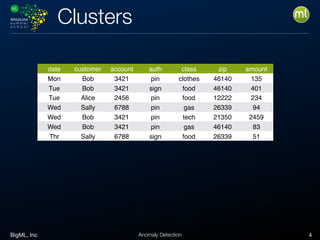
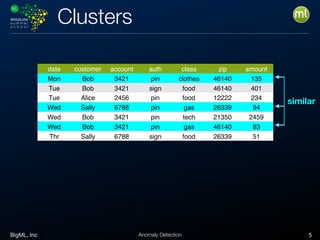
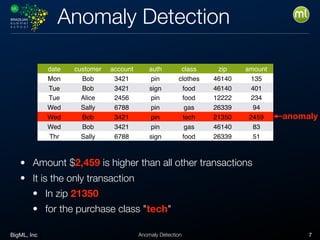
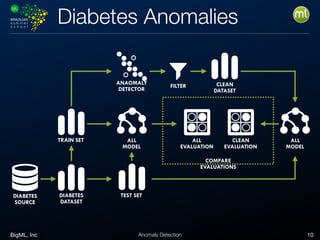
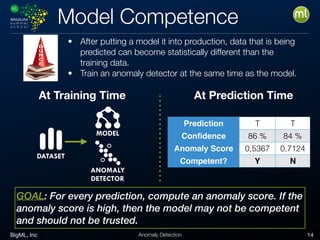
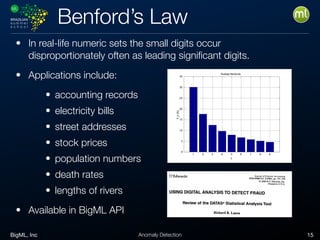
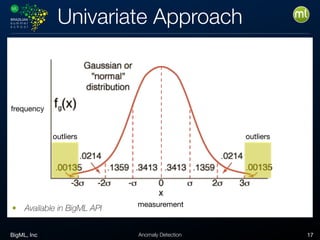
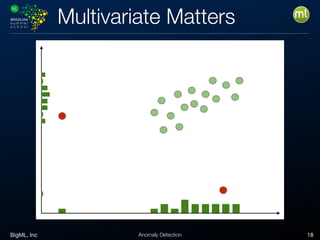
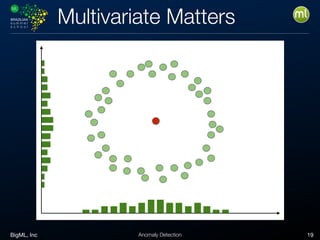
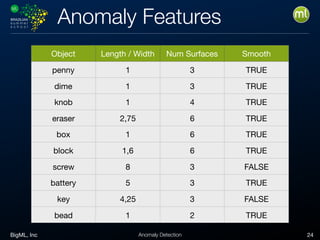
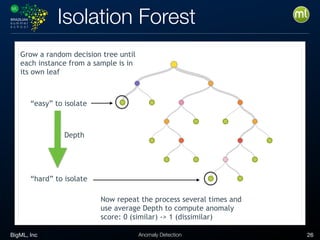
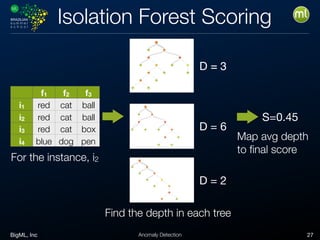
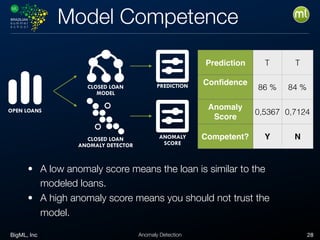
Anomaly detection is an unsupervised learning technique to find unusual instances without labels. It works by defining an anomaly score where higher scores indicate more unusual instances. Techniques include univariate analysis using standard deviation, isolation forests, and Benford's law. Applications include filtering data to improve models, detecting fraud, intrusions, and mistakes. Anomaly detection also helps determine when models need retraining due to changes in input data.