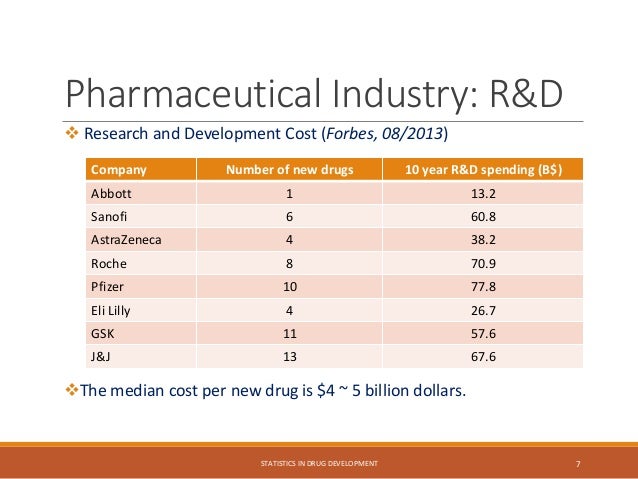
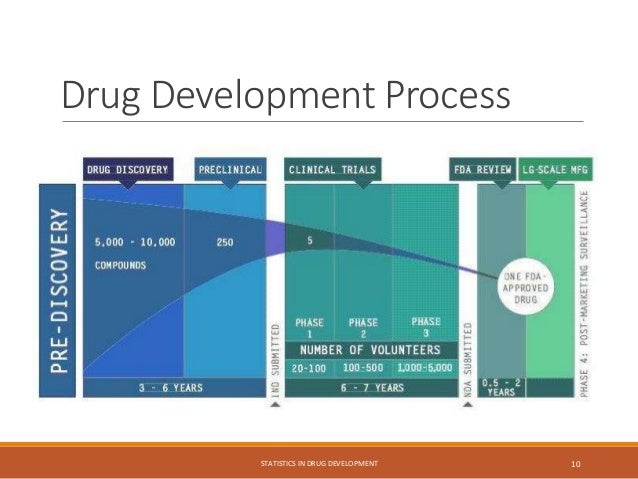
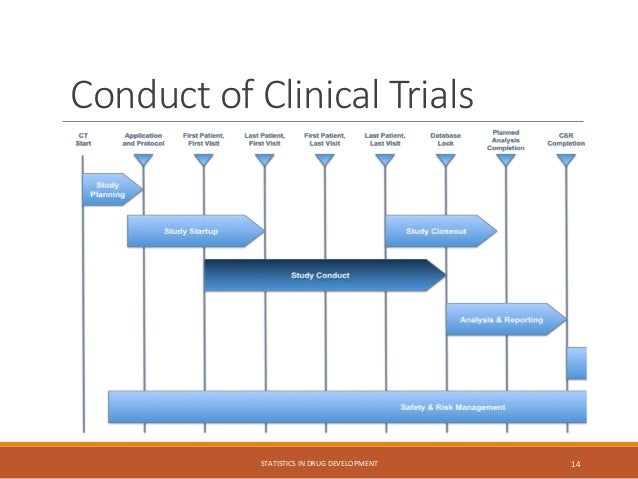
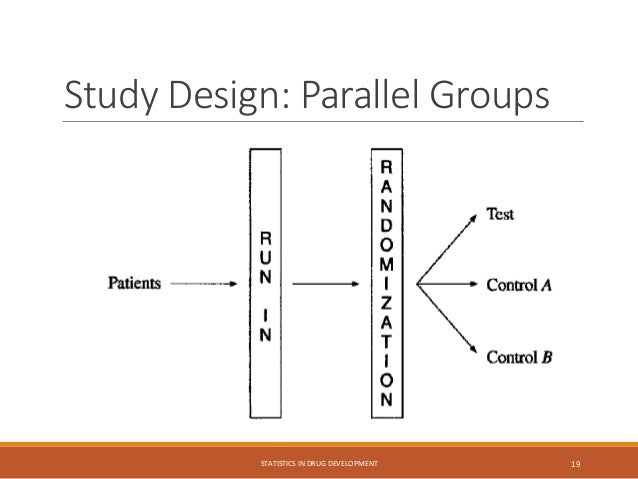
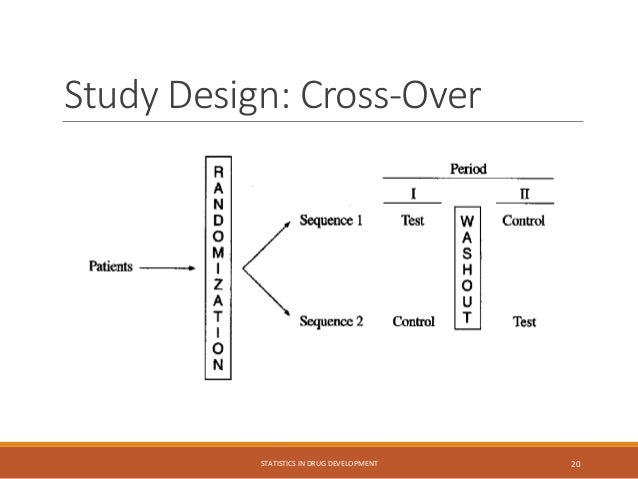
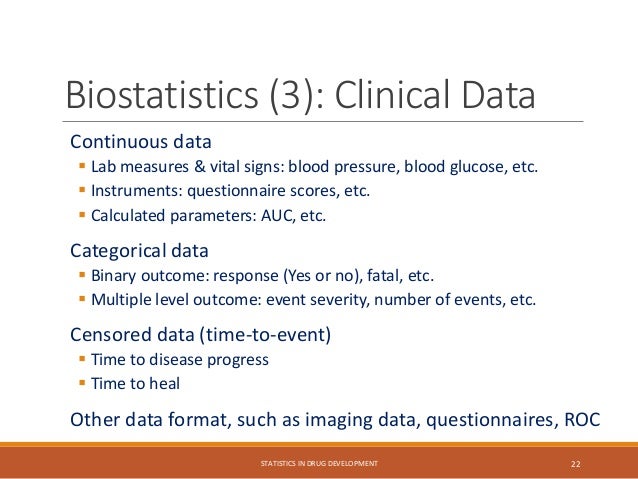
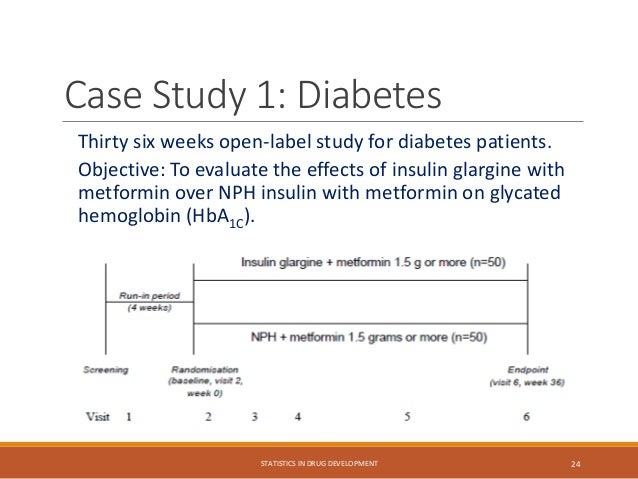
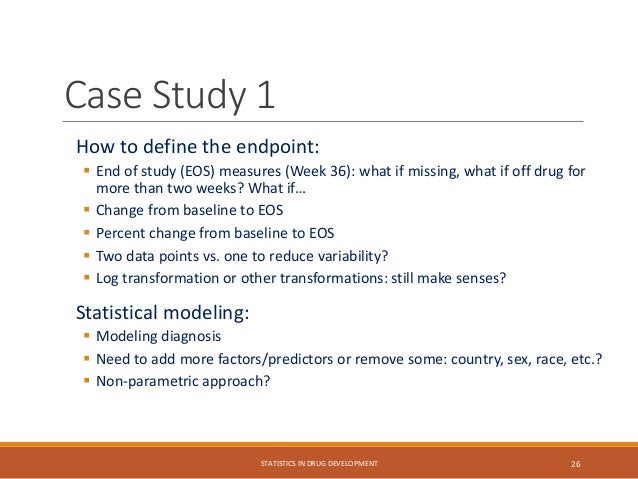
