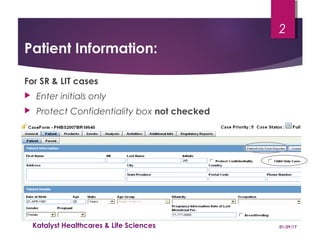
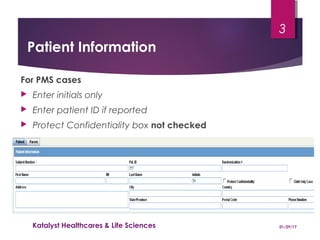
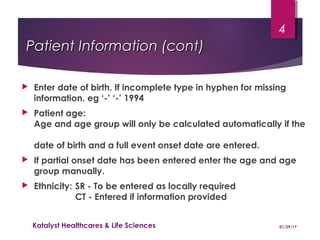
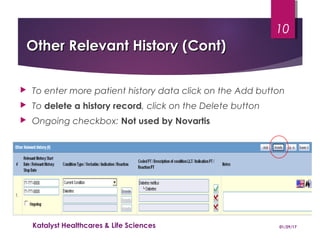
This document provides instructions for entering patient information, medical history, and laboratory data into the ARGUS patient screening system. It describes how to enter initials only for patient name, date of birth using hyphens for missing parts, and age manually if date of birth is partial. Relevant medical history, including conditions, historical drugs, and family history should be included. Laboratory results should be entered in the coded field if abnormal and relevant to events, and normal tests or those not codable go in the free text field. Dates and details like units should be included.