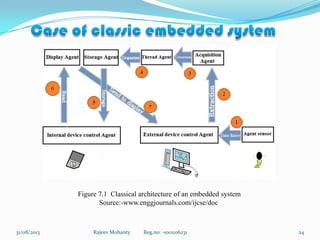
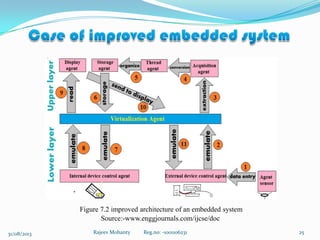
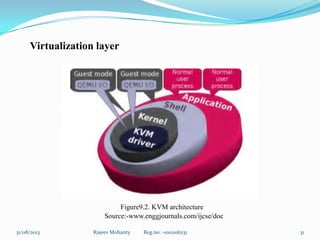
The document discusses embedded systems and virtualization techniques. It begins with an introduction to embedded systems, their basic principles and characteristics. Examples of embedded systems are provided. The document then discusses the state of the art in multi-agent systems, embedded systems, and virtualization techniques. It describes insulation, para-virtualization, and full virtualization. The document proposes a solution using an agent-based model and describes a prototype implementation of a virtualized embedded system using a Linux kernel and KVM that provides the benefits of virtualization for embedded systems.




















![31/08/2013 Rajeev Mohanty Reg.no: -1001106231 34
1. Doc Searls, The Next Bang: The Explosive Combination of Embedded
Linux, XML and Instant Messaging'', , September 2000, Linux
Journal, http://www.linuxjournal.com/lj-issues/issue77/4195.html
2. D. Kalinsky, R. Kalinsky ; « Introduction to I2C », Embedded.com. 2001.
http://embedded.com/story/OEG20010718S0073 [18] M. Khemakhem, A.
Belghith, « Agent
Based Architecture for Parallel and Distributed Complex Information
processing », January 2007, Vol. 2. n. 1,
3. J. Ferber: Les systèmes multi-agents, vers une intelligence
collective, Paris, InterEditions, 1995.
4. Guessoum Z., Un environnement opérationnel de conception et de
réalisation de systèmes multi-agents, Thèse de doctorat, Université Paris
6, mai 1996
5. R. El Bejjet, H. Medromi, « A Generic Platform for a Multi-Agent Systems
Simulation », September 2010, Vol. 5. n. 5, pp. 505-509.
6. Craigh Hollabaugh, Embedded Linux; Sams 2002](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myppt-130830103231-phpapp02/85/Architecture-design-of-a-virtual-embedded-system-ppt-34-320.jpg)