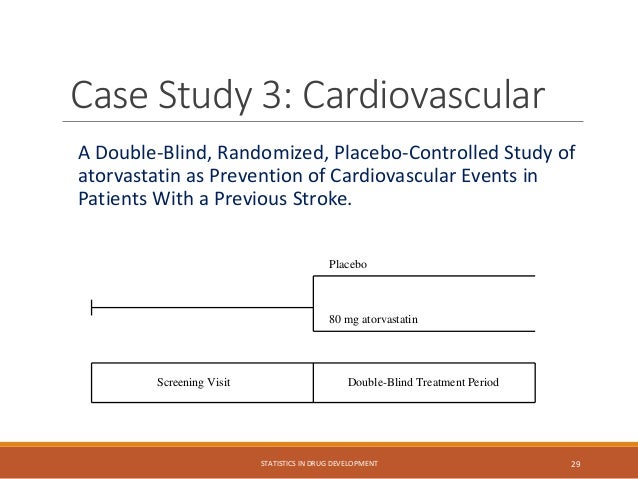
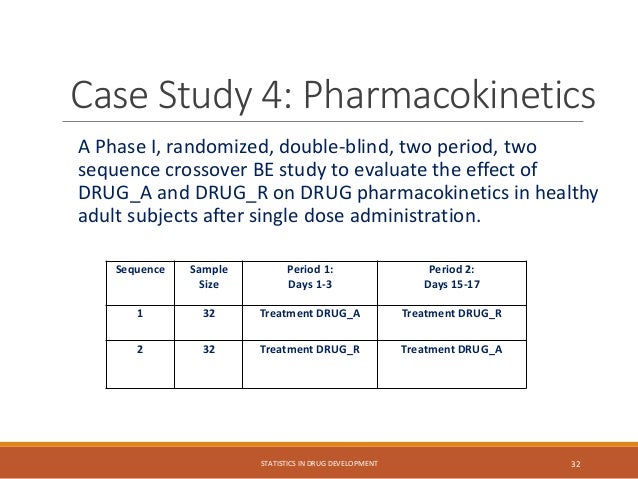
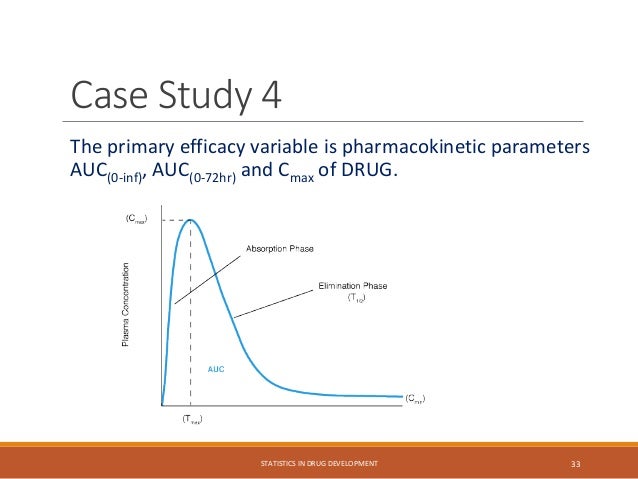
The document provides an overview of biostatistics in drug development and clinical trials. It discusses key topics including the drug development process, clinical trial phases, study designs, clinical data types, and case studies. The drug development process involves preclinical research followed by phase 1-4 clinical trials to test drugs for safety and efficacy. Common study designs include parallel group and crossover designs. Biostatisticians are responsible for study design, statistical analysis planning, and interpreting clinical trial results.