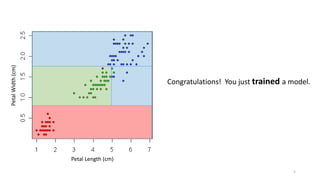
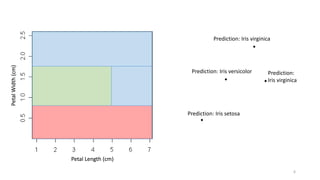
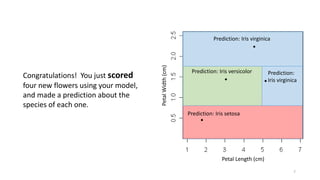
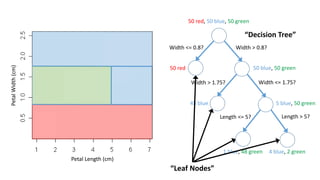
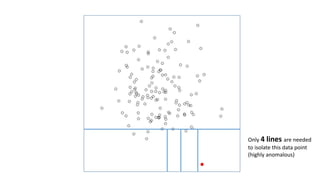
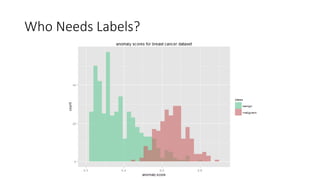
This document discusses using anomaly detection techniques to identify minority classes without labels. It summarizes using anomaly detection on an unlabeled cancer biopsy dataset to identify malignant biopsies as anomalies without knowing their labels. This "minority report" approach is well-suited for large unlabeled datasets where an adversarial minority class is expected, like credit card fraud or network intrusions, as it can identify outliers without predefined labels of what to look for.