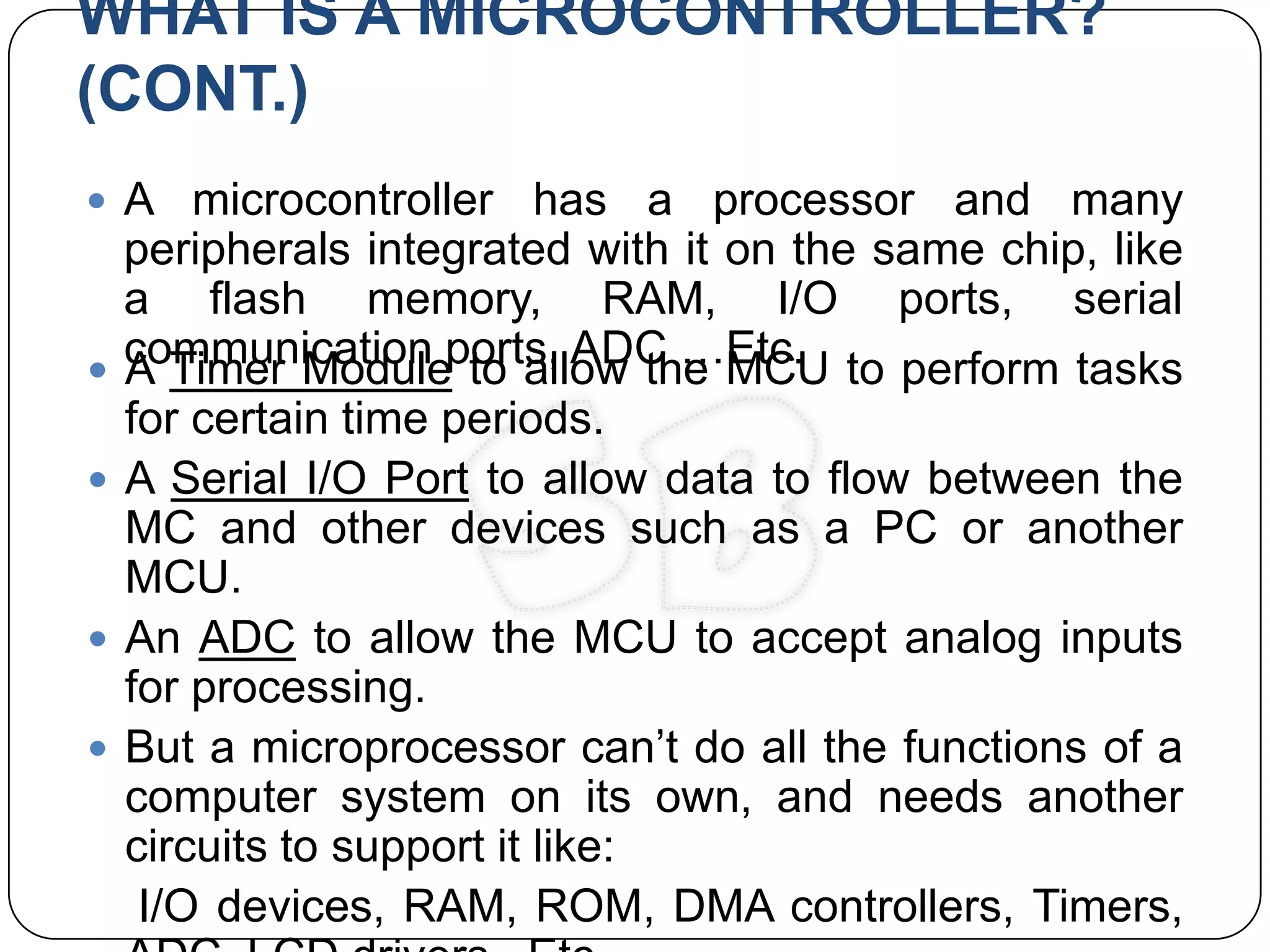
This document provides an introduction to microcontrollers and embedded systems. It defines embedded systems as specialized electronic devices that perform dedicated functions. Microcontrollers are described as computer systems on a single chip that contain a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals. Popular microcontroller examples include the 8051, PIC, and 68HC05. The document outlines the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, noting that microcontrollers have integrated memory and peripherals, require less external hardware, and have specialized instruction sets.