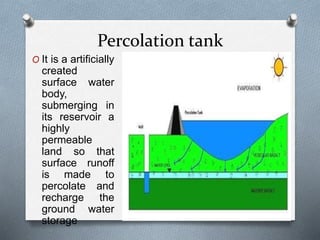
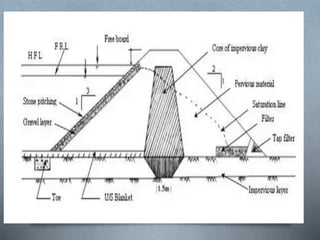
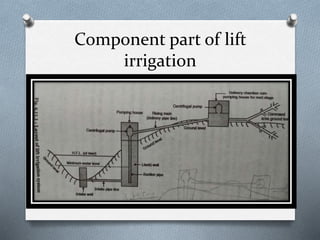
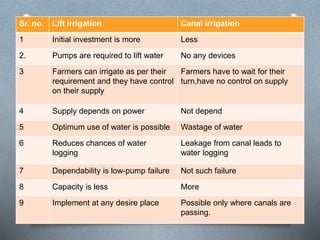
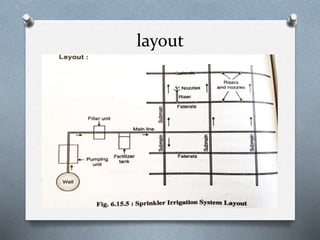
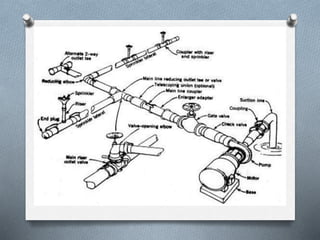
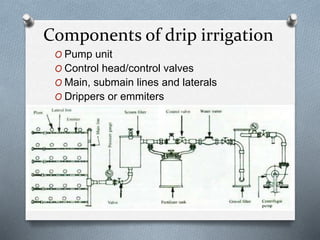
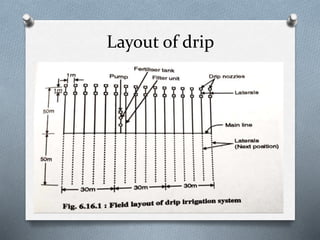
The document discusses various irrigation techniques including minor and micro irrigation systems, percolation tanks, lift irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, and drip irrigation, outlining their construction, components, advantages, and disadvantages. It emphasizes the importance of site selection for effective implementation and provides a detailed comparison between different irrigation methods regarding their costs, efficiency, and operational aspects. Additionally, it addresses maintenance requirements, particularly for drip irrigation systems, to prevent clogging and ensure optimal performance.