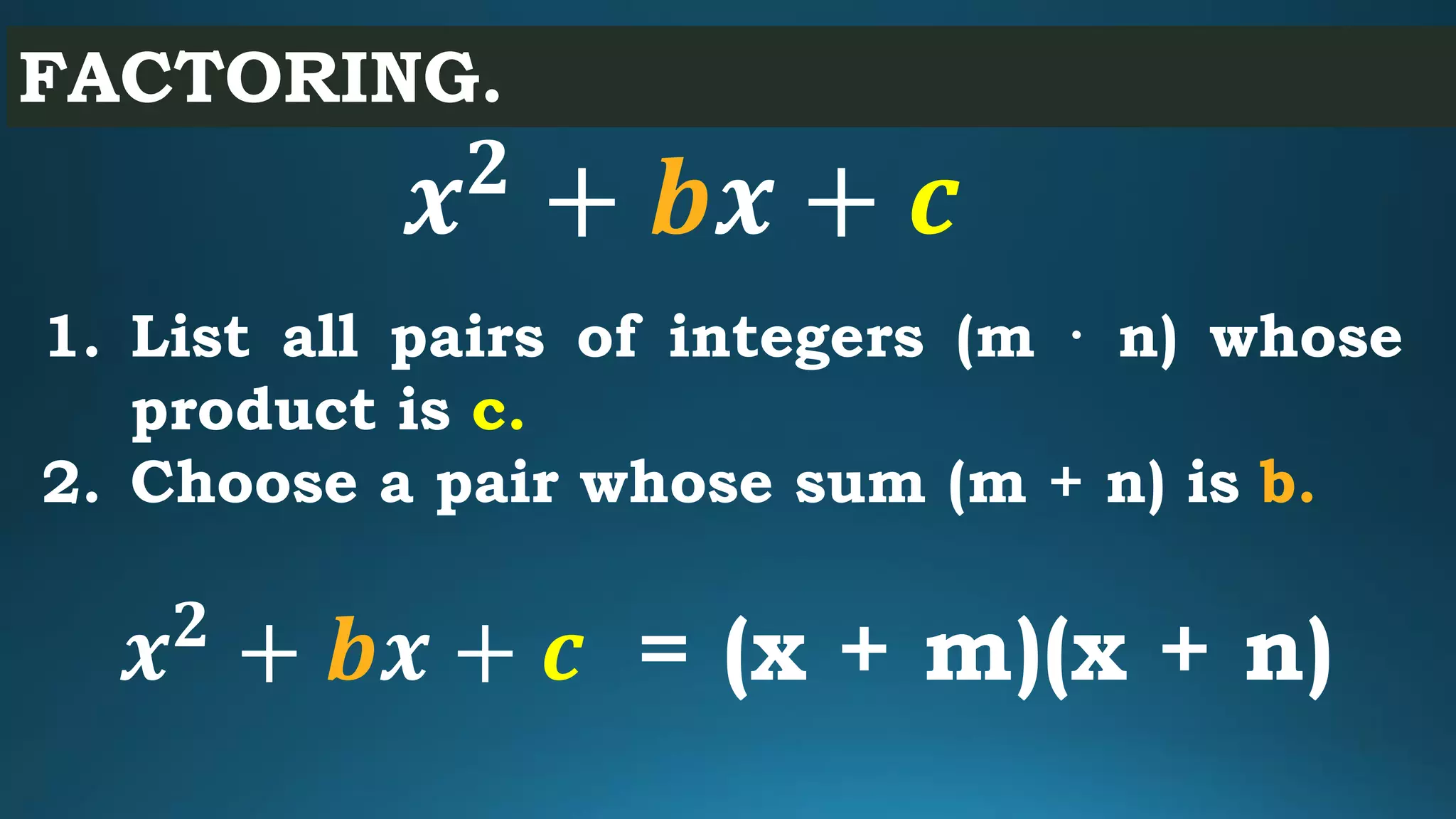This document focuses on factoring quadratic trinomials of the form x² + bx + c and solving related polynomial problems. It provides examples of factoring, listing integer pairs that relate to the coefficients, and offers practice problems involving factoring. The importance of identifying integer pairs that yield specific products and sums is emphasized throughout.